9.2.1.3 Application Curves
Table 10 lists the components that were used for the measurements contained in the following pages.
Table 10. Components for Application Characteristic Curves
| REFERENCE |
DESCRIPTION |
PART NUMBER |
MANUFACTURER |
| C1 |
Capacitor, 10 µF, 10 V, 0603, ceramic |
GRM188R61A106ME69 |
Murata |
| C2, C3 |
Capacitor, 22 µF, 10 V, 0603, ceramic |
GRM187R61A226ME15 |
Murata |
| L1 |
Inductor, 0.47 µH |
XFL4015-471MEC |
Coilcraft |
| U1 |
Integrated circuit |
TPS63810YFF |
Texas Instruments |
WHITESPACE
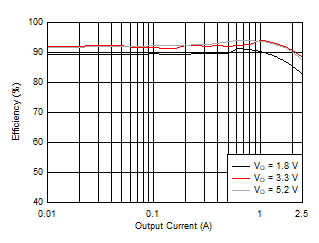 Figure 32. Efficiency versus Output Current
Figure 32. Efficiency versus Output Current 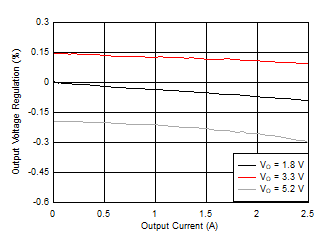
| VI = 3.6 V |
FPWM |
TA = 25°C |
Figure 34. Load Regulation 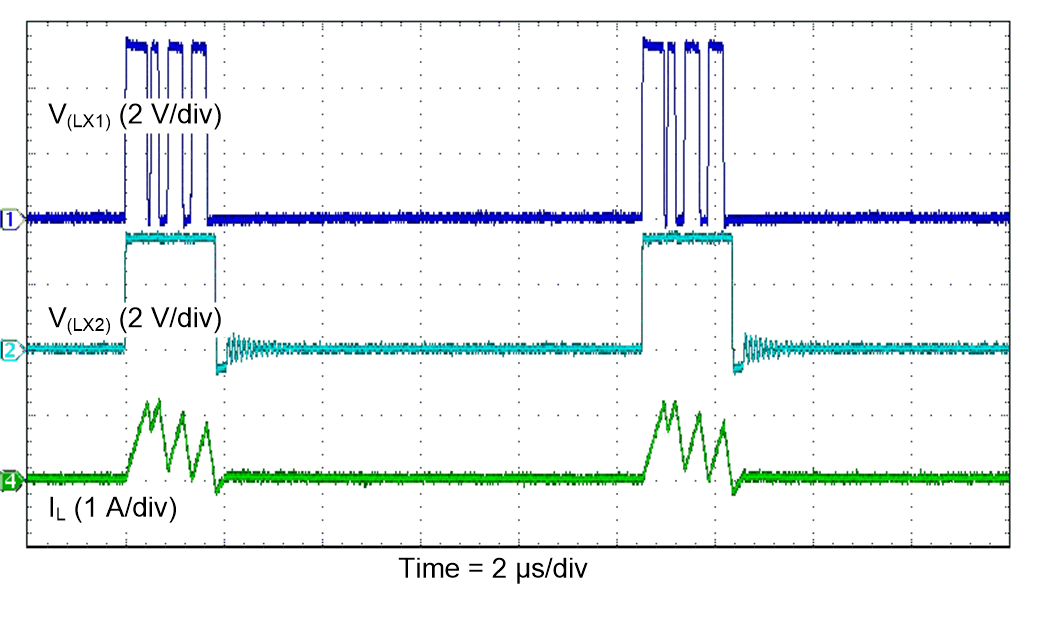
| VI = 5 V |
PSM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
IO = 100 mA |
|
Figure 36. PFM Switching Waveforms
(Buck Operation) 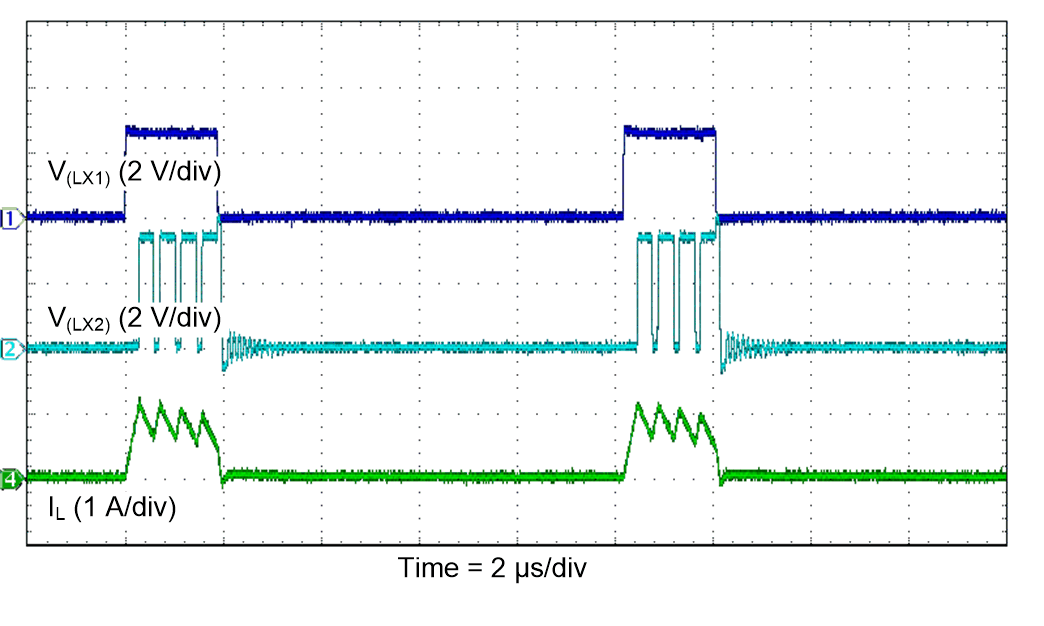
| VI = 2.5 V |
PSM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
IO = 100 mA |
|
Figure 38. PFM Switching Waveforms
(Boost Operation) 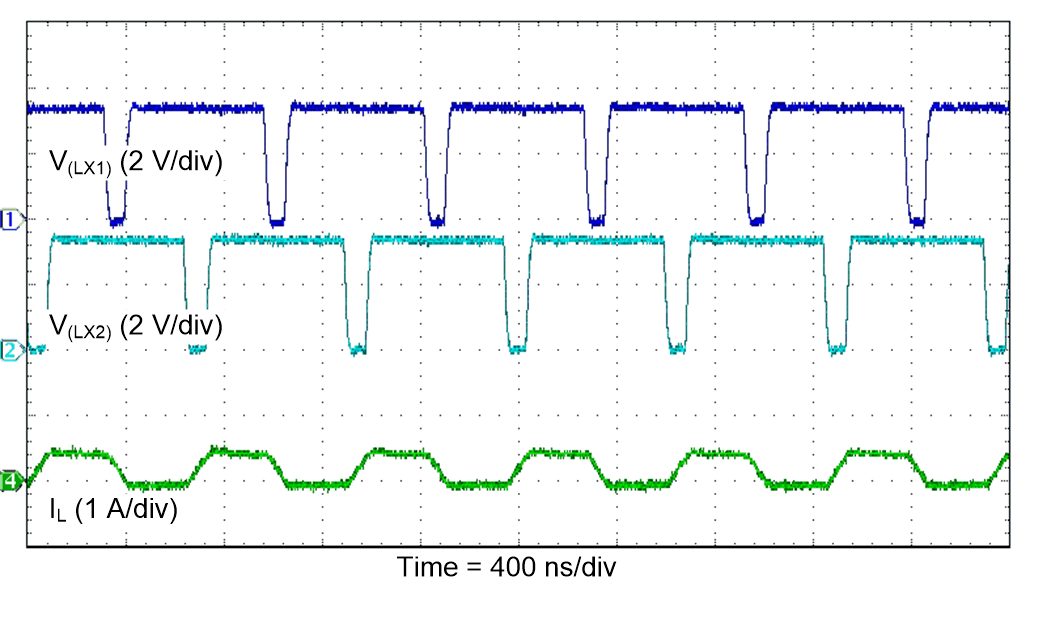
| VI = 3.3 V |
FPWM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
IO = 100 mA |
|
Figure 40. PWM Switching Waveforms
(Buck-Boost Operation) 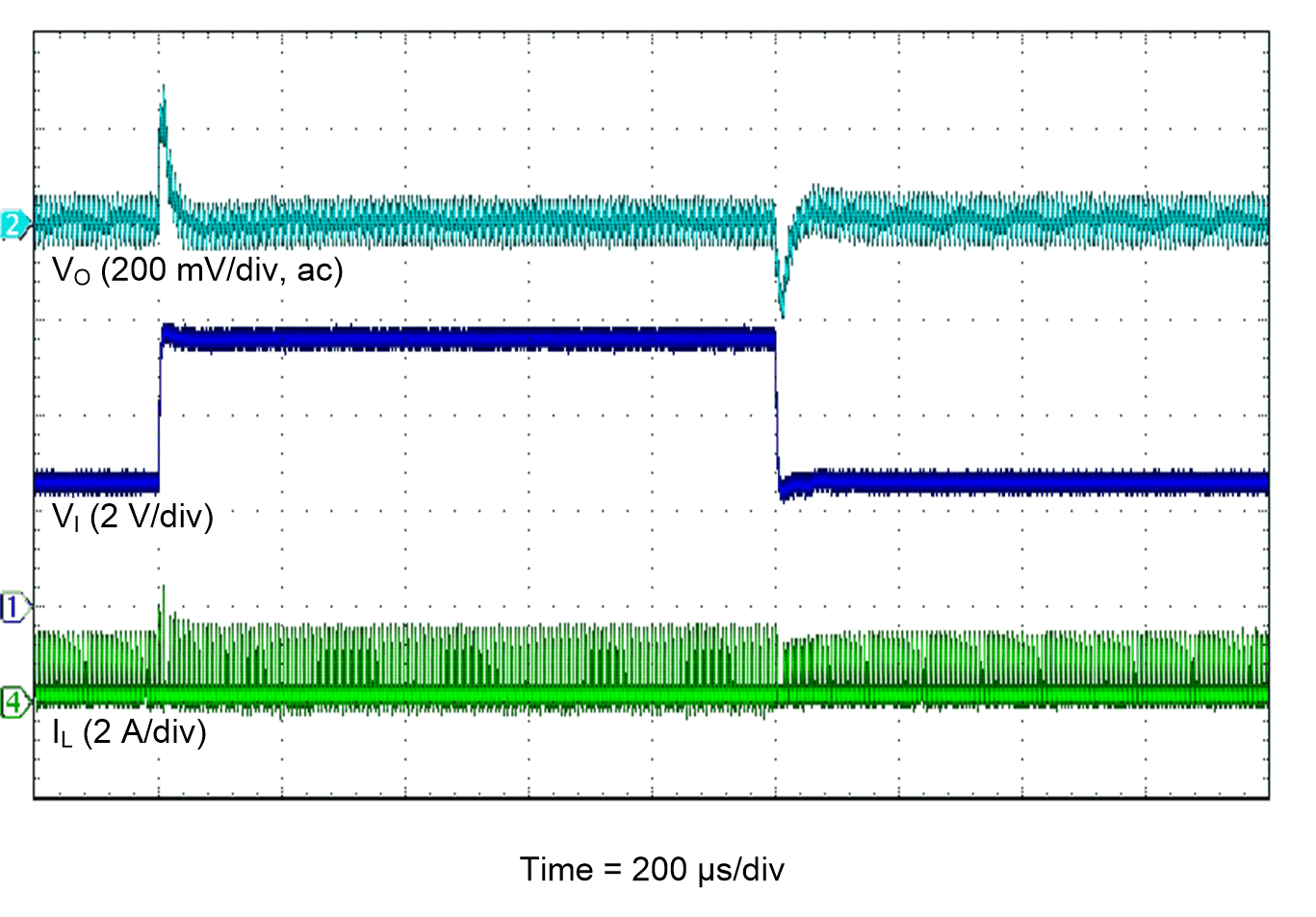
| VI = 2.5 V to 5.5 V |
PSM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
IO = 200 mA |
|
Figure 42. Line Transient Response 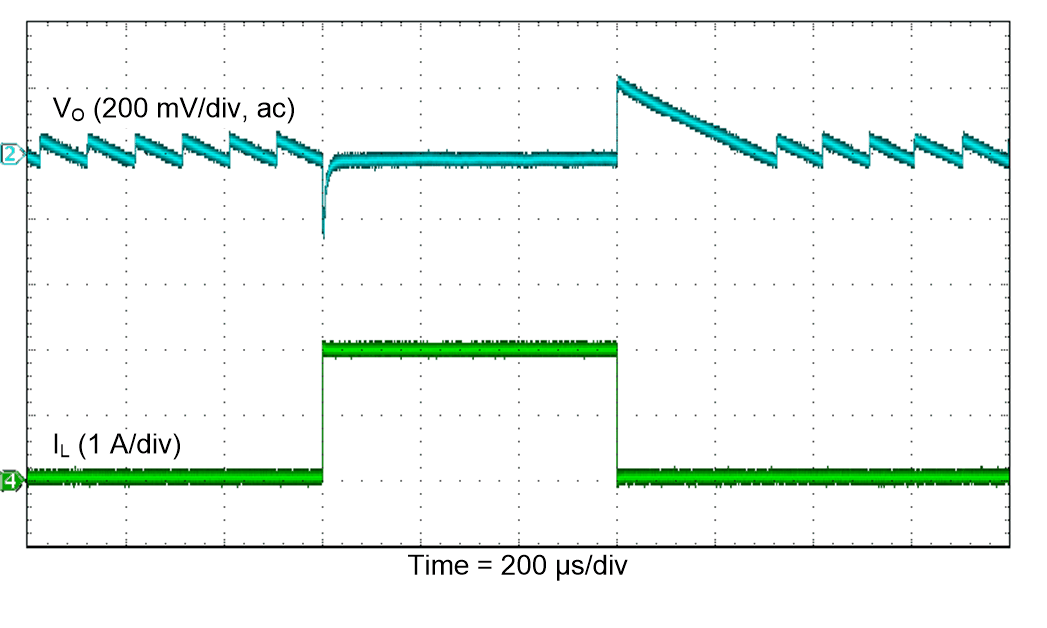
| VI = 4.2 V |
PSM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
IO = 10 mA to 2 A |
|
Figure 44. Load Transient Response (Buck) 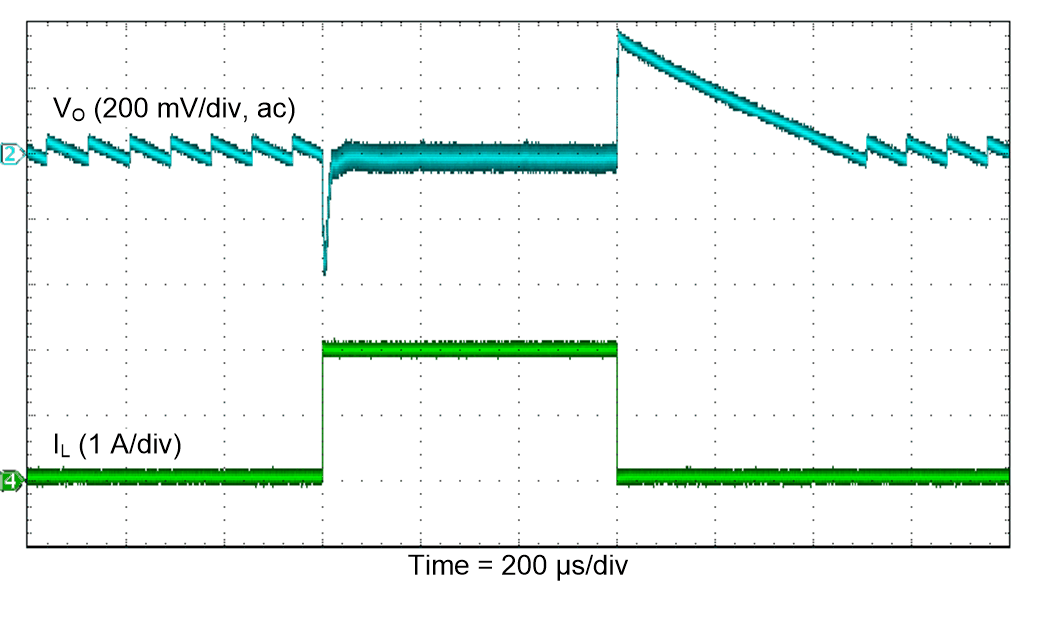
| VI = 2.6 V |
PSM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
IO = 10 mA to 2 A |
|
Figure 46. Load Transient Response (Boost) 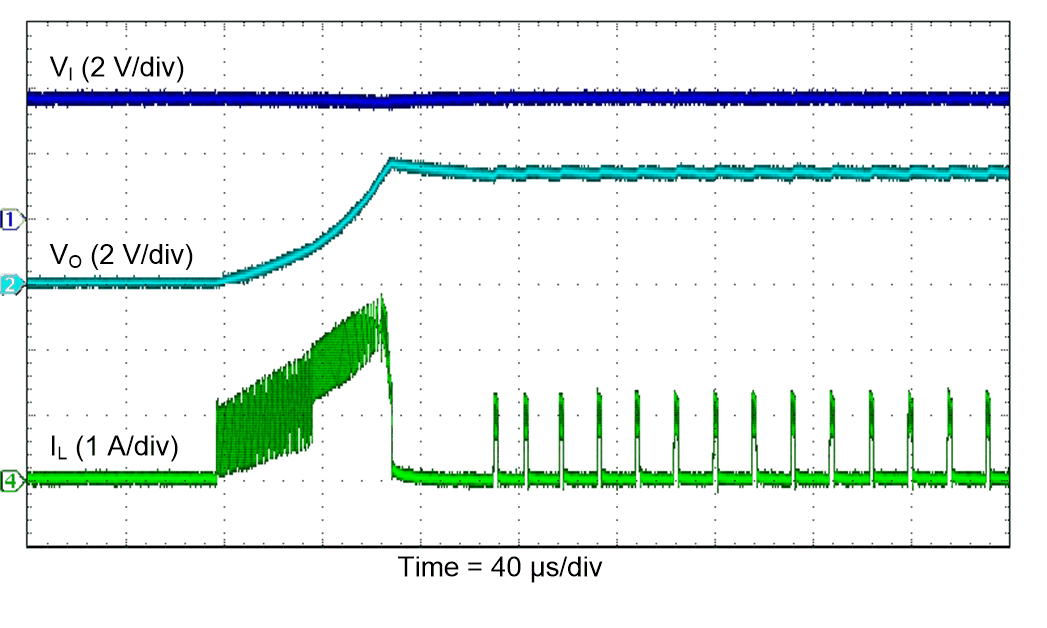
| VI = 3.6 V |
PSM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
RL = 33 Ω |
|
Figure 48. Start-Up Waveforms
(Light Load) 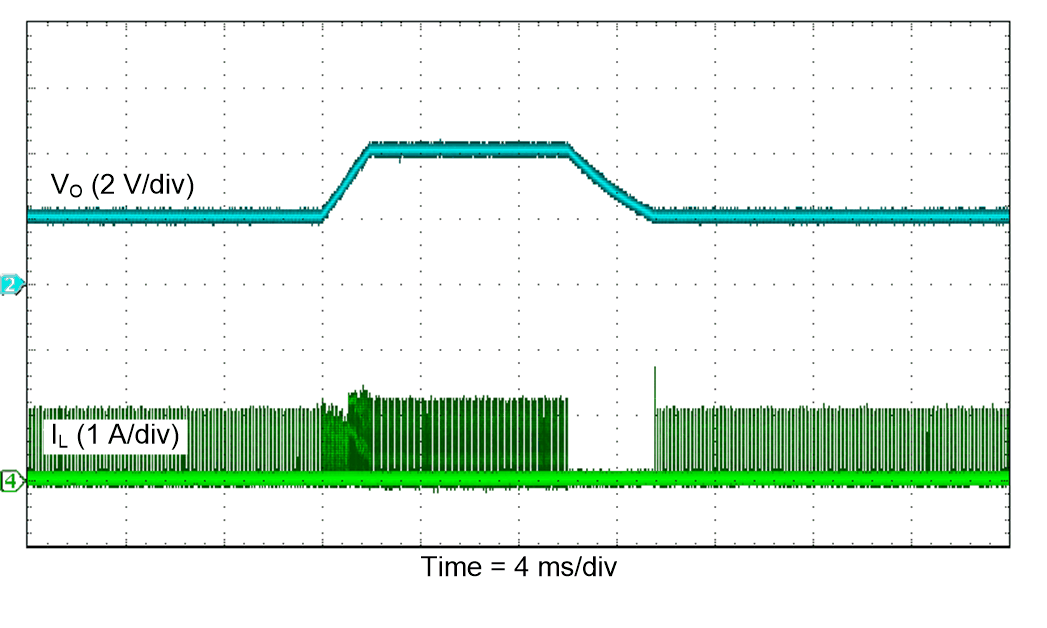
| VI = 3.6 V |
PSM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 2 V to 4 V |
RL = 330 Ω |
|
Figure 50. Dynamic Voltage Scaling (PFM) 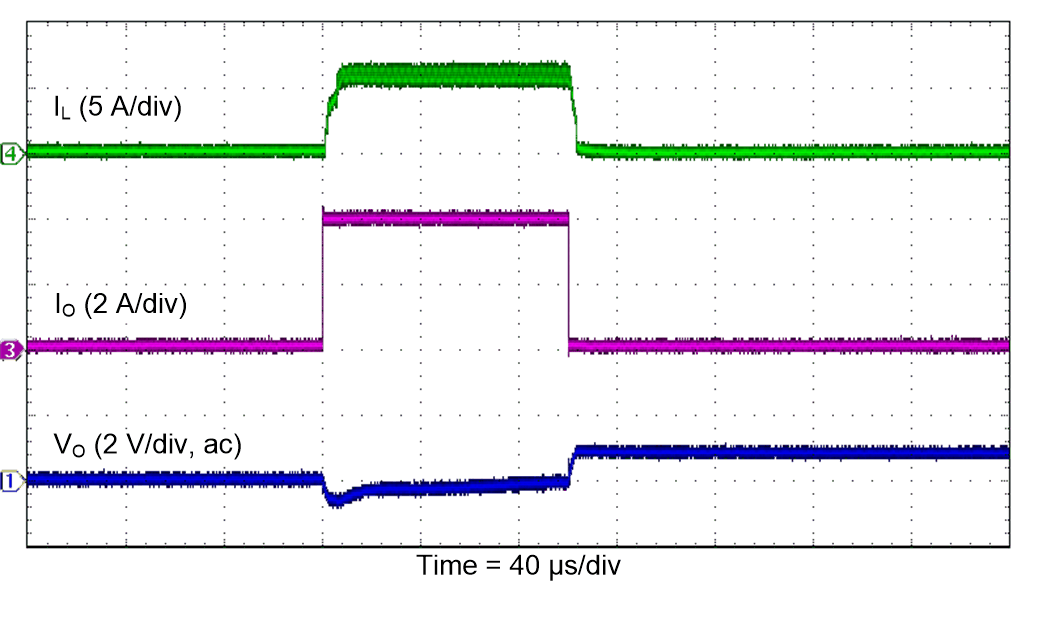
| VI = 3.6 V |
PSM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
|
|
Figure 52. Overcurrent Protection 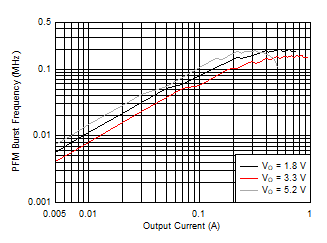 Figure 54. Burst Switching Frequency versus Output Current
Figure 54. Burst Switching Frequency versus Output Current
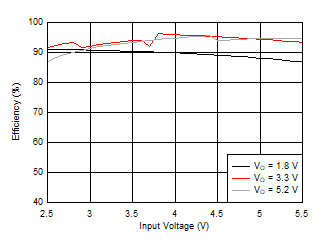 Figure 33. Efficiency versus Input Voltage
Figure 33. Efficiency versus Input Voltage 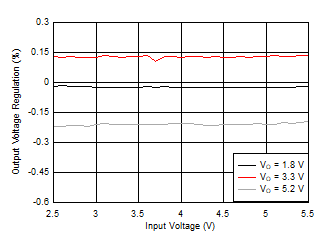 Figure 35. Line Regulation
Figure 35. Line Regulation 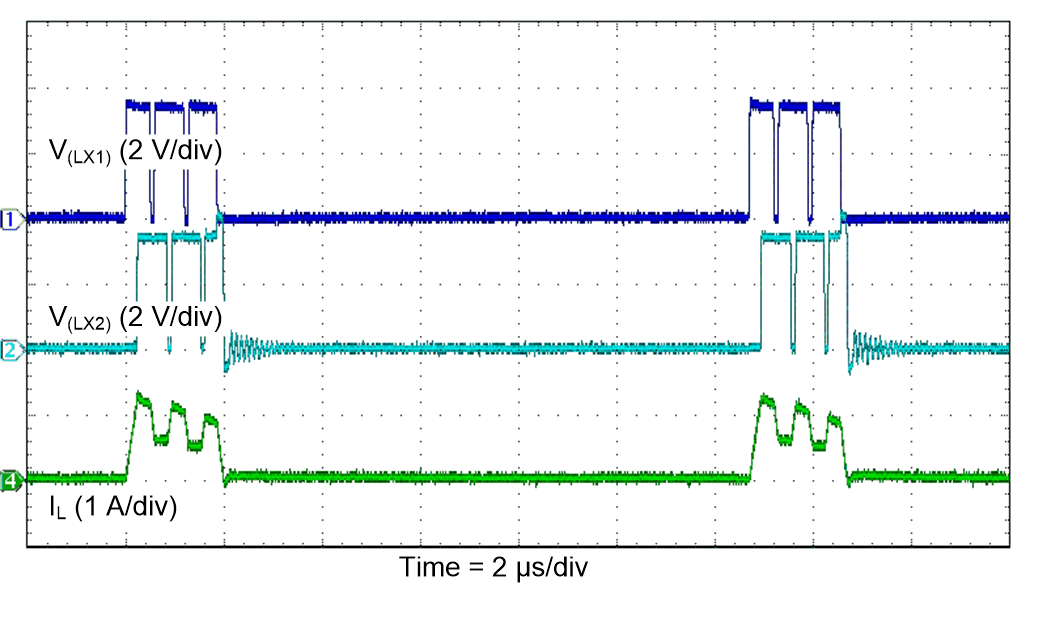
| VI = 3.3 V |
PSM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
IO = 100 mA |
|
Figure 37. PFM Switching Waveforms
(Buck-Boost Operation) 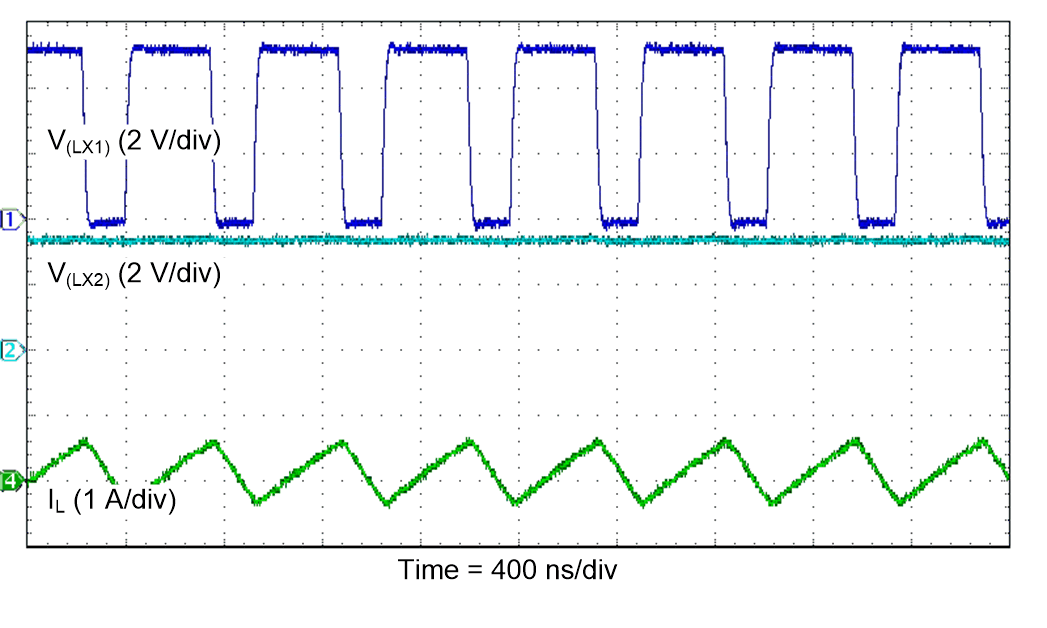
| VI = 5 V |
FPWM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
IO = 100 mA |
|
Figure 39. PWM Switching Waveforms
(Buck Operation) 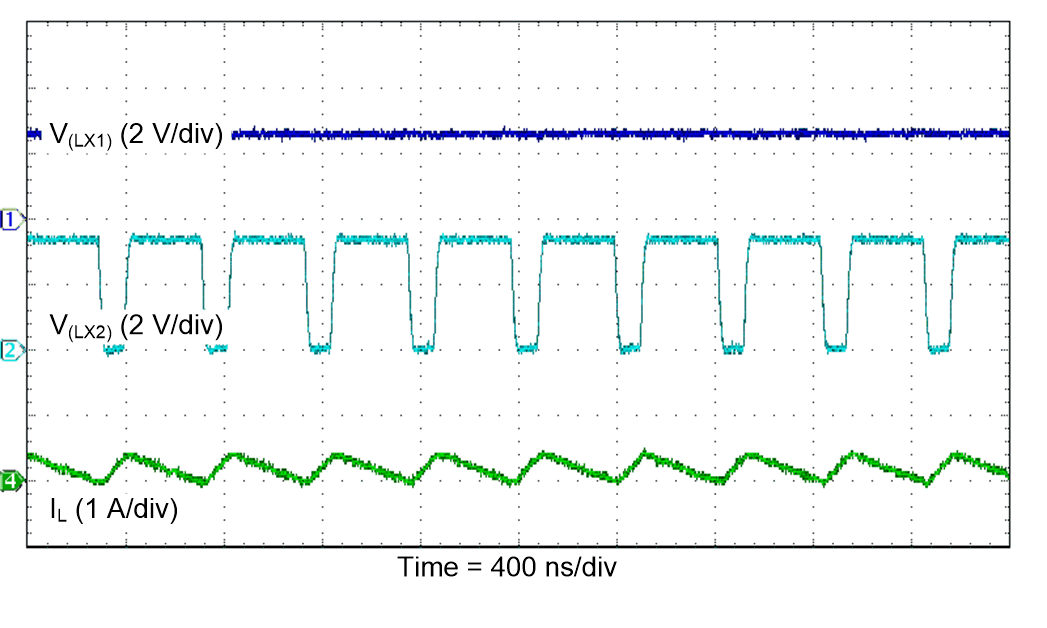
| VI = 2.5 V |
FPWM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
IO = 100 mA |
|
Figure 41. PWM Switching Waveforms
(Boost Operation) 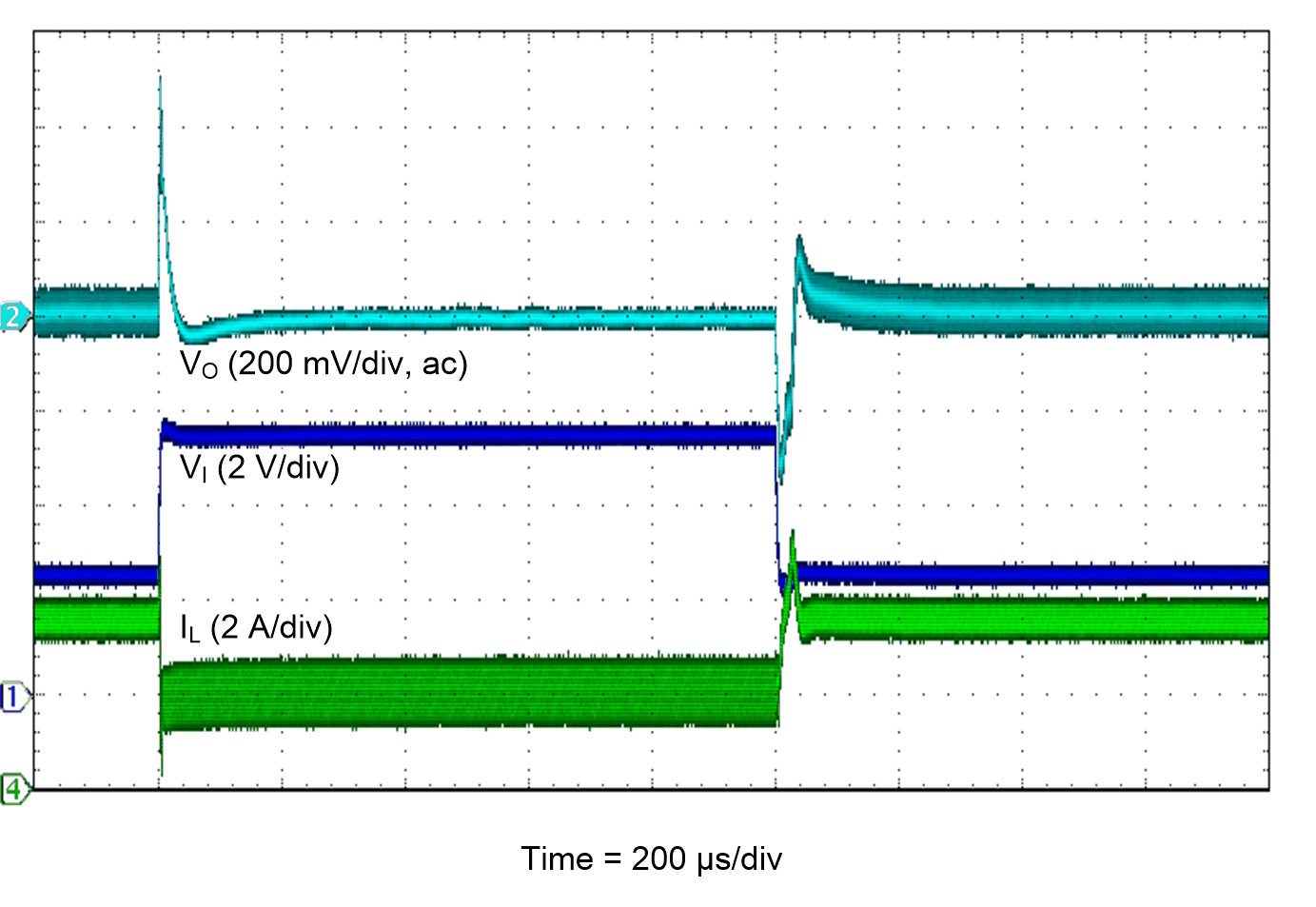
| VI = 2.5 V to 5.5 V |
PSM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
IO = 2 A |
|
Figure 43. Line Transient Response 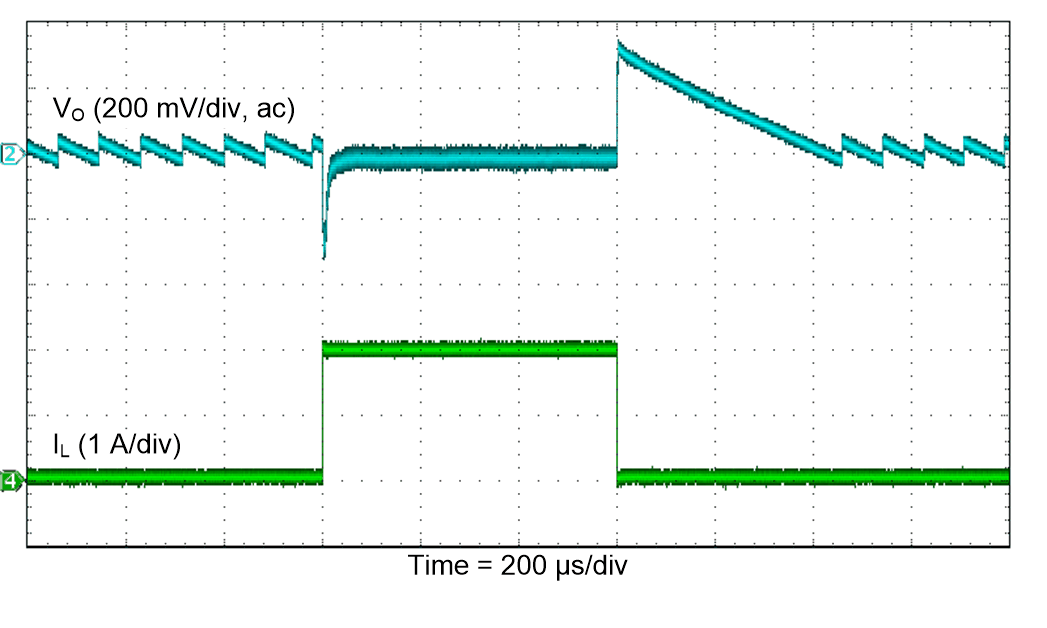
| VI = 3.3 V |
PSM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
IO = 10 mA to 2 A |
|
Figure 45. Load Transient Response (Buck-Boost) 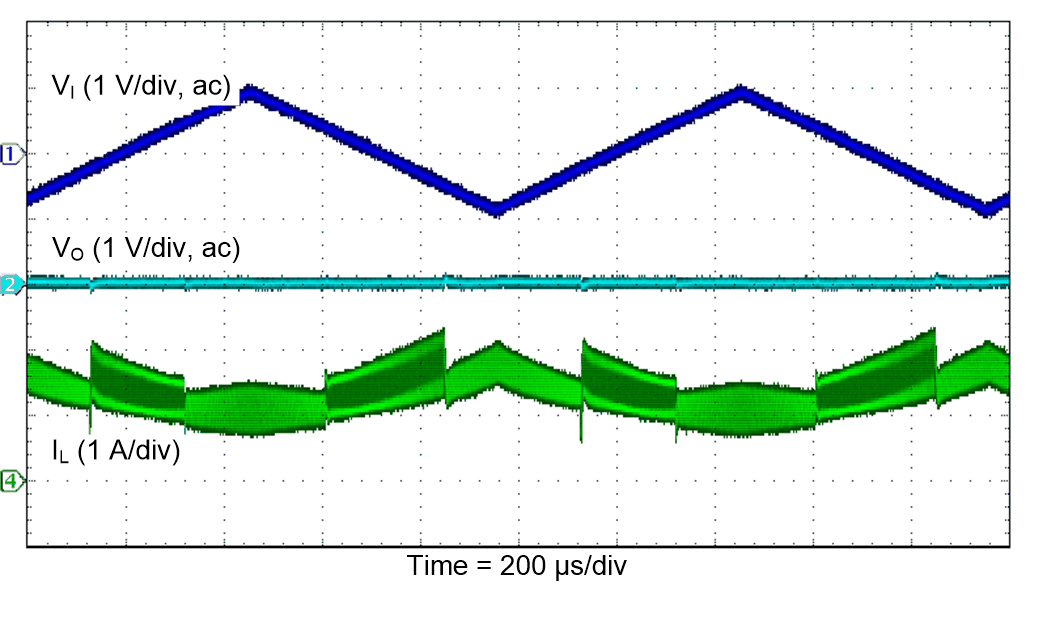
| VI = 3.3 V ±0.9 V |
FPWM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
RL = 3 Ω |
|
Figure 47. Line Sweep (PWM) 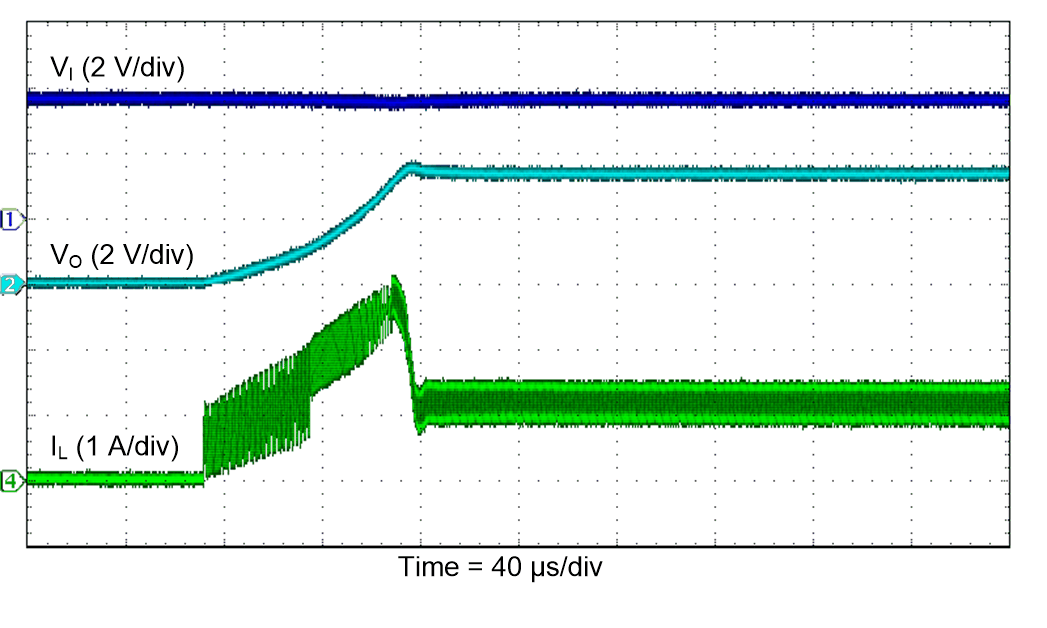
| VI = 3.6 V |
PSM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 3.3 V |
RL = 3.3 Ω |
|
Figure 49. Start-Up Waveforms
(Heavy Load) 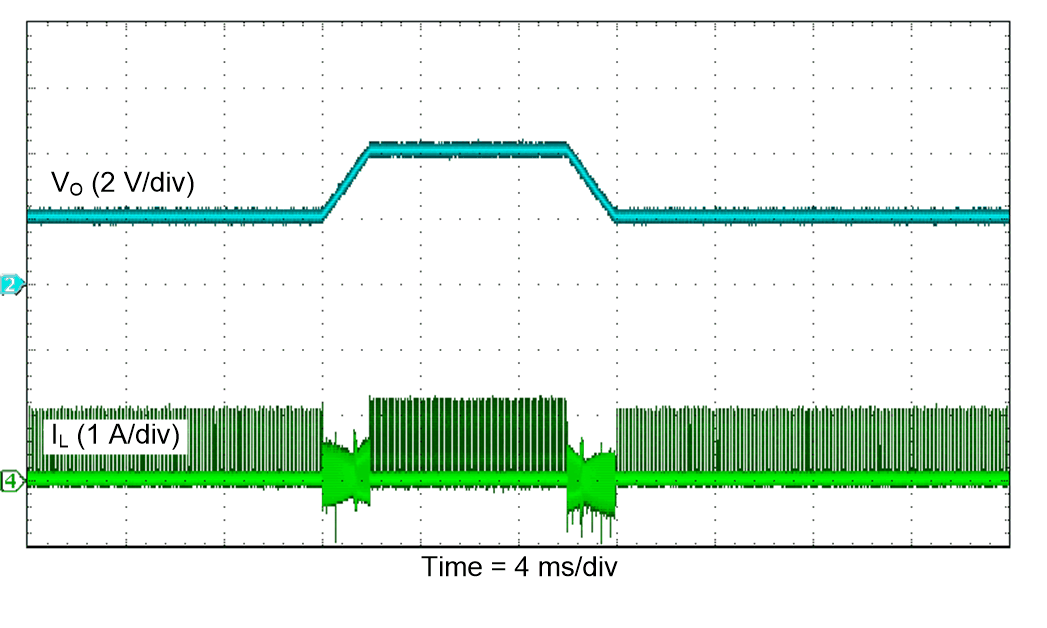
| VI = 3.6 V |
PSM |
TA = 25°C |
| VO = 2 V to 4 V |
RPWM |
RL = 330 Ω |
Figure 51. Dynamic Voltage Scaling (RPWM) 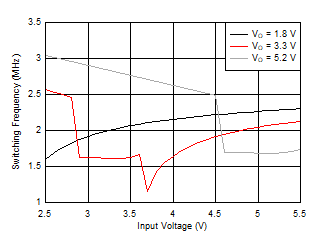
| IO = 1 A |
FPWM |
TA = 25°C |
| VI rising |
|
|
Figure 53. Switching Frequency versus Input Voltage 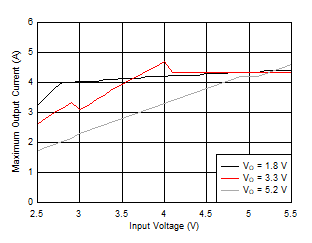 Figure 55. Maximum Output Current versus Input Voltage
Figure 55. Maximum Output Current versus Input Voltage























