SBVS054K November 2004 – June 2025 TPS730
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
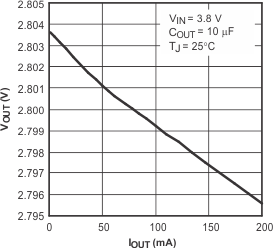
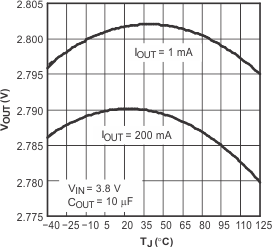
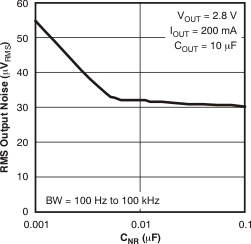
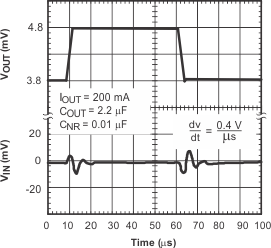
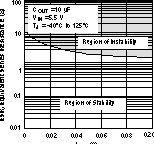
5.6 Typical Characteristics
over recommended operating temperature range TJ = –40°C to +125°C, VEN = VIN, VIN = VOUT(nom) + 1 V, IOUT = 1 mA, COUT = 10 μF, CNR = 0.01 μF, VOUT(nom) = 2.8 V (unless otherwise noted). Typical values are at TJ = 25°C.
| Legacy chip |
| Legacy chip |

| Legacy chip |

| Legacy chip |
| Legacy chip |

| New chip |

| New chip |

| Legacy chip |
| Legacy chip |

| Legacy chip |

| Legacy chip |

| Legacy chip |

| Legacy chip |

| New chip |

| New chip |

| New chip |

| COUT = 10uF (new chip) |

| Legacy chip |

| Legacy chip |

| New chip |

| New chip |

| New chip |

| New chip |

| New chip |

| New chip |
| Legacy chip |