SCBA020A October 1999 – March 2020 TMS3705
4.1 Initialization
For proper mode control write, it is essential to know if the TMS3705 is in idle or sleep state.
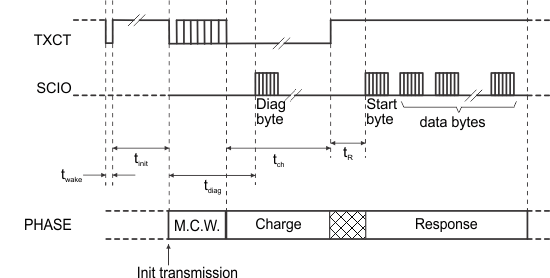
Independent of the sleep or idle state of the IC, the timing in Figure 2 can be used. The timing is given for a read-only transponder, but the wake sequence can also be used for other transponder types.
The wake pulse (low) must be shorter than tmcr (twake << tmcr; twake = 50 µs typical) to avoid the wake pulse being interpreted as a start of transmission.
After the wake pulse, the TXCT signal must be high for at least the maximum of the minimum initialization time tinit min.
The proposed timing assures that an IC in sleep mode switches to idle state. If the IC was already in idle state, the wake pulse has no effect and the IC remains in idle state.