SLVSE38A April 2018 – July 2018 DRV8306
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Three Phase Smart Gate Drivers
- 7.3.2 DVDD Linear Voltage Regulator
- 7.3.3 Pulse-by-Pulse Current Limit
- 7.3.4 Hall Comparators
- 7.3.5 FGOUT Signal
- 7.3.6 Pin Diagrams
- 7.3.7 Gate-Driver Protective Circuits
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RSM|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RSM|32
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.3.1 Example
The goal of this example is to set the VDS monitor to trip at a current greater than 50 A. According to the CSD18514Q5A 40 V N-Channel NexFET™ Power MOSFET data sheet, the RDS(on) value is 1.8 times higher at 175°C, and the maximum RDS(on) value at a VGS of 10 V is 4.9 mΩ. From these values, the approximate worst-case value of RDS(on) is 1.8 × 4.9 mΩ = 8.82 mΩ.
Using Equation 10 with a value of 8.82 mΩ for RDS(on) and a worst-case motor current of 50 A, Equation 11 shows the calculated the value of the VDS monitors.
Equation 11. 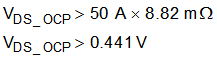
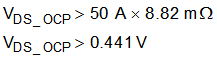
For this example, the value of VDS_OCP was selected as 0.51 V.
The deglitch time for the VDS overcurrent monitor is fixed at 4 µs.