SLOS751E March 2013 – January 2023 DRV2667
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Support for Haptic Piezo Actuators
- 7.3.2 Flexible Front End Interface
- 7.3.3 Ramp Down Behavior
- 7.3.4 Low Latency Startup
- 7.3.5 Low Power Standby Mode
- 7.3.6 Device Reset
- 7.3.7 Amplifier Gain
- 7.3.8 Adjustable Boost Voltage
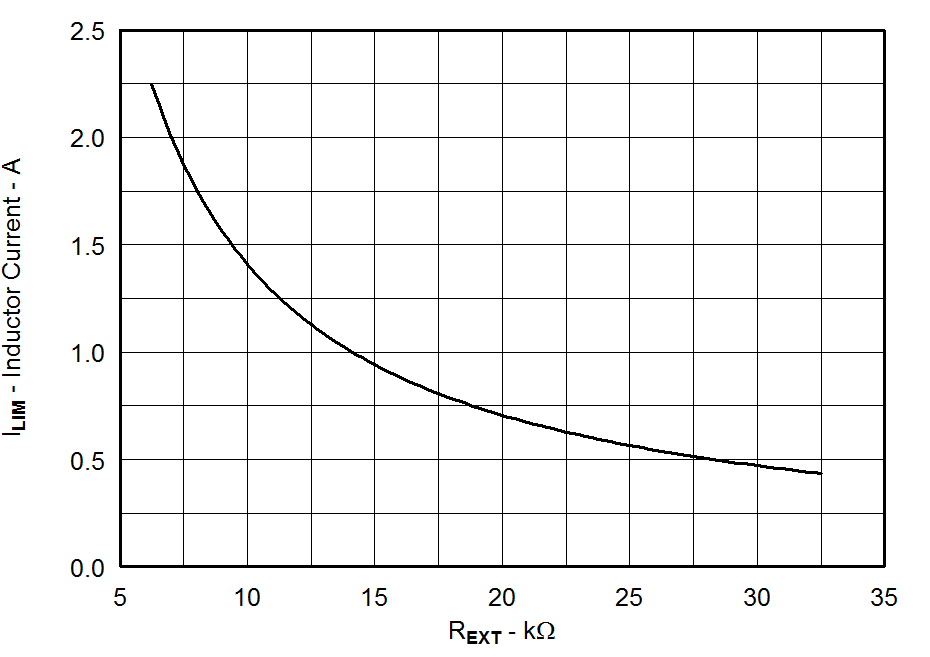
- 7.3.9 Adjustable Current Limit
- 7.3.10 Internal Charge Pump
- 7.3.11 Device Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Map
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGP|20
Orderable Information
6.8 Typical Characteristics

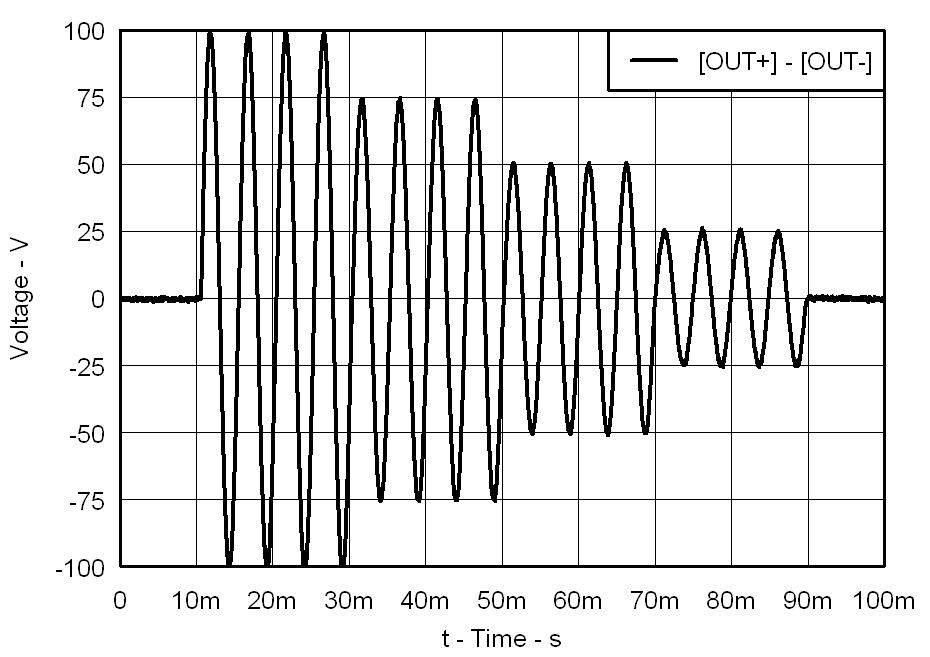
| f = 200 Hz | PVDD = 105 V |
| CLOAD = 47 nF | Gain = 40 dB |

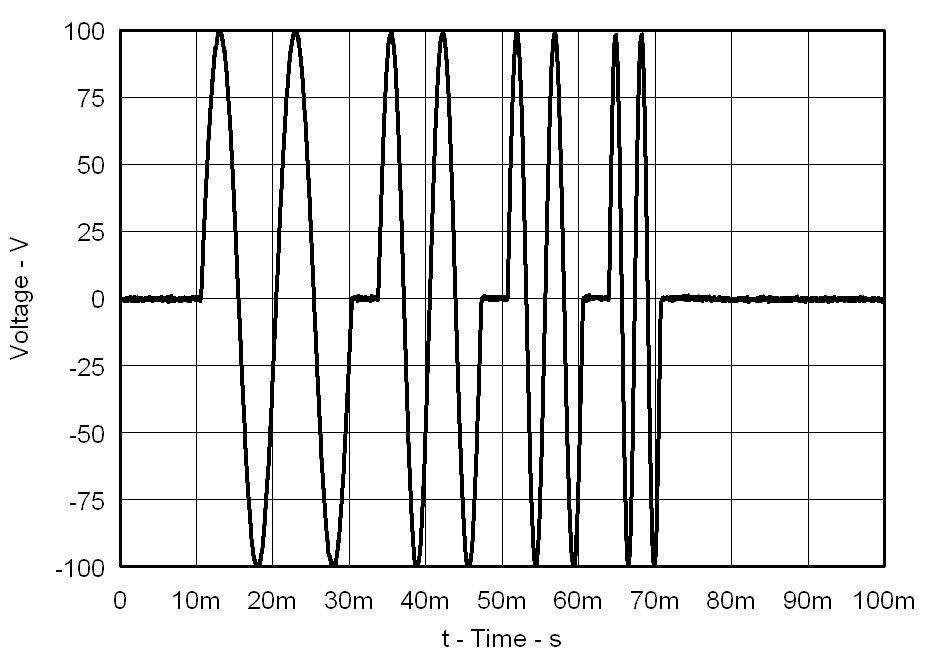
| f = 200 Hz | PVDD = 55 V |
| CLOAD = 330 nF | Gain = 34 dB |

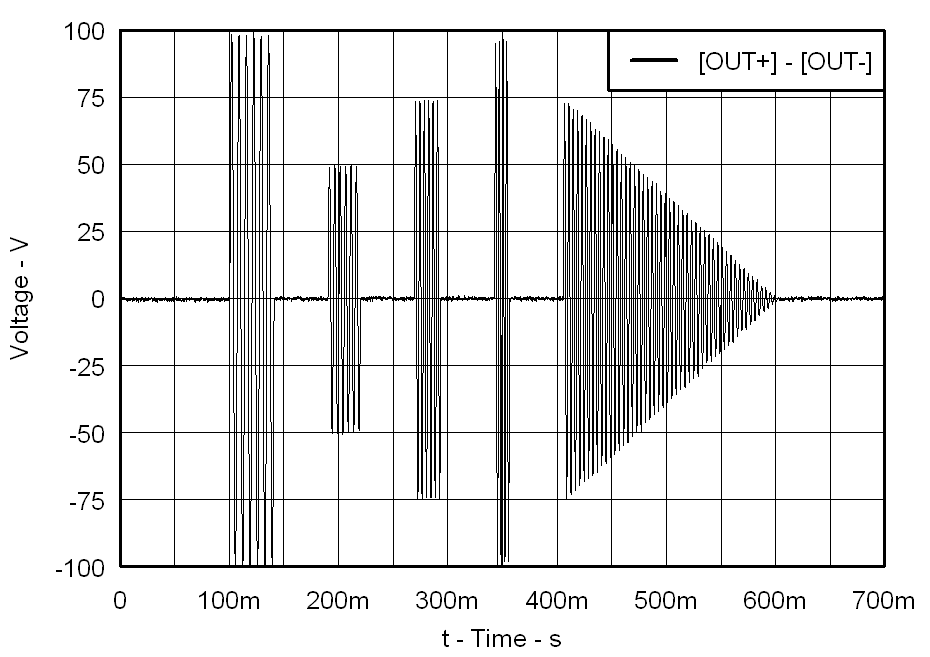
| f = 200 Hz | PVDD = 30 V |
| CLOAD = 680 nF | Gain = 28 dB |

| f = 200 Hz | PVDD = 105 V |
| CLOAD = 47 nF | Gain = 40 dB |

| f = 200 Hz | PVDD = 55 V |
| CLOAD = 330 nF | Gain = 34 dB |

| f = 200 Hz | PVDD = 30 V |
| CLOAD = 680 nF | Gain = 28 dB |
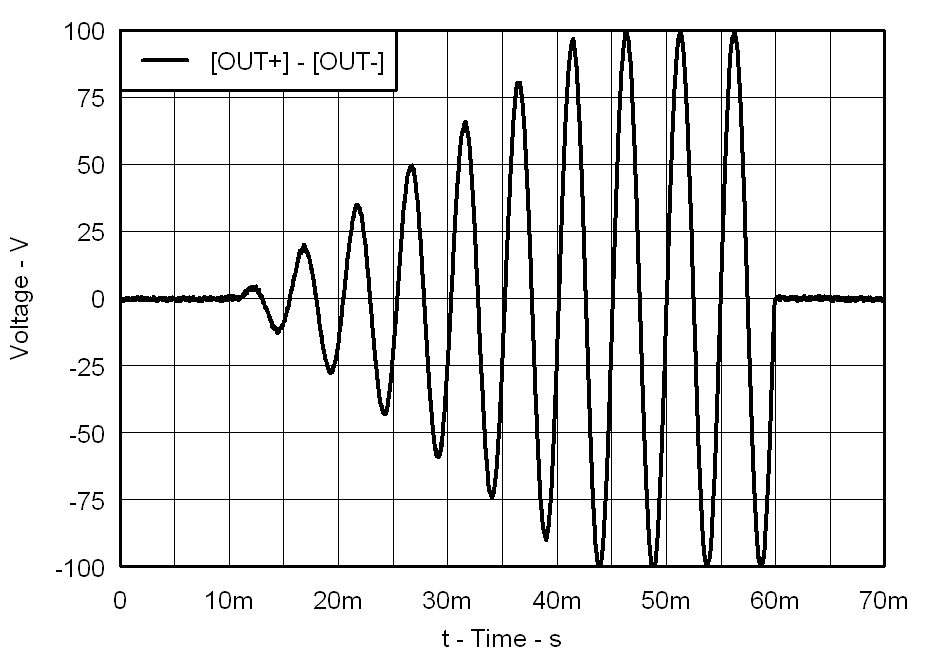
| f = 200 Hz | PVDD = 105 V |
| CLOAD = 47 nF | Gain = 40 dB |
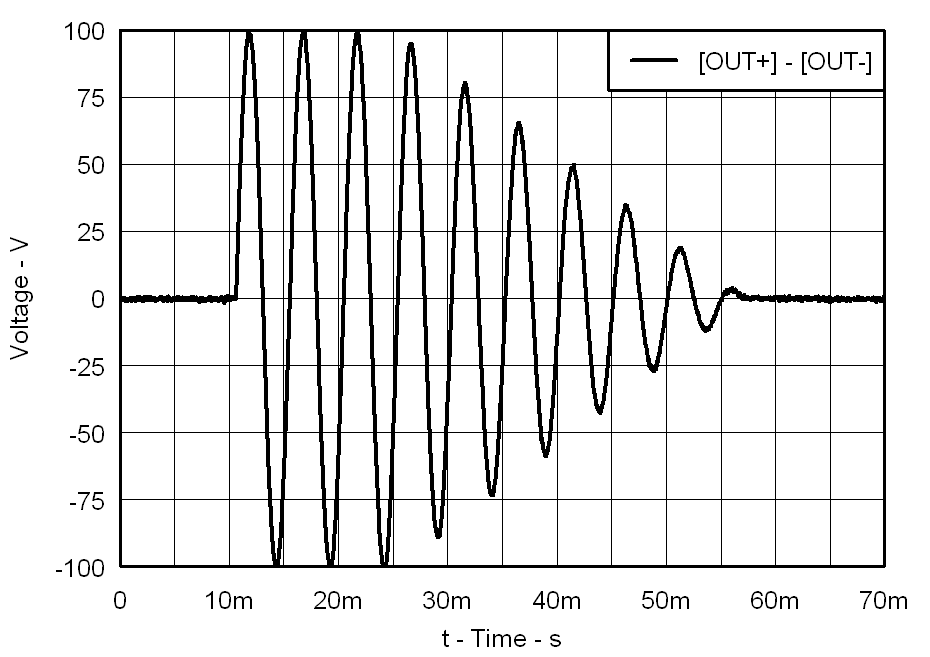
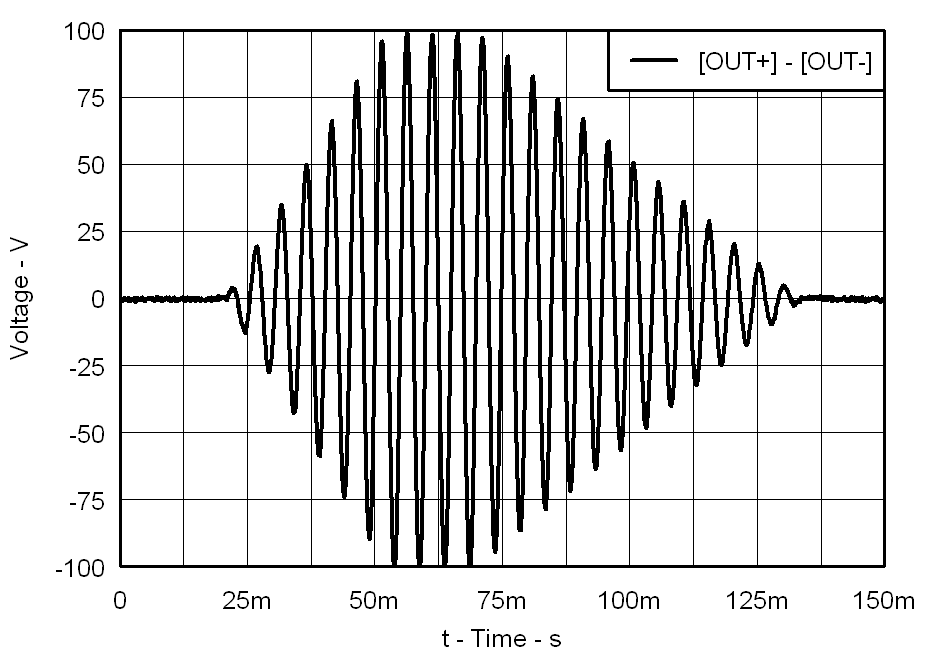
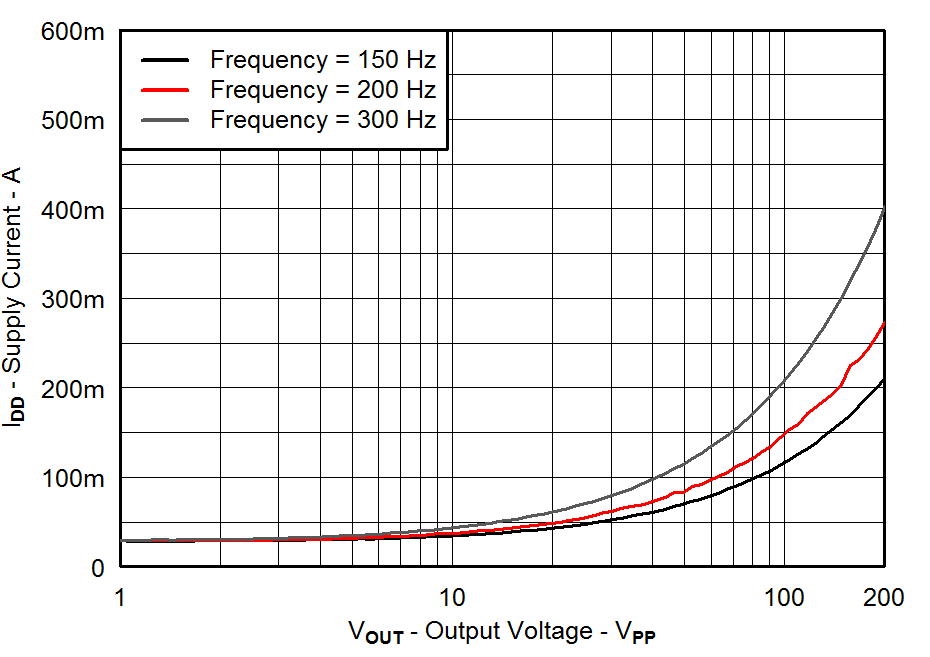
| VDD = 3.6 V | PVDD = 105 V |
| CLOAD = 47 nF | Gain = 40 dB |
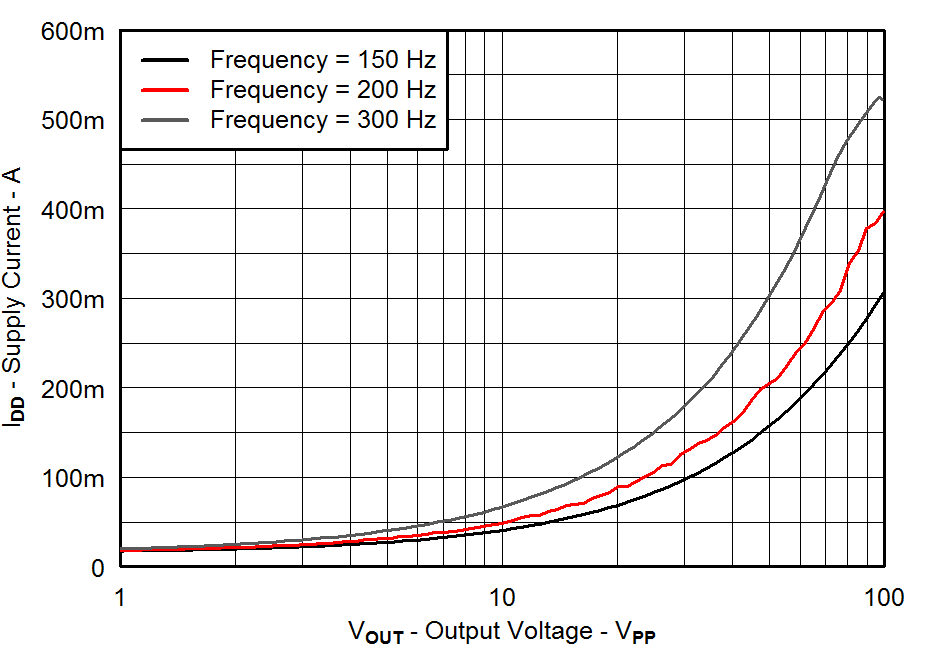
| VDD = 3.6 V | PVDD = 55 V |
| CLOAD = 330 nF | Gain = 34 dB |
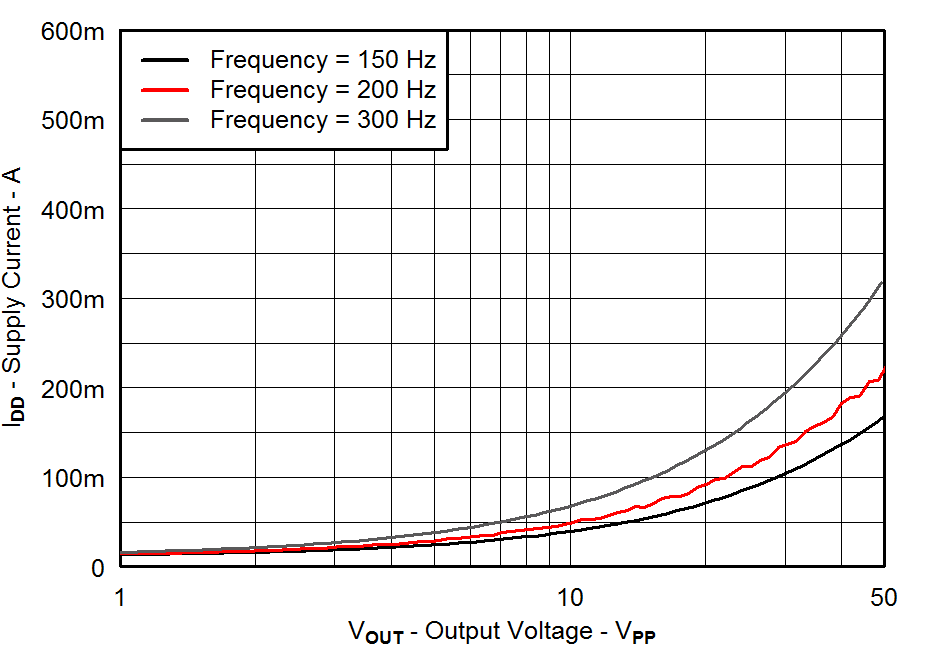
| VDD = 3.6 V | PVDD = 30 V |
| CLOAD = 680 nF | Gain = 28 dB |
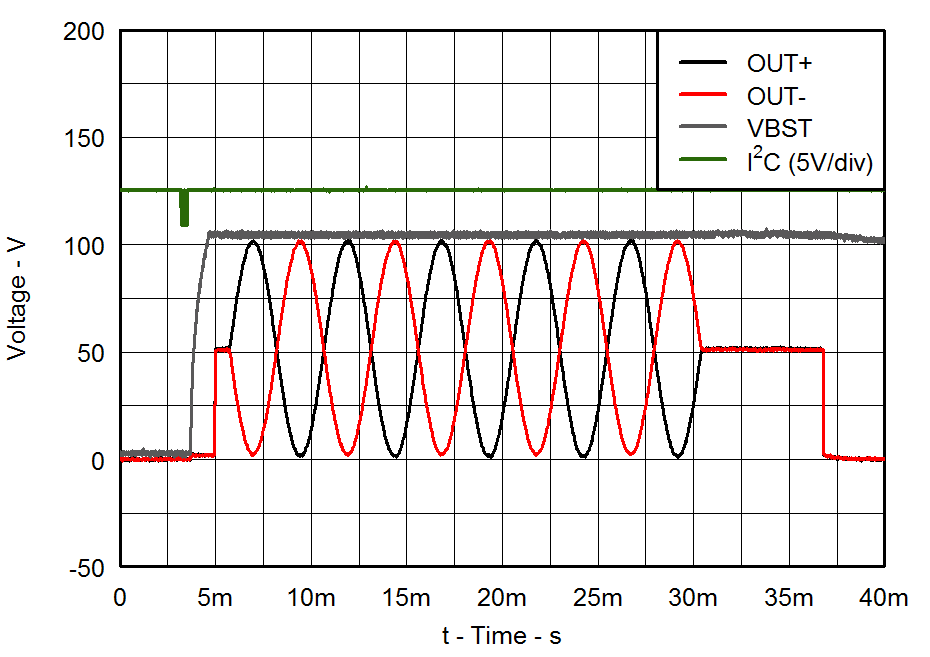
| VDD = 3.6 V | PVDD = 105 V |
| CLOAD = 47 nF | Gain = 40 dB |
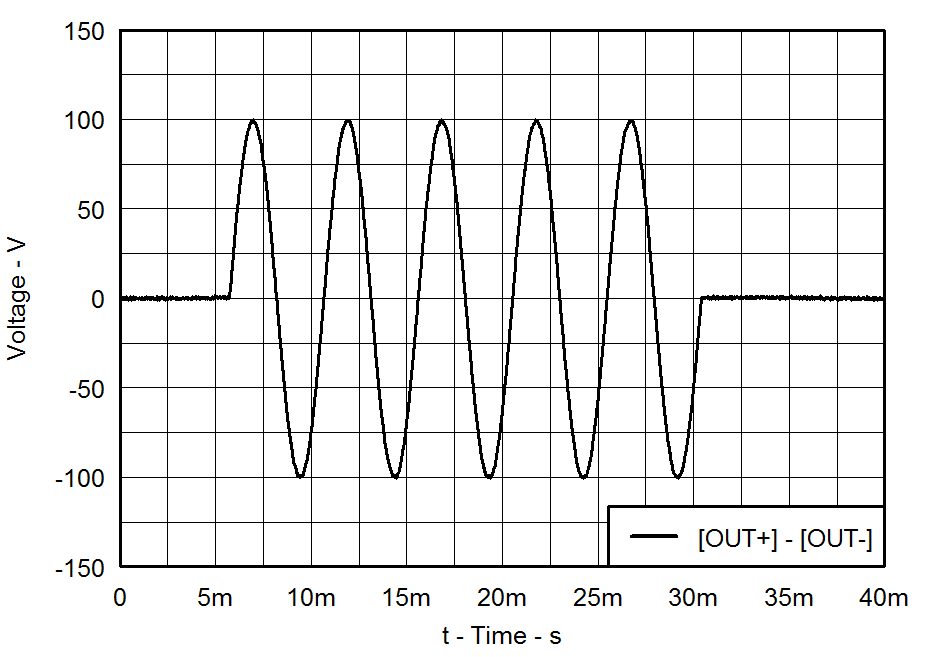
| VDD = 3.6 V | PVDD = 55 V |
| CLOAD = 330 nF | Gain = 34 dB |
| VDD = 3.6 V | PVDD = 30 V |
| CLOAD = 680 nF | Gain = 28 dB |