SWRU577 July 2021 CC3100 , CC3200
3 Setup
The UART interface must be connected between the CC3100 or CC3200 device and the main processor. Only two pins are required, UART TX and UART RX. Flow control is not required.
The common configuration that applies to all chipsets follows:
- Baud rate of 921600 bps
- 8 bits
- No parity
- 1 stop bit
In addition, the nHib/nReset pin is required and it must be have the ability to be temporarily pulled to GND during a reset to make the device go into bootloader mode.
For the CC3200 device, an additional SOP1 pin must be pulled up during the device reset to make the device go into bootloader mode.
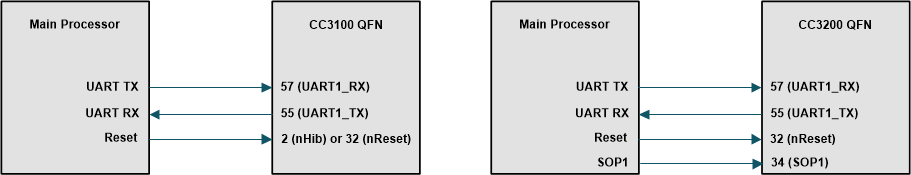 Figure 3-1 CC3200 and CC3200 QFN
Programming Setup
Figure 3-1 CC3200 and CC3200 QFN
Programming Setup