SLVA857B July 2018 – January 2023 TPS50601-SP , TPS50601A-SP , TPS7H1101-SP , TPS7H1101A-SP , TPS7H3301-SP , TPS7H4001-SP
3.3 Results
The oscilloscope plots in Figure 3-6 and Figure 3-7 show the start-up behavior of each of these voltage rails while connected to the RTG4 development kit fulfilling the two requirements discussed in Section 2.
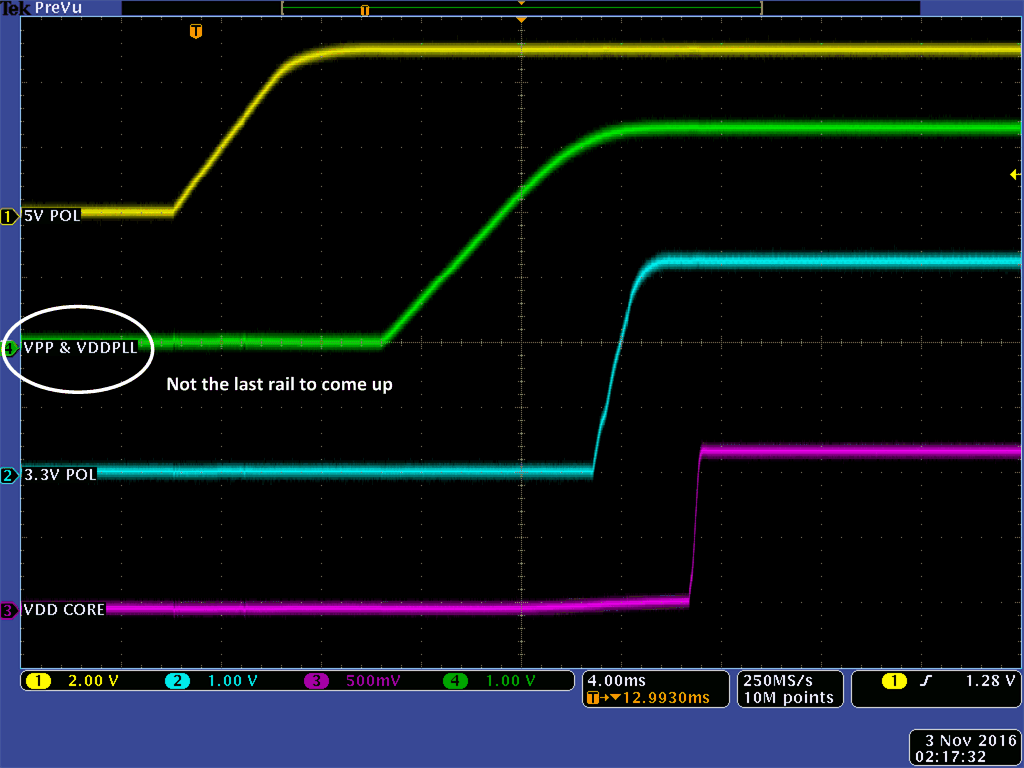 Figure 3-6 RTG4 Modified Development
Board Fulfilling the First Power-Up Requirement
Figure 3-6 RTG4 Modified Development
Board Fulfilling the First Power-Up Requirement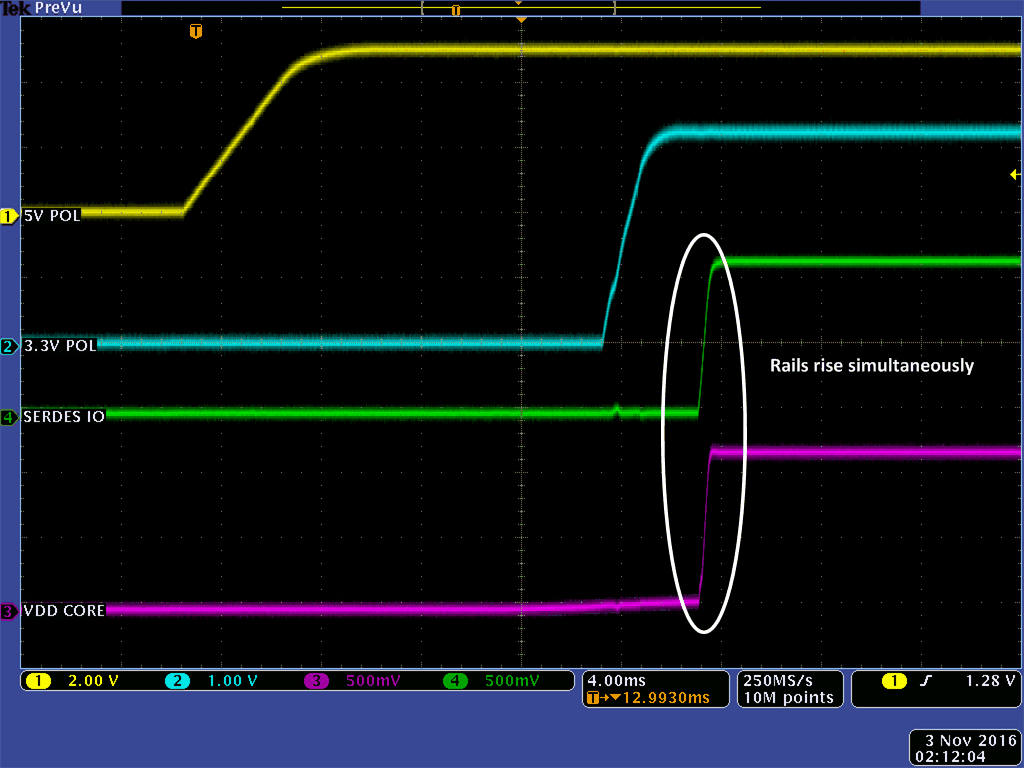 Figure 3-7 RTG4 Modified Development
Board Fulfilling the Second Power-Up Requirement
Figure 3-7 RTG4 Modified Development
Board Fulfilling the Second Power-Up RequirementAs shown in Figure 3-6 and Figure 3-7, both power sequencing requirements have been met and a clean monotonic power-up behavior is observed. Once the voltage rails come up, the RTG4 begins executing its software and the core starts to draw approximately 5-A of current. The software is the SERDES EPCS demo software (DG0624) provided by Microsemi.