SLLSFQ7 November 2023 MCF8329A
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Three Phase BLDC Gate Drivers
- 7.3.2 Gate Drive Architecture
- 7.3.3 AVDD Linear Voltage Regulator
- 7.3.4 DVDD Voltage Regulator
- 7.3.5 Low-Side Current Sense Amplifier
- 7.3.6 Device Interface Modes
- 7.3.7 Motor Control Input Options
- 7.3.8 Bootstrap Capacitor Initial Charging
- 7.3.9 Starting the Motor Under Different Initial Conditions
- 7.3.10 Motor Start Sequence (MSS)
- 7.3.11 Closed Loop Operation
- 7.3.12 Maximum Torque Per Ampere (MTPA) Control
- 7.3.13 Flux Weakening Control
- 7.3.14 Motor Parameters
- 7.3.15 Motor Parameter Extraction Tool (MPET)
- 7.3.16 Anti-Voltage Surge (AVS)
- 7.3.17 Output PWM Switching Frequency
- 7.3.18 Active Braking
- 7.3.19 Dead Time Compensation
- 7.3.20 Voltage Sense Scaling
- 7.3.21 Motor Stop Options
- 7.3.22 FG Configuration
- 7.3.23 DC Bus Current Limit
- 7.3.24
Protections
- 7.3.24.1 PVDD Supply Undervoltage Lockout (PVDD_UV)
- 7.3.24.2 AVDD Power on Reset (AVDD_POR)
- 7.3.24.3 GVDD Undervoltage Lockout (GVDD_UV)
- 7.3.24.4 BST Undervoltage Lockout (BST_UV)
- 7.3.24.5 MOSFET VDS Overcurrent Protection (VDS_OCP)
- 7.3.24.6 VSENSE Overcurrent Protection (SEN_OCP)
- 7.3.24.7 Thermal Shutdown (OTSD)
- 7.3.24.8 Hardware Lock Detection Current Limit (HW_LOCK_ILIMIT)
- 7.3.24.9 Lock Detection Current Limit (LOCK_ILIMIT)
- 7.3.24.10 Motor Lock (MTR_LCK)
- 7.3.24.11 Motor Lock Detection
- 7.3.24.12 MPET Faults
- 7.3.24.13 IPD Faults
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 External Interface
- 7.6 EEPROM access and I2C interface
- 7.7 EEPROM (Non-Volatile) Register Map
- 7.8 RAM (Volatile) Register Map
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- Detailed Design Procedure
- Bootstrap Capacitor and GVDD Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1 Selection of External MOSFET for VREG Power Supply
- Gate Drive Current
- Gate Resistor Selection
- System Considerations in High Power Designs
- Capacitor Voltage Ratings
- External Power Stage Components
- 8.2.2 Application curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- REE|36
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.1 Bulk Capacitance
Having an appropriate local bulk capacitance is an important factor in motor drive system design. It is generally beneficial to have more bulk capacitance, while the disadvantages are increased cost and physical size.
The amount of local capacitance needed depends on a variety of factors, including:
- The highest current required by the motor system
- The capacitance and current capability of the power supply
- The amount of parasitic inductance between the power supply and motor system
- The acceptable voltage ripple
- The type of motor used (brushed DC, brushless DC, stepper)
- The motor braking method
The inductance between the power supply and the motor drive system limits the rate at which current can change from the power supply. If the local bulk capacitance is too small, the system responds to excessive current demands or dumps from the motor with a change in PVDD voltage. When adequate bulk capacitance is used, the PVDD voltage remains stable and high current can be quickly supplied.
The data sheet generally provides a recommended value, but system-level testing is required to determine the appropriate bulk capacitor. The voltage rating for bulk capacitors should be higher than the operating voltage, to provide margin for cases when the motor transfers energy to the supply.
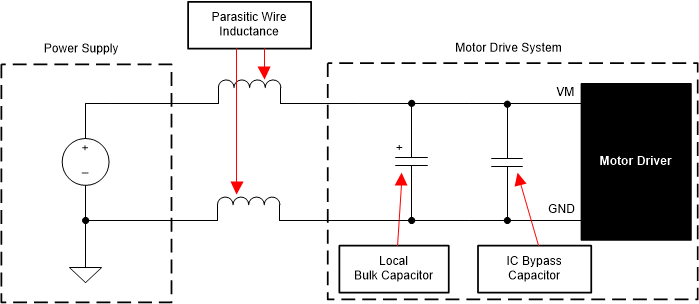 Figure 9-1 Example Setup of Motor Drive System With External Power Supply
Figure 9-1 Example Setup of Motor Drive System With External Power Supply