SLOA277B january 2019 – july 2023 LM124 , LM124-N , LM124A , LM158 , LM158-N , LM158A , LM224 , LM224-N , LM224A , LM258 , LM258-N , LM258A , LM2902 , LM2902-N , LM2902-Q1 , LM2902K , LM2902KAV , LM2904 , LM2904-N , LM2904-Q1 , LM2904B , LM2904B-Q1 , LM2904BA , LM321 , LM324 , LM324-N , LM324A , LM358 , LM358-N , LM358A , LM358B , LM358BA , TS321 , TS321-Q1
4.5 Second Crossover Example
Crossover can also occur when the load current changes from an external source as seen in Figure 4-7. The LM358 is set up as a reference voltage buffer and the load current alternates between 1 mA and –1 mA.
 Figure 4-7 Second Crossover Test Schematic
Figure 4-7 Second Crossover Test SchematicThe LM358 load current is stepped ±1 mA using a pulse generator square wave and a series resistor. Ideally, the output voltage should be constant at 5 V. However the output voltage jumps by 2 V, or about 3 × VBE, before the other output driver can provide current flow. At 25°C, the time needed to correct the output signal back to 5 V is about
The LM358 has a slower typical slew rate than the LM324. Consequently, the time delay is greater in the LM358. The oscilloscope capture in Figure 4-8 shows as example output waveform in red and a pulse generator output in dotted blue. From this real-world data, we see that output crossover can create output steps and flat waveforms followed by a correction period.
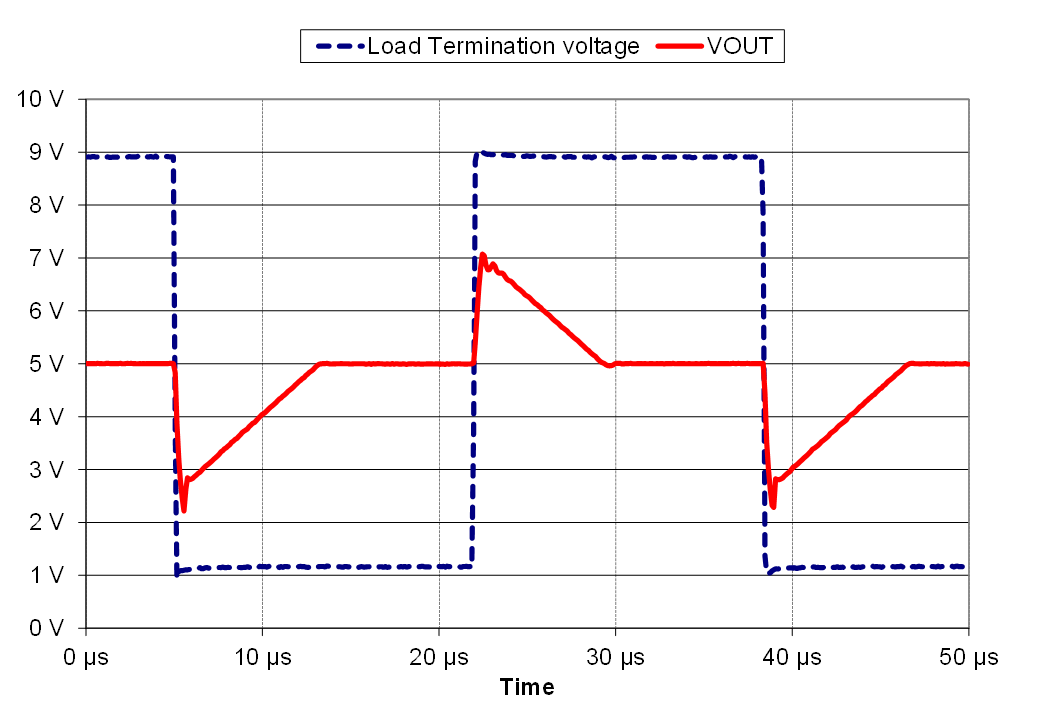 Figure 4-8 LM358 Crossover Test
Waveforms
Figure 4-8 LM358 Crossover Test
Waveforms