SBOU180B november 2016 – july 2023 INA260
2 INA260EVM-PDK Hardware
Figure 2-1 shows the overall system setup for the INA260EVM-PDK. To monitor the power source, connect the power source to the EVM input terminals. The computer runs the GUI software that enables power to the INA260 and communicate with the device. The user can send commands through the USB port of the computer to the SM-USB-DIG board to translate these commands into I2C format before sending the commands to the EVM.
With power enabled, the INA260 responds to these I2C commands by sending the requested data back to the SM-USB-DIG board over the I2C. The SM-USB-DIG converts the received data to USB format and sends the data back to the computer, where it is then appropriately processed and displayed to the user.
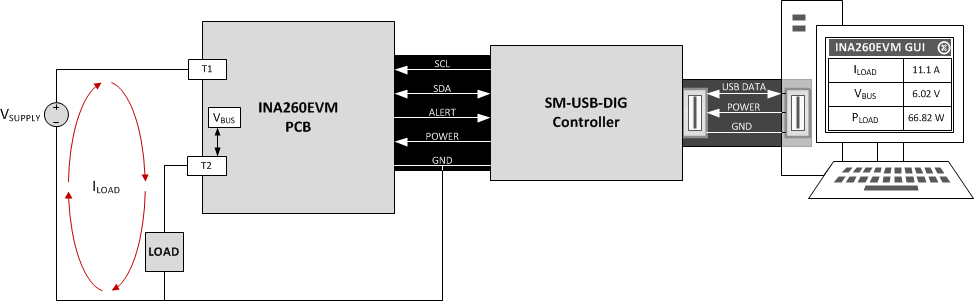 Figure 2-1 INA260EVM-PDK Hardware Setup
Figure 2-1 INA260EVM-PDK Hardware Setup