SLAA392A March 2008 – August 2018 MSP430BT5190 , MSP430F1101 , MSP430F1101A , MSP430F1111A , MSP430F112 , MSP430F1121 , MSP430F1121A , MSP430F1122 , MSP430F1132 , MSP430F122 , MSP430F1222 , MSP430F123 , MSP430F1232 , MSP430F133 , MSP430F135 , MSP430F147 , MSP430F1471 , MSP430F148 , MSP430F1481 , MSP430F149 , MSP430F1491 , MSP430F155 , MSP430F156 , MSP430F157 , MSP430F1610 , MSP430F1611 , MSP430F1612 , MSP430F167 , MSP430F168 , MSP430F169 , MSP430F2001 , MSP430F2002 , MSP430F2003 , MSP430F2011 , MSP430F2012 , MSP430F2013 , MSP430F2013-EP , MSP430F2101 , MSP430F2111 , MSP430F2112 , MSP430F2121 , MSP430F2122 , MSP430F2131 , MSP430F2132 , MSP430F2232 , MSP430F2234 , MSP430F2252 , MSP430F2252-Q1 , MSP430F2254 , MSP430F2272 , MSP430F2272-Q1 , MSP430F2274 , MSP430F233 , MSP430F2330 , MSP430F235 , MSP430F2350 , MSP430F2370 , MSP430F2410 , MSP430F2416 , MSP430F2417 , MSP430F2418 , MSP430F2419 , MSP430F247 , MSP430F2471 , MSP430F248 , MSP430F2481 , MSP430F249 , MSP430F2491 , MSP430F2616 , MSP430F2617 , MSP430F2618 , MSP430F2619 , MSP430F412 , MSP430F413 , MSP430F4132 , MSP430F415 , MSP430F4152 , MSP430F417 , MSP430F423 , MSP430F423A , MSP430F425 , MSP430F4250 , MSP430F425A , MSP430F4260 , MSP430F427 , MSP430F4270 , MSP430F427A , MSP430F435 , MSP430F4351 , MSP430F436 , MSP430F4361 , MSP430F437 , MSP430F4371 , MSP430F438 , MSP430F439 , MSP430F447 , MSP430F448 , MSP430F4481 , MSP430F449 , MSP430F4491 , MSP430F4616 , MSP430F46161 , MSP430F4617 , MSP430F46171 , MSP430F4618 , MSP430F46181 , MSP430F4619 , MSP430F46191 , MSP430F47126 , MSP430F47127 , MSP430F47163 , MSP430F47166 , MSP430F47167 , MSP430F47173 , MSP430F47176 , MSP430F47177 , MSP430F47183 , MSP430F47186 , MSP430F47187 , MSP430F47193 , MSP430F47196 , MSP430F47197 , MSP430F477 , MSP430F478 , MSP430F4783 , MSP430F4784 , MSP430F479 , MSP430F4793 , MSP430F4794 , MSP430F5131 , MSP430F5132 , MSP430F5151 , MSP430F5152 , MSP430F5171 , MSP430F5172 , MSP430F5304 , MSP430F5308 , MSP430F5309 , MSP430F5310 , MSP430F5324 , MSP430F5325 , MSP430F5326 , MSP430F5327 , MSP430F5328 , MSP430F5329 , MSP430F5333 , MSP430F5336 , MSP430F5338 , MSP430F5340 , MSP430F5341 , MSP430F5342 , MSP430F5418 , MSP430F5418A , MSP430F5419 , MSP430F5419A , MSP430F5435 , MSP430F5435A , MSP430F5436 , MSP430F5436A , MSP430F5437 , MSP430F5437A , MSP430F5438 , MSP430F5438A , MSP430F5500 , MSP430F5501 , MSP430F5502 , MSP430F5503 , MSP430F5504 , MSP430F5505 , MSP430F5506 , MSP430F5507 , MSP430F5508 , MSP430F5509 , MSP430F5510 , MSP430F5513 , MSP430F5514 , MSP430F5515 , MSP430F5517 , MSP430F5519 , MSP430F5521 , MSP430F5522 , MSP430F5524 , MSP430F5525 , MSP430F5526 , MSP430F5527 , MSP430F5528 , MSP430F5529 , MSP430F5630 , MSP430F5631 , MSP430F5632 , MSP430F5633 , MSP430F5634 , MSP430F5635 , MSP430F5636 , MSP430F5637 , MSP430F5638 , MSP430F6433 , MSP430F6435 , MSP430F6436 , MSP430F6438 , MSP430F6630 , MSP430F6631 , MSP430F6632 , MSP430F6633 , MSP430F6634 , MSP430F6635 , MSP430F6636 , MSP430F6637 , MSP430F6638 , MSP430FE423 , MSP430FE4232 , MSP430FE423A , MSP430FE4242 , MSP430FE425 , MSP430FE4252 , MSP430FE425A , MSP430FE427 , MSP430FE4272 , MSP430FE427A , MSP430FG4250 , MSP430FG4260 , MSP430FG4270 , MSP430FG437 , MSP430FG438 , MSP430FG439 , MSP430FG4616 , MSP430FG4617 , MSP430FG4618 , MSP430FG4619 , MSP430FG477 , MSP430FG478 , MSP430FG479 , MSP430FW423 , MSP430FW425 , MSP430FW427 , MSP430G2001 , MSP430G2101 , MSP430G2102 , MSP430G2111 , MSP430G2112 , MSP430G2121 , MSP430G2131 , MSP430G2132 , MSP430G2152 , MSP430G2201 , MSP430G2201-Q1 , MSP430G2211 , MSP430G2212 , MSP430G2221 , MSP430G2231 , MSP430G2231-Q1 , MSP430G2232 , MSP430G2252 , MSP430G2302 , MSP430G2312 , MSP430G2332 , MSP430G2352 , MSP430G2402 , MSP430G2432 , MSP430G2452 , MSP430L092
2.3.2 Reliability Tests
In general, reliability is defined as the probability that a device or a system will perform a required task under stated conditions for a stated period of time. The chosen functionality under specific conditions can be predicted with a good degree of confidence with this measure. For the present subject, the functionality is flash data retention, and the conditions are changes in temperature. In general, failure in devices follows a bathtub curve shown in Figure 3. The curve can be divided into three regions of interest: infant mortality, normal life of operation, and wear-out phase. The chances of failures are higher during infant mortality and the wear-out phase and almost a negligible constant during normal life of operation. In Section 2.3.1, screening out devices that fall under the infant mortality part of the curve was mentioned.
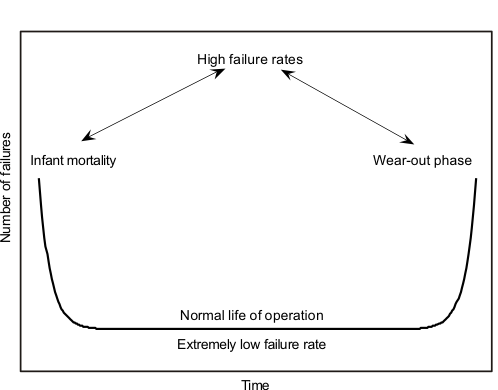 Figure 3. Bathtub Curve for Failures
Figure 3. Bathtub Curve for Failures The interpretation of test results to indicate the reliability of a device requires the definition and understanding of a few key parameters. A brief introduction to these terminologies follows:
Failure Rate (λ)
Failure rate is the number of failures per unit time. It follows the bathtub curve of Figure 3.
Failure-In-Time (FIT) Rate
FIT is a direct measure of failure rate in 109 device hours or the number of devices that failed after 109 hours. It is inversely proportional to number of devices tested and the duration of the tests.
Acceleration Factor (AF)
AF is an outcome of an accelerated life test done on the device to predict its long-term performance. Its role in the Arrhenius equation was shown in previous sections. This factor also contributes inversely to the FIT.
Confidence Level (CL)
CL is the probability level estimated based on sample tests conducted for failures. It also is a confidence in the integrity of numbers used to determine the failure rate. It follows a chi-square (χ2) distribution and depends on the number of failures. In most cases, the confidence level is chosen to be 60% or 90%. It directly contributes to the FIT.
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
MTBF is the inverse of the FIT for a repairable device and is a classic measure of reliability of a system or of a product. It is figure that goes through constant update with number of samples tested and failed.
Reliability [R(t)]
R(t) is defined for fixed time periods to predict the number of devices that would perform reliably. It is a byproduct of the FIT and expressed as a percentage.
From this point on, it is a simple task of putting these numbers in their respective formulas to get reliability data. Section 2.3.2.1 and Section 2.3.2.2 show examples for the tests discussed in Section 2.3.1.