SPRS565D April 2009 – June 2014 TMS320C6743
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1TMS320C6743 Fixed- and Floating-Point Digital Signal Processor
- 2Revision History
-
3Device Overview
- 3.1 Device Characteristics
- 3.2 Device Compatibility
- 3.3 DSP Subsystem
- 3.4 Memory Map Summary
- 3.5 Pin Assignments
- 3.6
Terminal Functions
- 3.6.1 Device Reset and JTAG
- 3.6.2 High-Frequency Oscillator and PLL
- 3.6.3 External Memory Interface A (ASYNC)
- 3.6.4 External Memory Interface B (SDRAM only)
- 3.6.5 Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (SPI0)
- 3.6.6 Enhanced Capture/Auxiliary PWM Modules (eCAP0, eCAP1, eCAP2)
- 3.6.7 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulators (eHRPWM0, eHRPWM1, eHRPWM2)
- 3.6.8 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse Module (eQEP)
- 3.6.9 Boot
- 3.6.10 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters (UART0, UART2)
- 3.6.11 Inter-Integrated Circuit Modules (I2C0, I2C1)
- 3.6.12 Timers
- 3.6.13 Multichannel Audio Serial Ports (McASP0, McASP1)
- 3.6.14 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 3.6.15 Multimedia Card/Secure Digital (MMC/SD)
- 3.6.16 General-Purpose IO Only Terminal Functions
- 3.6.17 Reserved and No Connect Terminal Functions
- 3.6.18 Supply and Ground Terminal Functions
- 4Device Configuration
-
5Device Operating Conditions
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Junction Temperature Range (Unless Otherwise Noted)
- 5.2 Handling Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Notes on Recommended Power-On Hours (POH)
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Ranges of Supply Voltage and Operating Junction Temperature (Unless Otherwise Noted)
-
6Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
- 6.1 Parameter Information
- 6.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 6.3 Power Supplies
- 6.4 Reset
- 6.5 Crystal Oscillator or External Clock Input
- 6.6 Clock PLLs
- 6.7 DSP Interrupts
- 6.8 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 6.9 EDMA
- 6.10 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA)
- 6.11 External Memory Interface B (EMIFB)
- 6.12 Memory Protection Units
- 6.13 MMC / SD / SDIO (MMCSD)
- 6.14 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 6.15 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- 6.16 Multichannel Audio Serial Ports (McASP0, McASP1)
- 6.17
Serial Peripheral Interface Ports (SPI0)
- 6.17.1 SPI Peripheral Registers Description(s)
- 6.17.2
SPI Electrical Data/Timing
- 6.17.2.1
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Timing
- Table 6-49 General Timing Requirements for SPI0 Master Modes
- Table 6-50 General Timing Requirements for SPI0 Slave Modes
- Table 6-51 Additional SPI0 Master Timings, 4-Pin Enable Option
- Table 6-52 Additional SPI0 Master Timings, 4-Pin Chip Select Option
- Table 6-53 Additional SPI0 Master Timings, 5-Pin Option
- Table 6-54 Additional SPI0 Slave Timings, 4-Pin Enable Option
- Table 6-55 Additional SPI0 Slave Timings, 4-Pin Chip Select Option
- Table 6-56 Additional SPI0 Slave Timings, 5-Pin Option
- 6.17.2.1
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Timing
- 6.18 Enhanced Capture (eCAP) Peripheral
- 6.19 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder (eQEP) Peripheral
- 6.20 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (eHRPWM) Modules
- 6.21 Timers
- 6.22 Inter-Integrated Circuit Serial Ports (I2C0, I2C1)
- 6.23 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 6.24 Power and Sleep Controller (PSC)
- 6.25 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS)
- 6.26 Emulation Logic
- 6.27 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZKB|256
- PTP|176
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PTP|176
Orderable Information
6.5 Crystal Oscillator or External Clock Input
The device includes two choices to provide an external clock input, which is fed to the on-chip PLL to generate high-frequency system clocks. These options are illustrated in Figure 6-6 and Figure 6-7. For input clock frequencies between 12 and 20 MHz, a crystal with 80 ohm max ESR is recommended. For input clock frequencies between 20 and 30 MHz, a crystal with 60 ohm max ESR is recommended. Typical load capacitance values are 10-20 pF, where the load capacitance is the series combination of C1 and C2.
The CLKMODE bit in the PLLCTL register must be 0 to use the on-chip oscillator. If CLKMODE is set to 1, the internal oscillator is disabled.
- Figure 6-6 illustrates the option that uses on-chip 1.2V oscillator with external crystal circuit.
- Figure 6-7 illustrates the option that uses an external 1.2V clock input.
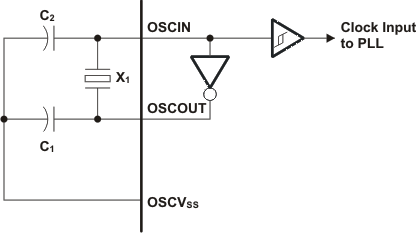 Figure 6-6 On-Chip 1.2V Oscillator
Figure 6-6 On-Chip 1.2V Oscillator Table 6-2 Oscillator Timing Requirements
| NO | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fosc | Oscillator frequency range (OSCIN/OSCOUT) | 12 | 30 | MHz |
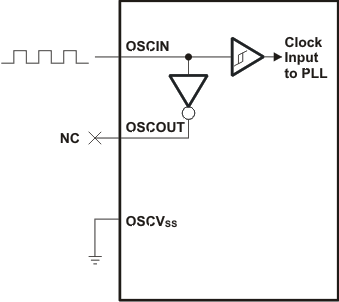 Figure 6-7 External 1.2V Clock Source
Figure 6-7 External 1.2V Clock Source Table 6-3 OSCIN Timing Requirements for Externally Driven Clock
| NO | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fOSCIN | OSCIN frequency range (OSCIN) | 12 | 50 | MHz |
| tc(OSCIN) | Cycle time, external clock driven on OSCIN | 20 | ns | |
| tw(OSCINH) | Pulse width high, external clock on OSCIN | 0.4 tc(OSCIN) | ns | |
| tw(OSCINL) | Pulse width low, external clock on OSCIN | 0.4 tc(OSCIN) | ns | |
| tt(OSCIN) | Transition time, OSCIN | 0.25P or 10(1) | ns | |
| tj(OSCIN) | Period jitter, OSCIN | 0.02P | ns |