TIDUE53I march 2018 – july 2023 TMS320F28P550SJ , TMS320F28P559SJ-Q1
- 1
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
-
3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 3.1 Required Hardware and Software
- 3.2 Testing and Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Trademarks
- 6About the Authors
- 7Revision History
3.2.5.1.3 Efficiency and THD Results at 220 VRMS, 50 Hz – PFC Mode
This section covers the efficiency and THD results for the converter operating in PFC mode at 220 VRMS. Table 3-8 summarizes the results obtained from power analyzer results when the load is varied from 200 W to 5 kW and DC bus voltage is kept constant at 800 V.
| PHASE - A VOLTAGE | PHASE - B VOLTAGE | PHASE - C CURRENT | PHASE - A CURRENT (A) | PHASE - B CURRENT | PHASE - C CURRENT | OUTPUT DC CURRENT (A) | OUTPUT POWER (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
220.3 | 219.94 | 220.15 | 0.398 | 0.573 | 0.405 | 0.25 | 200 |
220.1 | 219.98 | 220.04 | 0.974 | 1.124 | 0.97 | 0.753 | 600 |
220.09 | 220.02 | 219.98 | 2.55 | 2.64 | 2.48 | 2.018 | 1610 |
220.02 | 219.94 | 219.93 | 4.142 | 4.166 | 4.016 | 3.283 | 2619 |
220.01 | 219.97 | 219.94 | 5.281 | 5.262 | 5.111 | 4.182 | 3337 |
219.92 | 219.94 | 219.86 | 7.325 | 7.231 | 7.079 | 5.793 | 4624 |
220.01 | 219.97 | 220.03 | 7.89 | 7.81 | 7.76 | 6.278 | 5023 |
| OUTPUT
| EFFICIENCY (%) | CURRENT-THD (PHASE-A) | CURRENT-THD (PHASE-B) | CURRENT-THD (PHASE-C) | PFC- (PHASE-A) | PFC- (PHASE-B) | FC- (PHASE-C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
200 | 80.93 | 38.88 | 55.46 | 53.44 | 0.8098 | 0.8395 | 0.7934 |
600 | 92.06 | 13.22 | 23.44 | 18.54 | 0.9706 | 0.9621 | 0.9678 |
1610 | 96.06 | 5.26 | 9.59 | 6.89 | 0.9944 | 0.9923 | 0.9949 |
2619 | 96.9 | 3.09 | 5.63 | 4.53 | 0.9975 | 0.9968 | 0.9977 |
3337 | 97.11 | 2.33 | 4.32 | 3.66 | 0.9982 | 0.9978 | 0.9985 |
4624 | 97.29 | 1.724 | 3.034 | 2.712 | 0.9988 | 0.9987 | 0.9990 |
5023 | 97.37 | 1.47 | 2.76 | 1.98 | 0.9992 | 0.9991 | 0.9995 |
Figure 3-38, Figure 3-49, and Figure 3-50 show the efficiency, THD, and power factor under different load conditions.
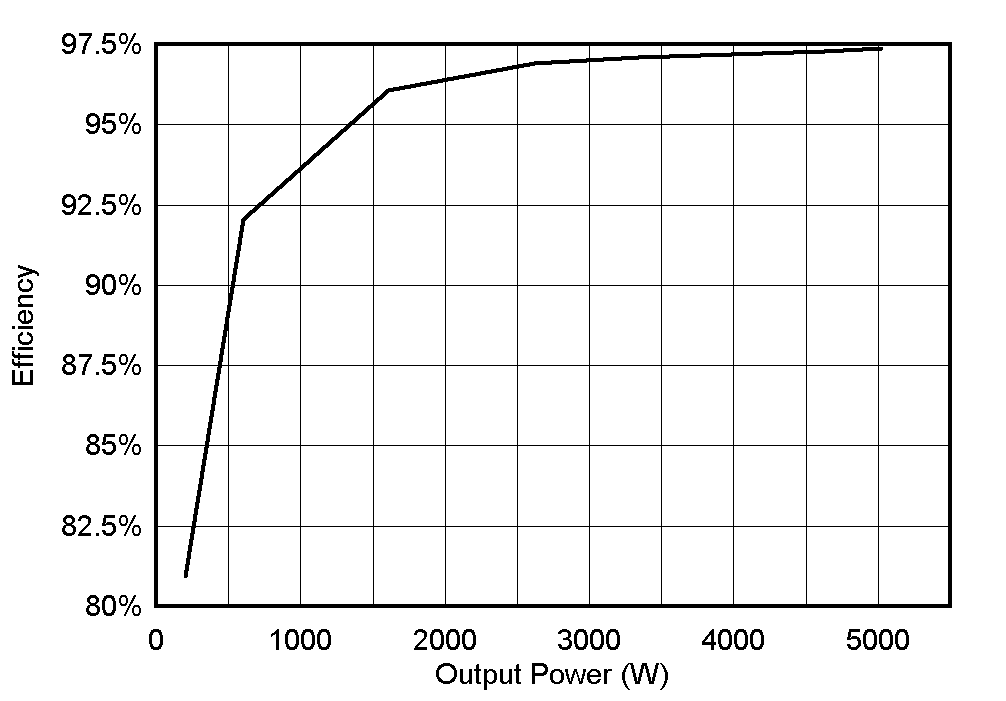 Figure 3-38 Efficiency Results - PFC Mode at 220 VRMS
Figure 3-38 Efficiency Results - PFC Mode at 220 VRMS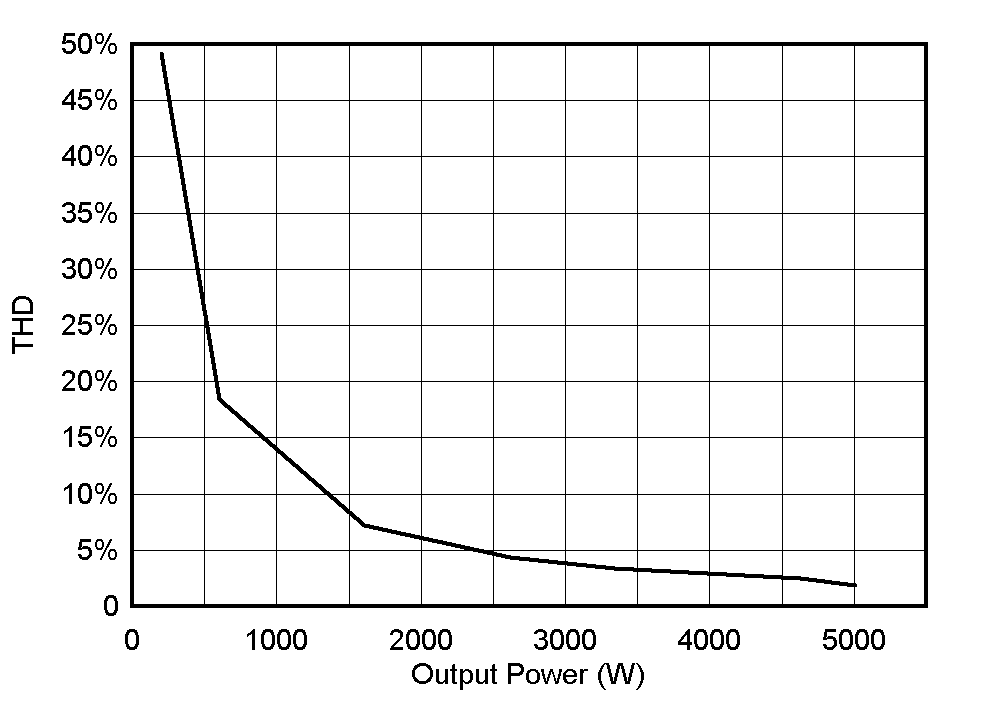 Figure 3-39 THD Results - PFC Mode at 220 VRMS
Figure 3-39 THD Results - PFC Mode at 220 VRMS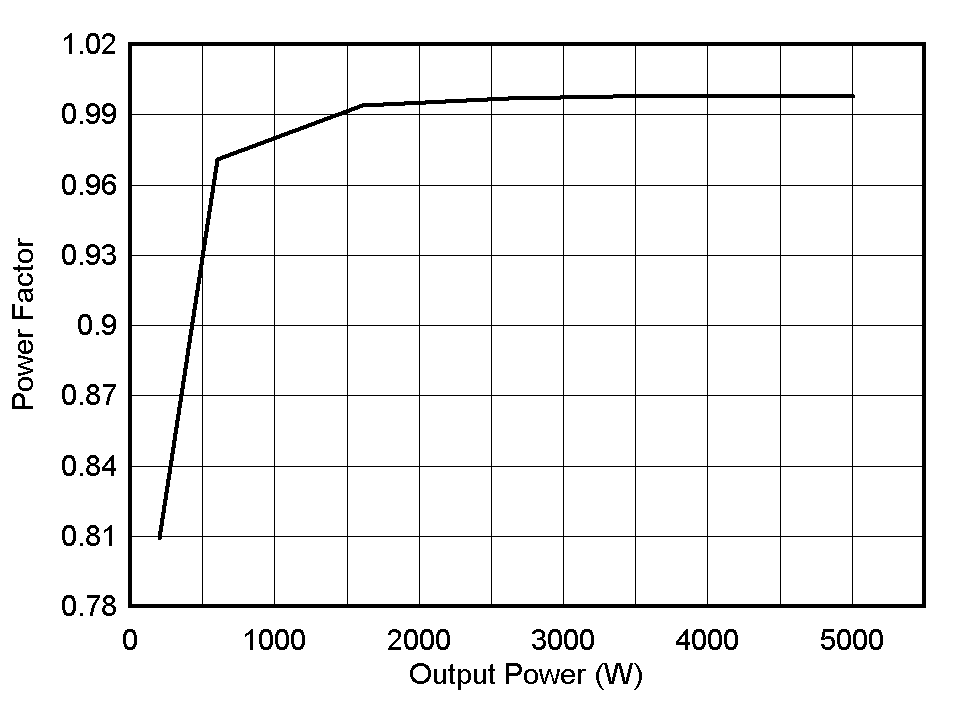 Figure 3-40 Power Factor Results - PFC Mode at 220 VRMS
Figure 3-40 Power Factor Results - PFC Mode at 220 VRMSFigure 3-41 shows thermal performance of the board at 4.7 kW.
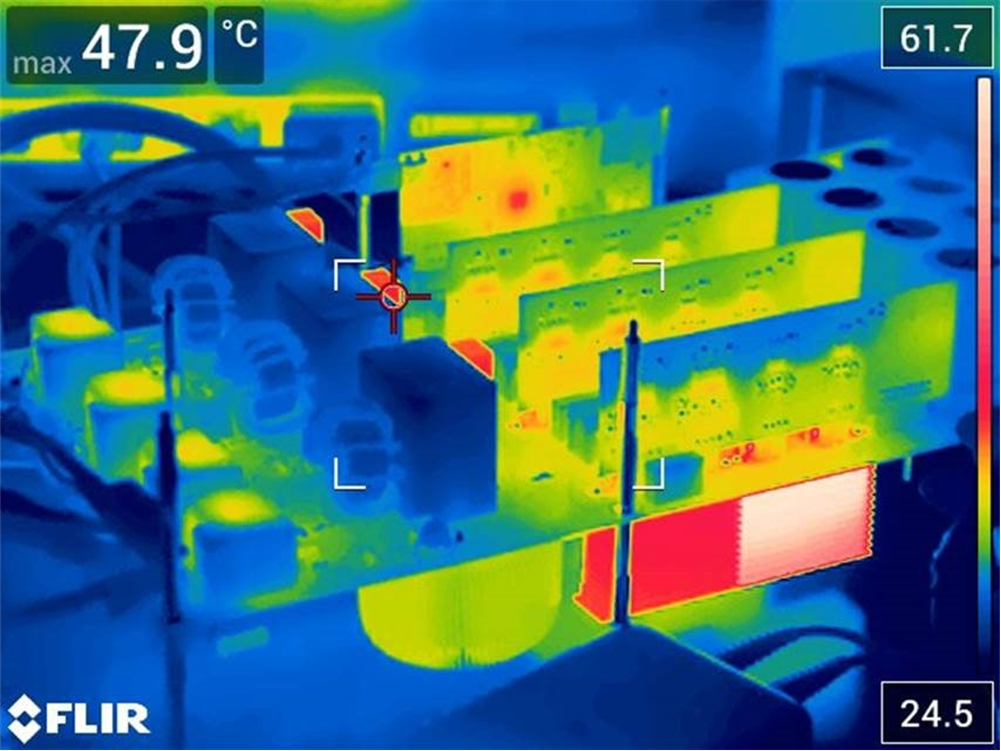 Figure 3-41 Thermal Image at 4.7 kW
Figure 3-41 Thermal Image at 4.7 kW