SBOA571 august 2023 OPA2387 , OPA387 , OPA4387
3.3 Noise Contribution of the Second Order Shelving Filter
The second order shelving filter comes at the penalty of more components and a slightly higher total noise due to the additional components. When selecting the component values, a compromise between the resistor value, capacitor value, and the total noise must be found. How the noise is distributed in the frequency spectrum is of interest. If FFTs are computed with 50 Hz wide frequency bins, the noise energy in the particular frequency bin matters. When sampling a system, the spectrum becomes periodic with the sampling frequency. From this sampling frequency, energy aliases back to the B0 bin. Therefore, the average noise in the B0 frequency bin was also computed with 50-Hz bandwidth. As expected due to the higher DC gain, the noise contribution in the DC band is the highest. From the plot below, we can estimate the output noise for the individual frequency bins. Again, B0 is the DC energy bin, B1 the AC fundamental bin, and Bn the AC harmonic bins.
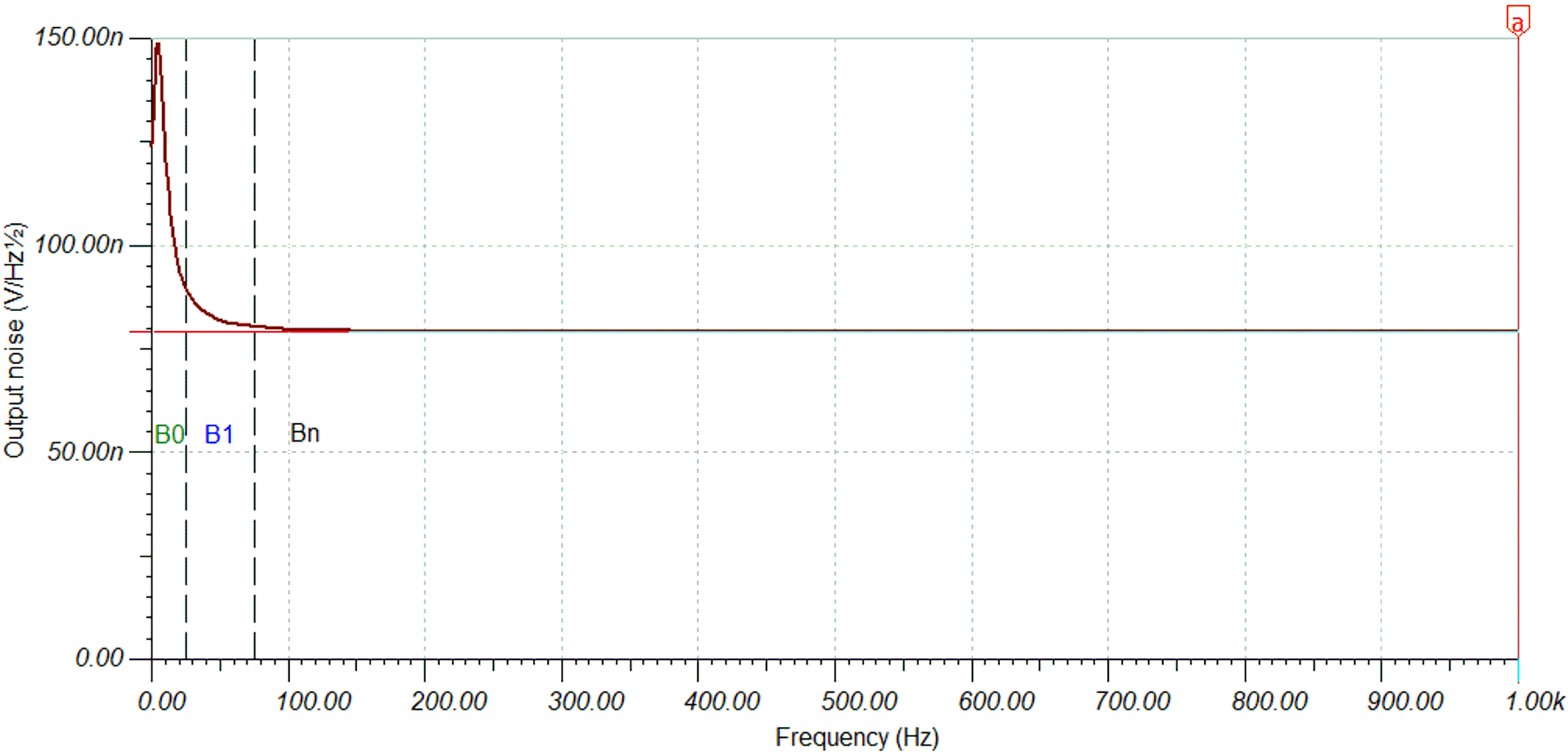 Figure 3-10 Noise Power Spectral Density Distribution Across FFT Bins
Figure 3-10 Noise Power Spectral Density Distribution Across FFT BinsThe output noise in the DC energy bin is approximately 1.6x higher than in the AC bins, but as we increase the DC signal content by a factor of 8x (18 dB), this increase still results in an improved SNR of 14 dB (5x) for the small DC signal.