SBOU180B november 2016 – july 2023 INA260
1.2 INA260EVM-PDK Features
- USB-powered; no external power supply is required
- Support for full ±15-A input current range and 36-V common-mode voltage range of the INA260
- EVM includes placeholders for transient voltage suppression (TVS) devices to protect the INA260 inputs from excessively high common-mode voltages
- Digital host controller included
- Intuitive GUI software supports all major INA260 functional modes and simplifies device configuration
Note:
To protect against voltage transients that may exceed the absolute maximum ratings, TI highly recommends installing the TVS devices (D3 and D4, as shown in Figure 1-2) with a minimum power rating of 1000 W to clamp the input voltages to less than 36 V.
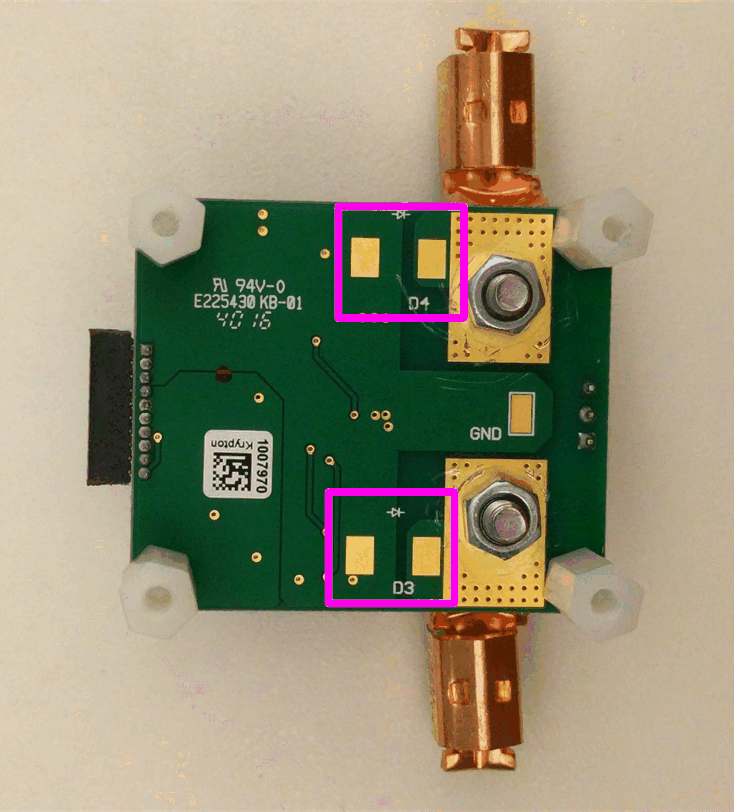 Figure 1-2 Placeholders for TVS
Devices
Figure 1-2 Placeholders for TVS
Devices