SLVAE49C April 2019 – April 2022 DRV8847 , DRV8873-Q1 , DRV8904-Q1 , DRV8906-Q1 , DRV8908-Q1 , DRV8910-Q1 , DRV8912-Q1
3 Active Open Load Detection
The active OLD is the diagnostic that is carried out during load operation (current through the load is not zero). This diagnostic feature ensures that the load is connected to the driver during operation. However, it cannot detect if the load's terminals are disconnected from the power-stage before the load operation begins.
Figure 3-1 shows the operation of the active OLD diagnostic. (Refer to DRV89XX-Q1 device family for more details). If any of the FETs are turned ON and the current flowing in the particular FET is less than the OLD's current threshold (IOLD) for time magnitude larger than the OLD deglitch time (tOLD), then an OLD is detected.
In stepper motor integrated drivers, the active OLD depends on the winding current in any of the coils. If the winding current in any coil drops below the open load current threshold (IOLD) and also on the ITRIP level set by the indexer, an open-load condition is detected.
In DRV8873, DRV8873-Q1 and the DRV824x-Q1 devices, the active OLD is based on the voltage in a high-side FET's body diode during the current re-circulation. The current re-circulation occurs through the high-side FET's body diode in asynchronous rectification. In the gate drivers, the active OLD is based on the voltage in both the high-side or low-side FET's body diode during the current re-circulation.
Figure 3-2 shows the flow of current during forward drive and during current re-circulation. The high-side FET of OUT1 is in operating state. The voltage across the body diode of the current re-circulation high-side FET is compared with the fixed reference OLD threshold voltage (VOL_HS) to detect the OLD event.
In gate drivers, each half-bridge's (phase's) active OLD is enabled independently. For OLD to occur, a load needs to be connected across an H-bridge configuration. An OLD occurs when the voltage drop across the body diode of the current re-circulation FET does not exhibit overshoot greater than the VOLA over VM during the current-re-circulation time. An OLD does not occur if the energy stored in the load is high enough to cause an overshoot greater than the VOLA over VM. The overshoot is caused by the negative-current flowing through the body diode of the current re-circulation FET.
Active OLD in DRV8873-Q1, DRV8873 and in BLDC gate drivers, when compared to the negative-current OLD diagnostic, are different since the former will flag the OLD in asynchronous rectification while the latter will flag the OLD in synchronous rectification.
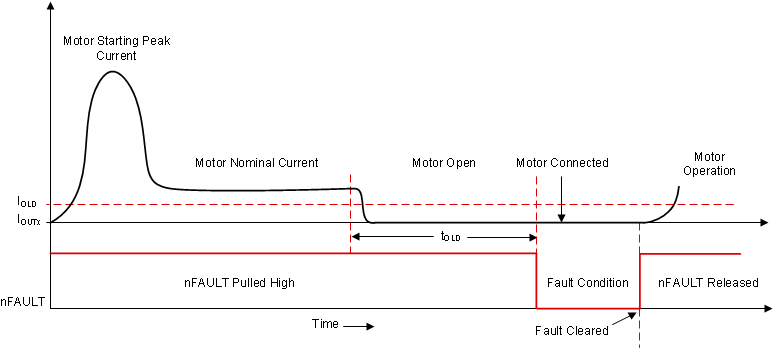 Figure 3-1 Active OLD Operation
Figure 3-1 Active OLD Operation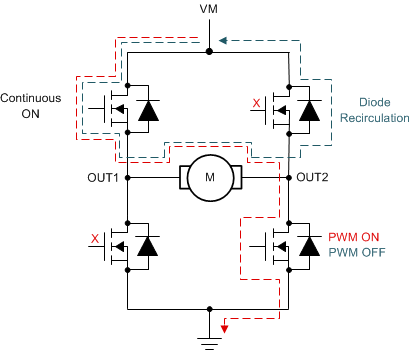 Figure 3-2 Forward Drive and Braking in
Asynchronous Rectification
Figure 3-2 Forward Drive and Braking in
Asynchronous Rectification