TIDT328 april 2023
2.1 Efficiency Graphs
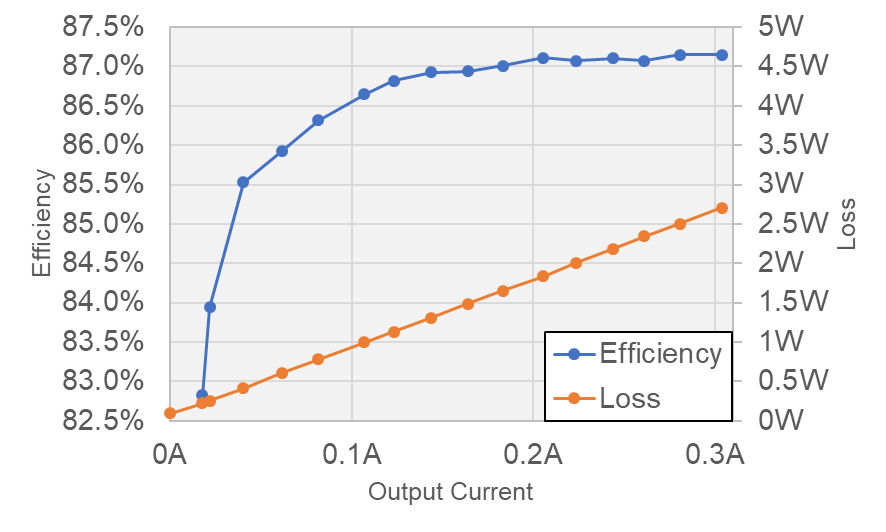 Figure 2-1 Efficiency and Loss vs
Output Current
Figure 2-1 Efficiency and Loss vs
Output CurrentDiscontinuous mode (DCM) lowers the typical efficiency of higher than 90%.
TIDT328 april 2023
 Figure 2-1 Efficiency and Loss vs
Output Current
Figure 2-1 Efficiency and Loss vs
Output CurrentDiscontinuous mode (DCM) lowers the typical efficiency of higher than 90%.