SLLS530C April 2002 – February 2019 SN65LVDT14 , SN65LVDT41
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Receiver Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Driver Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Device Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8 Receiver Switching Characteristics
- 6.9 Driver Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PW|20
Orderable Information
7 Parameter Measurement Information
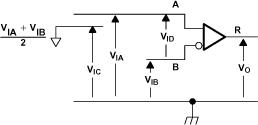 Figure 8. Receiver Voltage Definitions
Figure 8. Receiver Voltage Definitions Table 1. Receiver Minimum and Maximum Input Threshold Test Voltages
| APPLIED VOLTAGES | RESULTING DIFFERENTIAL
INPUT VOLTAGE |
RESULTING
COMMON-MODE INPUT VOLTAGE |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| VIA | VIB | VID | VIC |
| 1.25 V | 1.15 V | 100 mV | 1.2 V |
| 1.15 V | 1.25 V | –100 mV | 1.2 V |
| 2.4 V | 2.3 V | 100 mV | 2.35 V |
| 2.3 V | 2.4 V | –100 mV | 2.35 V |
| 0.1 V | 0.0 V | 100 mV | 0.05 V |
| 0.0 V | 0.1 V | –100 mV | 0.05 V |
| 1.5 V | 0.9 V | 600 mV | 1.2 V |
| 0.9 V | 1.5 V | –600 mV | 1.2 V |
| 2.4 V | 1.8 V | 600 mV | 2.1 V |
| 1.8 V | 2.4 V | –600 mV | 2.1 V |
| 0.6 V | 0.0 V | 600 mV | 0.3 V |
| 0.0 V | 0.6 V | –600 mV | 0.3 V |
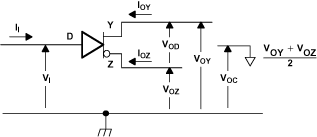 Figure 9. Driver Voltage and Current Definitions
Figure 9. Driver Voltage and Current Definitions 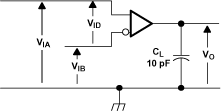 Figure 10. Receiver Timing Test Circuit
Figure 10. Receiver Timing Test Circuit 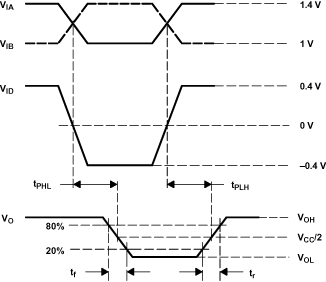
A. All input pulses are supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤ 1 ns, pulse repetition rate (PRR) = 1 Mpps, pulse width = 0.5 ± 0.05 µs. CL includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within 0,06 m of the D.U.T.
Figure 11. Receiver Timing Test Circuit Waveforms 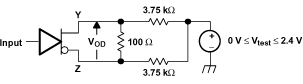 Figure 12. Driver VDO Test Circuit
Figure 12. Driver VDO Test Circuit 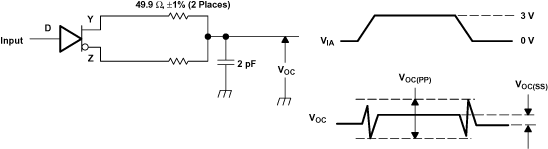
A. All input pulses are supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤ 1 ns, pulse repetition rate (PRR) = 0.5 Mpps, pulse width = 500 ± 10 ns. CL includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within 0.06 mm of the D.U.T. The measurement of VOC(PP) is made on test equipment with a –3-dB bandwidth of at least 1 GHz.
Figure 13. Test Circuit and Definitions for the Driver Common-Mode Output Voltage 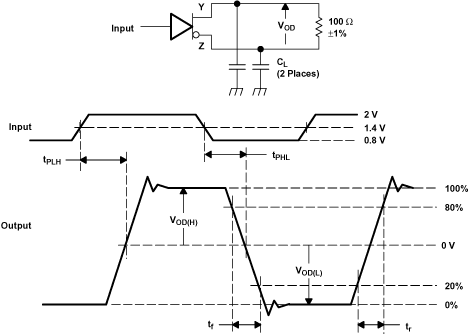
A. All input pulses are supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤ 1 ns, pulse repetition rate (PRR) = 1 Mpps, pulse width = 0.5 ± 0.05 µs. CL includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within 0.06 mm of the D.U.T.
Figure 14. Test Circuit, Timing, and Voltage Definitions for the Differential Output Signal