SLASEN3B January 2018 – August 2018 TPA3220
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Audio Characteristics (BTL)
- 7.7 Audio Characteristics (PBTL)
- 7.8 Typical Characteristics, BTL Configuration, AD-mode
- 7.9 Typical Characteristics, PBTL Configuration, AD-mode
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4
Device Functional Modes
- 9.4.1 Powering Up
- 9.4.2 Powering Down
- 9.4.3 Device Reset
- 9.4.4 Device Soft Mute
- 9.4.5
Device Protection System
- 9.4.5.1 Overload and Short Circuit Current Protection
- 9.4.5.2 Signal Clipping and Pulse Injector
- 9.4.5.3 DC Speaker Protection
- 9.4.5.4 Pin-to-Pin Short Circuit Protection (PPSC)
- 9.4.5.5 Overtemperature Protection OTW and OTE
- 9.4.5.6 Undervoltage Protection (UVP) and Power-on Reset (POR)
- 9.4.5.7 Fault Handling
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDW|44
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.8 Typical Characteristics, BTL Configuration, AD-mode
All Measurements taken at audio frequency = 1 kHz, PVDD_X = 30 V, VDD = 5 V, GVDD = 5 V, RL = 4 Ω, fS = 480 kHz, TA = 25°C, Output Filter: LDEM = 10 μH, CDEM = 1 µF, AD Modulation, AES17 + AUX-0025 measurement filters, unless otherwise noted.
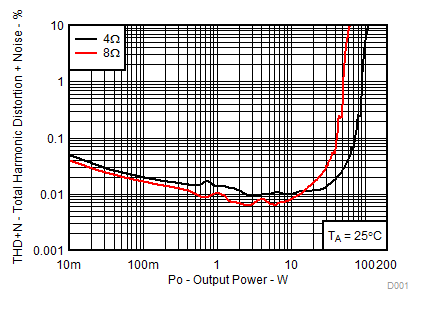
| RL = 3 Ω, 4 Ω, 8 Ω | TA = 25°C | |
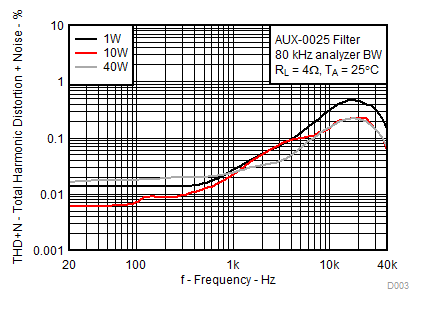
| RL =4 Ω | P = 1W, 10W, 40W | |
| AUX-0025 filter, 80 kHz analyzer BW | TA = 25°C | |
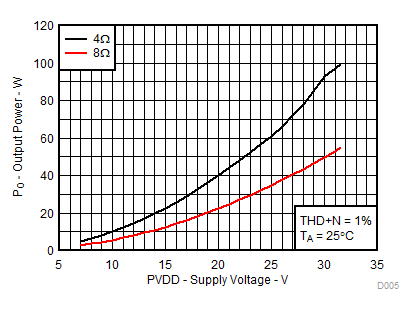
A.
Figure 5. Output Power vs Supply Voltage, AD-mode | RL = 4 Ω, 8 Ω | THD+N = 1% | |
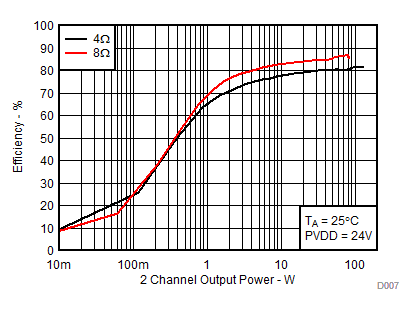
| RL = 4 Ω, 8 Ω | PVDD = 24V | |
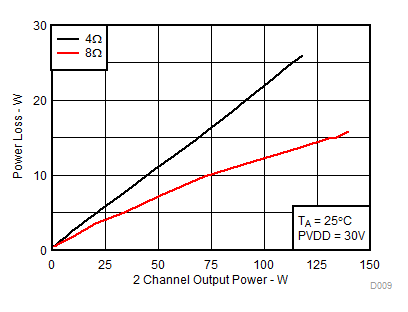
| RL = 4 Ω, 8 Ω |
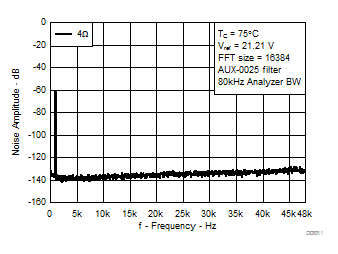
A.
Figure 11. Noise Amplitude vs Frequency, AD-mode | RL = 4 Ω |
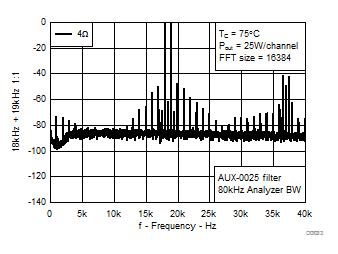
1.
Figure 13. CCIF Intermodulation, AD-Mode, 25 W 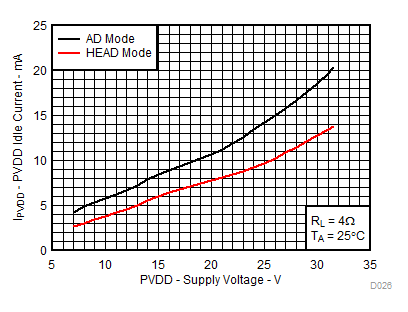
1.
Figure 15. Idle Current vs Supply Voltage, AD vs HEAD 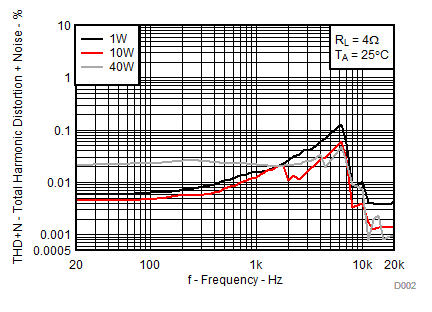
| RL = 4 Ω | P = 1W, 10W, 40W | TA = 25°C |
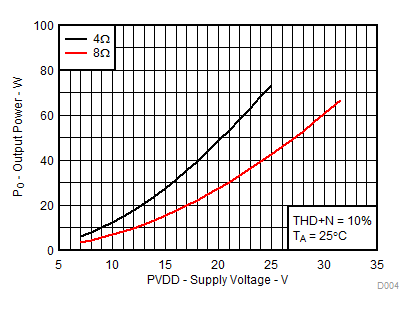
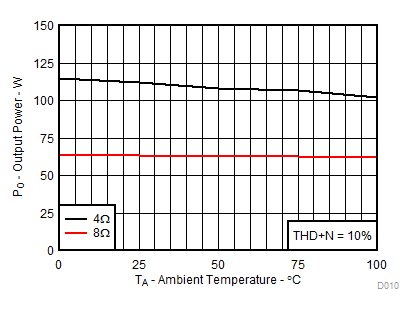
| RL = 4 Ω, 8 Ω | THD+N = 10% | |
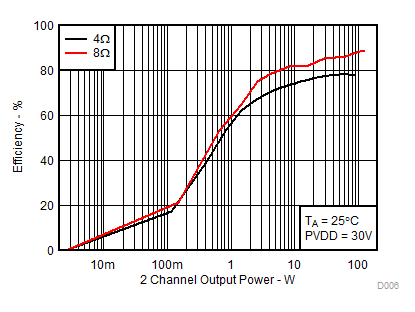
A.
Figure 6. System Efficiency vs Output Power, AD-mode | RL = 4 Ω, 8 Ω | PVDD = 30V |
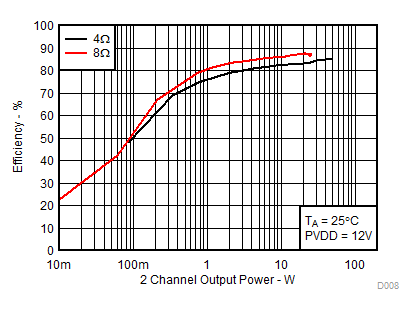
| RL = 4 Ω, 8 Ω | PVDD = 12V | |
A.
Figure 10. Output Power vs Ambient Temperature, AD-mode | RL = 4 Ω, 8 Ω |
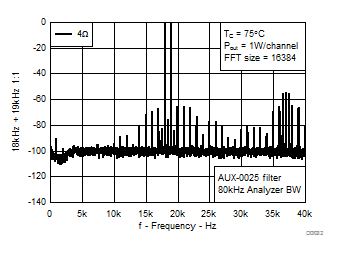
| 18 kHz + 19 kHz | Ratio 1 : 1 |
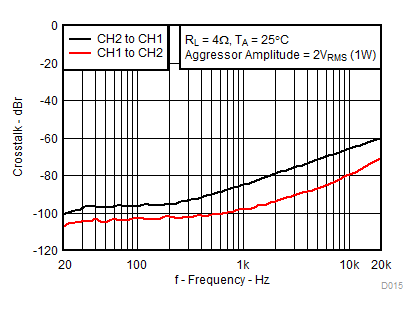
1.
Figure 14. Channel-to-Channel Crosstalk vs Frequency, AD-mode 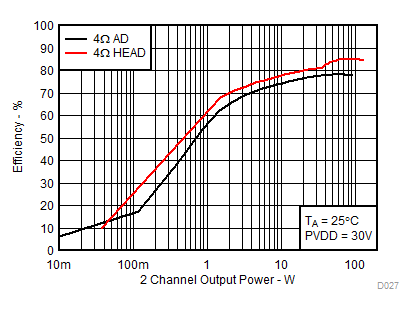
1.
Figure 16. Efficiency vs Output Power, AD vs HEAD