DLPS167 March 2024 DLPC964
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3 Feature Description
- 6.4
Device Functional
Modes
- 6.4.1 DLPC964 Aurora 64B/66B Input Data and Command Write Cycle
- 6.4.2 DMD Row Operation
- 6.4.3 Block Load Address Select
- 6.4.4 Block Mode Select
- 6.4.5 Mirror Clocking Pulse (MCP)
- 6.5
Register Map
- 6.5.1
Register Table Overview
- 6.5.1.1 FPGA_INTERRUPT_STATUS Register
- 6.5.1.2 FPGA_INTERRUPT_ENABLE_CONTROL Register
- 6.5.1.3 FPGA_MAIN_STATUS Register
- 6.5.1.4 FPGA_VERSION Register
- 6.5.1.5 FPGA_MAIN_CTRL Register
- 6.5.1.6 SELF_TEST_REG Register
- 6.5.1.7 DMDIF_ERROR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 6.5.1.8 DMDIF_ERROR_STATUS Register
- 6.5.1.9 PRBS7_MACRO0_TEST_RESULT Register
- 6.5.1.10 PRBS7_MACRO1_TEST_RESULT Register
- 6.5.1.11 PRBS7_MACRO2_TEST_RESULT Register
- 6.5.1.12 PRBS7_MACRO3_TEST_RESULT Register
- 6.5.1.13 PRBS7_TEST_CONTROL Register
- 6.5.1.14 PRBS7_TEST_RUNSTATUS Register
- 6.5.1.15 LS_BUS_TEST_RESULT Register
- 6.5.1.16 DMD_TYPE Register
- 6.5.1.17 HSS_RESET Register
- 6.5.1.18 HSS_CHANNEL_STATUS Register
- 6.5.1.19 HSS_LANE_STATUS Register
- 6.5.1.20 HSS_CH0_SOFTERROR_COUNT Register
- 6.5.1.21 HSS_CH1_SOFTERROR_COUNT Register
- 6.5.1.22 HSS_CH2_SOFTERROR_COUNT Register
- 6.5.1.23 HSS_CH3_SOFTERROR_COUNT Register
- 6.5.1.24 HSS_SOFTERROR_COUNT_RESET Register
- 6.5.1.25 HSSI_Channel_0_DMD_Data_GT_Cell_Control Register
- 6.5.1.26 HSSI_Channel_0_DMD_Clock_GT_Cell_Control Register
- 6.5.1.27 HSSI_Channel_1_DMD_Data_GT_Cell_Control Register
- 6.5.1.28 HSSI_Channel_1_DMD_Clock_GT_Cell_Control Register
- 6.5.1.29 HSSI_Channel_2_DMD_Data_GT_Cell_Control Register
- 6.5.1.30 HSSI_Channel_2_DMD_Clock_GT_Cell_Control Register
- 6.5.1.31 HSSI_Channel_3_DMD_Data_GT_Cell_Control Register
- 6.5.1.32 HSSI_Channel_3_DMD_Clock_GT_Cell_Control Register
- 6.5.1.33 HSSI_DMD_Vcm_Value Register
- 6.5.1.34 TEST_DMD_ID Register
- 6.5.1.35 TEST_DMD_FUSE1 Register
- 6.5.1.36 TEST_DMD_FUSE2 Register
- 6.5.1.37 TEST_DMD_FUSE3 Register
- 6.5.1.38 TEST_DMD_FUSE4 Register
- 6.5.1
Register Table Overview
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2 Typical Application
- 7.3 Interfacing to DLPC964 Controller High Speed Serial (HSS) Aurora 64B/66B Inputs
- 7.4 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.5 Layout
- 7.6 Layout Example
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DLP|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.1.1 Block Start with Block Control Word
The AMD Aurora 64B/66B high speed serial (HSS) interface is a generic data transport link without any concept of how the DMD block data structure must be arranged. To define the start of a DMD block, the APPS FPGA logic must send a block control word data packet through channel 0 of the Aurora 64B/66B User-K data port before DMD data transmission can begin.
Table 7-1 below contains detailed information regarding the Aurora User-K interface port. The User-K interface ports are used to implement application-specific control functions, are independent, and are higher priority than the data interface.
| Name | Direction | Clock Domain | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| USER_S_S_AXIS_TX | |||
| s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[0:(64n-1)] or s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[(64n-1):0](1) | Input | user_clk | USER-K block data is 64-bit aligned. Signal Mapping per lane: |
| Default: | |||
| s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata={{4'h0,user_k_blk_no[0:3],user_k_data[55:0]}*n} | |||
| Little endian format: | |||
| s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata={{user_k_data[55:0],4'h0,user_k_blk_no[3:0]}*n} | |||
| s_axi_user_k_tx_tvalid | Input | user_clk | Indicates valid User-K data on the s_axi_userk_tx_tdata port. |
| s_axi_user_k_tx_tready | Output | user_clk | Indicates the Aurora 64B/66B core is ready to accept data on the s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata interface. |
| USER_K_M_AXIS_RX | |||
| m_axi_rx_user_k_tvalid | Output | user_clk | Indicates valid User-K data on the m_axi_user_k_tx_tdata port. |
| m_axi_rx_user_k_tdata or m_axi_rx_user_k_tdata[(64n-1):0](1) | Output | user_clk | Received USER-K blocks from the Aurora 64B/66B lane are 64-bit aligned. |
| Signal Mapping per lane: | |||
| Default: | |||
| m_axi_rx_user_k_tdata= {{4'h0,user_k_blk_no[0:3],user_k_data[55:0]}*n} | |||
| Little endian format: | |||
| m_axi_rx_user_k_tdata= {{user_k_data[55:0],4'h0,user_k_blk_no[3:0]}*n} | |||
As shown in Table 7-2 below, the HSS interface to the DLPC964 has four channels of User-K port interface exposed to the APPS FPGA user logics. Only Channel 0 is used to transmit the Block Control Word. Any Control Word packets sent over the User-K port of Channel 1, 2, and 3 are not used and are ignored by the DLPC964 Controller.
| Signal Name | Signal Direction | DLPC964 Application Usage |
|---|---|---|
| gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[191:0] | Input to Aurora Channel 0 | 192-bit block control word packet to be transmitted |
| gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tvalid | Input to Aurora Channel 0 | User logic asserts this signal high to indicate to Aurora core the Block Control word is valid to transmit. Aurora cores ignore word if TVALID is not-asserted. |
| gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tready | Output to Aurora Channel 0 | Aurora cores assert this signal high when the Block Control word is accepted. This signal is deasserted when words are ignored; that is, cores are not ready to accept input word. |
| gt1_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[191:0] | Input to Aurora Channel 1 | Unused |
| gt1_s_axi_user_k_tx_tvalid | Input to Aurora Channel 1 | Unused |
| gt1_s_axi_user_k_tx_tready | Output to Aurora Channel 1 | Unused |
| gt2_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[191:0] | Input to Aurora Channel 2 | Unused |
| gt2_s_axi_user_k_tx_tvalid | Input to Aurora Channel 2 | Unused |
| gt2_s_axi_user_k_tx_tready | Output to Aurora Channel 2 | Unused |
| gt3_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[191:0] | Input to Aurora Channel 3 | Unused |
| gt3_s_axi_user_k_tx_tvalid | Input to Aurora Channel 3 | Unused |
| gt3_s_axi_user_k_tx_tready | Output to Aurora Channel 3 | Unused |
Table 7-3 describes the various fields within the 192-bit block control word. The block control word not only defines the start of a DMD block, but also contains instructions and information to guide the DLPC964 Controller in processing the received DMD Block Data from the APPS FPGA.
| Field Position | Field Type | Field Description |
|---|---|---|
| gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[7:0] | USER_K_BLOCK_NUMBER | Must set to zeros (0x00). Values other than 0x00 are invalid. DLPC964 controller ignores the entire 192-bit control word if this field is not set to 0x00. |
| gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[11:8] | BLOCK_ADDRESS | Indicates the address of the DMD block to which the DLPC964 applies the operation: 0000: DMD Block 0, 0001: DMD Block 1, 0010: DMD Block 2, …1110: DMD Block 14, 1111: DMD Block 15 |
| gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[15:7] | Reserved, Unused | |
| gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[24:16] | ROW_LENGTH | Number of DMD row to be loaded by DLPC964. DLP991U DMD has 136 rows per block, thus valid range is 1-136. All other values, including 0 are invalid. Set to 136 for full block operation. Set to 1–135 for partial block operation. |
| NOTE: This field is only used if LOAD_TYPE = 000. | ||
| gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[34:32] | LOAD_TYPE | 000: Block Loading. The DLPC964 loads the user data to the DMD array defined by BLOCK_ADDRESS and ROW_LENGTH. |
| 001: Block Clear. The DLPC964 clears the DMD array to zeroes of the entire block defined by BLOCK_ADDRESS. | ||
| 010: Block Set. The DLPC964 sets the DMD array to ones of the entire block defined by BLOCK_ADDRESS. | ||
| Other values: reserved, do not use. | ||
| NOTE: when in 001 (Block Clear) or 010 (Block Set) operation, the ROW_LENGTH and NORTH_SOUTH_FLIP fields are ignored. Clear and Set operations affect the entire DMD Block array. Partial Block operation for Clear and Set operations is not supported. | ||
| gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[36] | NORTH_SOUTH_FLIP | Control the direction of data loading within a DMD Block. |
| 0: DLPC964 loads data starting and counting up from row 1. | ||
| 1: DLPC964 loads data starting and counting down from row 136 | ||
| NOTE: This field is only used if LOAD_TYPE is 000. | ||
| gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[29:28] | DMD_SEGMENT | When SINGLE_CHANNEL_MODE = '1', DMD_SEGMENT is used to select which DMD segment is selected for the operation. |
| 00: Segment 0 | ||
| 01: Segment 1 | ||
| 10: Segment 2 | ||
| 11: Segment 3 | ||
| NOTE: This field is ignored if SINGLE_CHANNEL_MODE = '0'. | ||
| gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[30] | SINGLE_CHANNEL_MODE | 1: Single Channel operation. DLPC964 Input Data for DMD is only received on Aurora Channel 0. |
| 0: Normal operation. DLPC964 Input Data for DMD is received on all four Aurora Channels. | ||
| gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[191:31] | Reserved, unused |
Figure 7-4 displays the transmission of the 192-bit block control word over the channel 0 User-K port at the start of an Aurora 64B/66B data block transfer. In this example, 136 rows of DMD block 1 are being loaded.
- With the proper Block Control word on bus gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tdata[191:0], the APPS FPGA user logics asserts the TVALID flag, gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tvalid, and waits for the Aurora core’s response.
- The Aurora core asserts the TREADY flag and gt0_s_axi_user_k_tx_tready, indicating the core has accepted the 192 bits User-K data.
- After the block control word is sent, the APPS FPGA user logics start the Aurora data block transfer on all four HSS data interfaces.
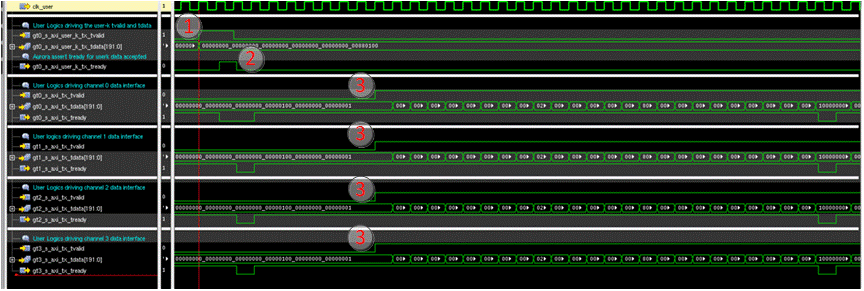 Figure 7-4 Block Start with Block Control
Word Waveform
Figure 7-4 Block Start with Block Control
Word Waveform