JAJU528B August 2022 – January 2023 OPA388-Q1
- 概要
- リソース
- 特長
- アプリケーション
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Hardware, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7Trademarks
- 8Revision History
3.2.2.2 Isolation Error at HV Positive
Simulate an isolation error condition by connecting the chassis ground line to HV positive. Change the switches on the load card appropriately to support the same. To understand the behavior of error conditions, the measurements were performed at different battery voltages.
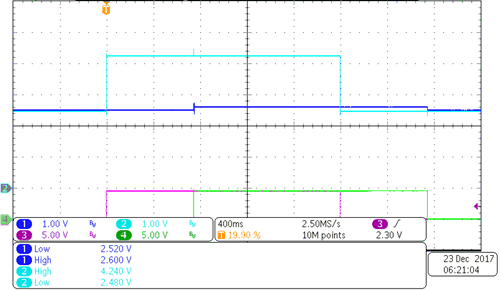 Figure 3-12 HV Positive Error 400 V at No Resistance Figure 3-12 HV Positive Error 400 V at No Resistance | No resistance from positive line to chassis ground |
| CH1: ISO_POS CH2: ISO_NEG CH3: RELAY_NEG CH4: RELAY_POS | |
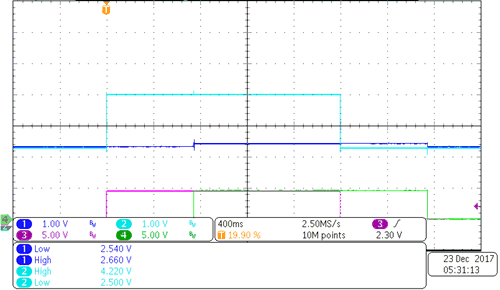 Figure 3-13 HV Positive Error 400 V at 100-kΩ Resistance Figure 3-13 HV Positive Error 400 V at 100-kΩ Resistance | 100-kΩ resistance from positive line to chassis ground |
| CH1: ISO_POS CH2: ISO_NEG CH3: RELAY_NEG CH4: RELAY_POS | |
Table 3-2 Measurements at HV Positive Error
| HV BATTERY VOLTAGE (SUPPLIED AND MEASURED) | MEASURED REFERENCE VOLTAGE | MEASURED PEAK ISO_POS VOLTAGE | MEASURED PEAK ISO_NEG VOLTAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100.006 | 2.505 | 2.606 | 3.027 |
| 150.008 | 2.504 | 2.606 | 3.236 |
| 200.003 | 2.504 | 2.608 | 3.444 |
| 250.004 | 2.504 | 2.608 | 3.652 |
| 300.004 | 2.504 | 2.608 | 3.861 |
| 350.004 | 2.504 | 2.608 | 4.069 |
| 400.006 | 2.504 | 2.608 | 4.278 |
| 450.007 | 2.504 | 2.608 | 4.484 |
Figure 3-14 shows the deviations of HV POS and HV NEG ADC voltages from the normal conditions. HV POS is above the reference voltage when U6 (positive relay) is closed. This behavior is observable only when the HV positive line is low ohmic or short to chassis ground.
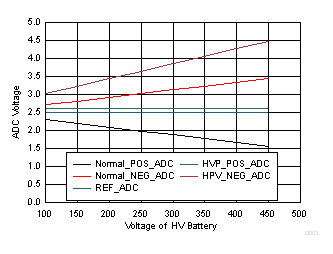 Figure 3-14 Behavior for HV Positive Isolation Error
Figure 3-14 Behavior for HV Positive Isolation Error