at TA = 25°C, VS+ = 2.5 V,
VS– = –2.5 V, VIN+ = 0 V, RF = 453 Ω, gain = 7
V/V, RL = 200 Ω, and output load referenced to midsupply (unless
otherwise noted)

| VOUT = 100 mVPP; for circuit
configuration, see Section 7 |
Figure 6-1 Small-Signal Frequency Response vs Gain Figure 6-3 Small-Signal Frequency Response vs Output Load
Figure 6-3 Small-Signal Frequency Response vs Output Load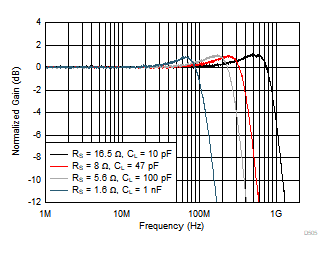
| VOUT = 100 mVPP; for circuit
configuration, see Figure 7-3 |
Figure 6-5 Small-Signal Frequency Response vs Capacitive Load Figure 6-7 Large-Signal Response for 0.1-dB Gain Flatness
Figure 6-7 Large-Signal Response for 0.1-dB Gain Flatness Figure 6-9 Closed-Loop Output Impedance vs Frequency
Figure 6-9 Closed-Loop Output Impedance vs Frequency Figure 6-11 Voltage and Current Noise Density vs Frequency
Figure 6-11 Voltage and Current Noise Density vs Frequency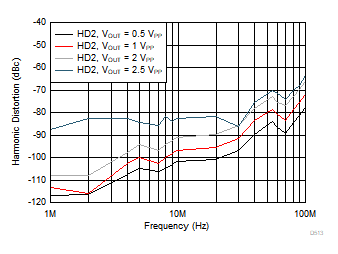 Figure 6-13 Harmonic Distortion (HD2) vs Output Swing
Figure 6-13 Harmonic Distortion (HD2) vs Output Swing Figure 6-15 Harmonic Distortion (HD2) vs Output Load
Figure 6-15 Harmonic Distortion (HD2) vs Output Load Figure 6-17 Harmonic Distortion (HD2) vs Gain
Figure 6-17 Harmonic Distortion (HD2) vs Gain
| Average rise-and-fall time (10%–90%) = 300 ps, |
| rise-and-fall time limited by test equipment |
Figure 6-19 Small-Signal Transient Response Figure 6-21 Small-Signal Transient Response vs Capacitive Load
Figure 6-21 Small-Signal Transient Response vs Capacitive Load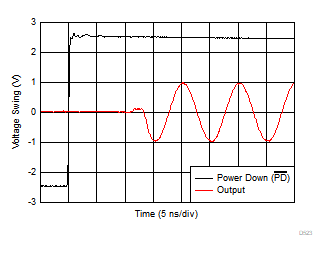 Figure 6-23 Turn-On Transient Response
Figure 6-23 Turn-On Transient Response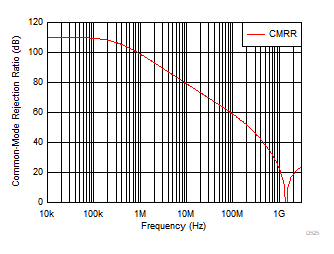 Figure 6-25 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio vs Frequency
Figure 6-25 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio vs Frequency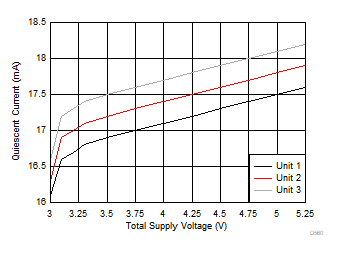 Figure 6-27 Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 6-27 Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage Figure 6-29 Offset Voltage vs Supply Voltage
Figure 6-29 Offset Voltage vs Supply Voltage
| 3
typical units, VS+ = 5 V, VS– = 0
V |
Figure 6-31 Offset Voltage vs Input Common-Mode Voltage
| 3
typical units, VS+ = 5 V, VS– = 0
V |
Figure 6-33 Offset Voltage vs Output Swing Figure 6-35 Input
Bias Current vs Ambient Temperature
Figure 6-35 Input
Bias Current vs Ambient Temperature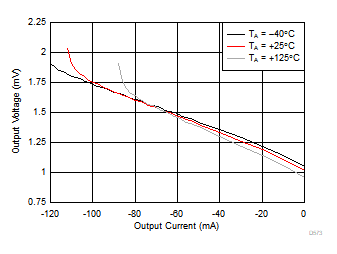 Figure 6-37 Output Swing vs Sinking Current
Figure 6-37 Output Swing vs Sinking Current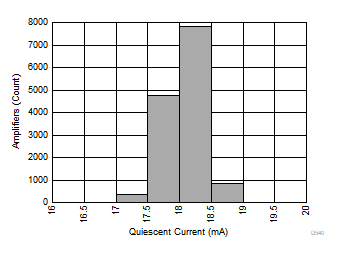
| 13780 units tested, µ = 17.6 mA, σ = 0.3 mA |
Figure 6-39 Quiescent Current Distribution
| 13780 units tested, µ = –11.2 µA, σ = 0.6 µA |
Figure 6-41 Input
Bias Current Distribution Figure 6-2 Small-Signal Frequency Response vs Supply Voltage
Figure 6-2 Small-Signal Frequency Response vs Supply Voltage
| Gain = 39.2 V/V, RF = 953
Ω, VOUT = 100 mVPP |
Figure 6-4 Small-Signal Frequency Response vs Ambient Temperature Figure 6-6 Large-Signal Frequency Response vs Gain
Figure 6-6 Large-Signal Frequency Response vs Gain Figure 6-8 Large-Signal Frequency Response vs Voltage Supply
Figure 6-8 Large-Signal Frequency Response vs Voltage Supply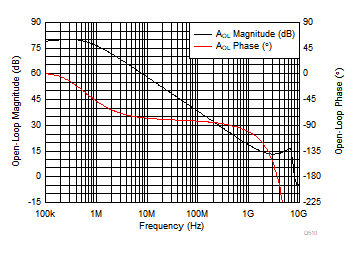 Figure 6-10 Open-Loop Magnitude and Phase vs Frequency
Figure 6-10 Open-Loop Magnitude and Phase vs Frequency Figure 6-12 Voltage Noise Density vs Ambient Temperature
Figure 6-12 Voltage Noise Density vs Ambient Temperature Figure 6-14 Harmonic Distortion (HD3) vs Output Swing
Figure 6-14 Harmonic Distortion (HD3) vs Output Swing Figure 6-16 Harmonic Distortion (HD3) vs Output Load
Figure 6-16 Harmonic Distortion (HD3) vs Output Load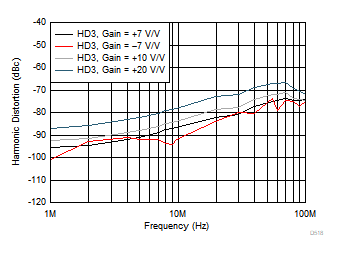 Figure 6-18 Harmonic Distortion (HD3) vs Gain
Figure 6-18 Harmonic Distortion (HD3) vs Gain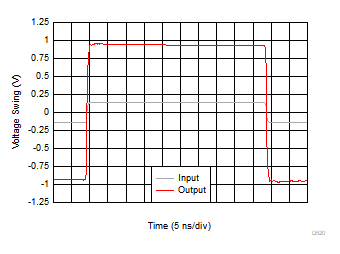
| Average rise and fall time (10%–90%) = 569 ps |
| |
Figure 6-20 Large-Signal Transient Response Figure 6-22 Output Overload Response
Figure 6-22 Output Overload Response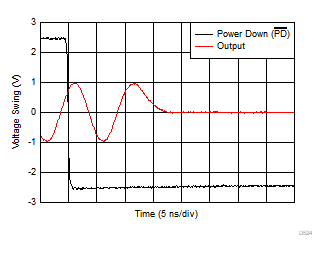 Figure 6-24 Turn-Off Transient Response
Figure 6-24 Turn-Off Transient Response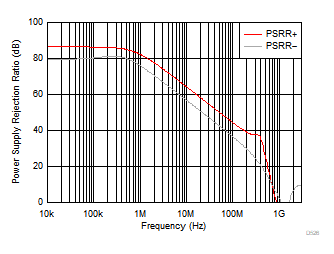 Figure 6-26 Power
Supply Rejection Ratio vs Frequency
Figure 6-26 Power
Supply Rejection Ratio vs Frequency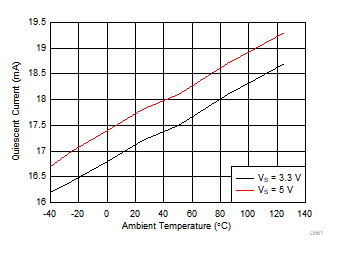 Figure 6-28 Quiescent Current vs Ambient Temperature
Figure 6-28 Quiescent Current vs Ambient Temperature
| 28
units tested, µ = 0.4 µV/°C, σ = 0.7 µV/°C |
Figure 6-30 Offset Voltage vs Ambient Temperature Figure 6-32 Offset Voltage vs Input Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 6-32 Offset Voltage vs Input Common-Mode Voltage Figure 6-34 Offset Voltage vs Output Swing
Figure 6-34 Offset Voltage vs Output Swing Figure 6-36 Input
Bias Current vs Input Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 6-36 Input
Bias Current vs Input Common-Mode Voltage Figure 6-38 Output Swing vs Sourcing Current
Figure 6-38 Output Swing vs Sourcing Current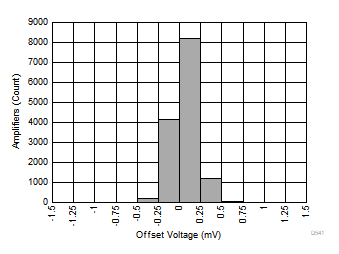
| 13780 units tested, µ = –0.2 mV, σ = 0.15 mV |
Figure 6-40 Offset Voltage Distribution
| 13780 units tested, µ = 0.04 µA, σ = 0.1 µA |
Figure 6-42 Input
Offset Current Distribution








































