SBOU180B november 2016 – july 2023 INA260
3.4 System Power-Up
Launch the INA260EVM GUI software. The Power button on the GUI is enabled by default, which allows the POWER LED on the EVM to immediately light up. The light shows that the EVM PCB is receiving power.
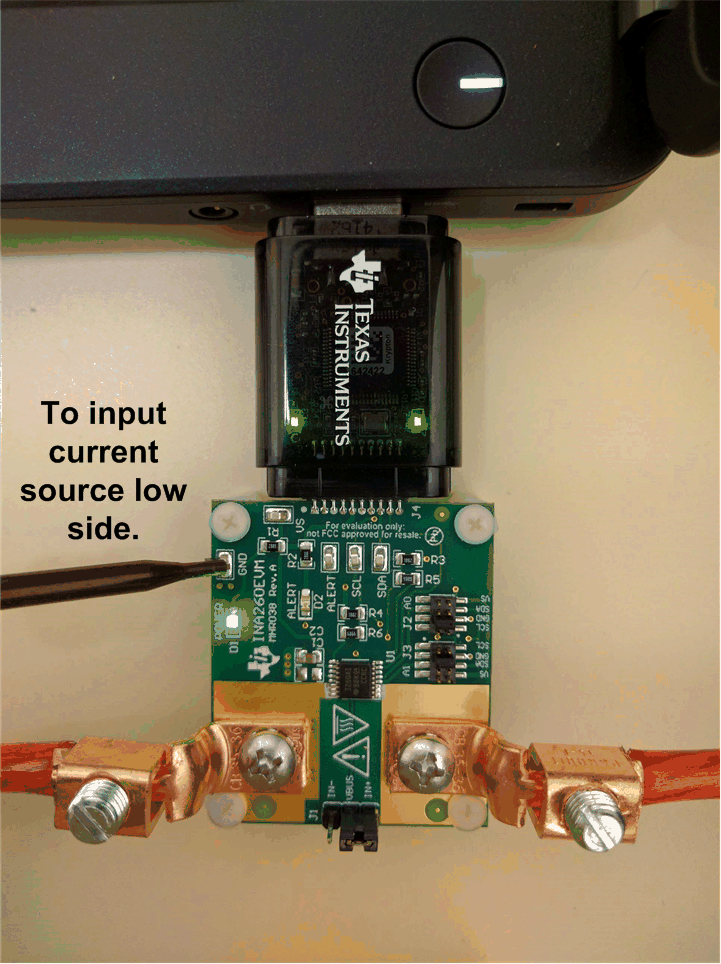 Figure 3-6 INA260EVM Powers Up Following the GUI Launch
Figure 3-6 INA260EVM Powers Up Following the GUI LaunchAdditionally, the supply voltage (VDUT) is set to 3.3 V by default, but the user can select the 5-V option, if necessary (see Figure 3-7).
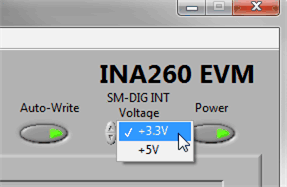 Figure 3-7 VDUT Selection
Figure 3-7 VDUT SelectionWith the INA260 powered on, the user can enable the analog input sources.
Section 4 discusses the GUI configuration and data collection using this setup.