SLYY109B February 2021 – March 2022 HD3SS3212 , HD3SS460 , TPD4S311A , TPD6S300A , TPD8S300 , TPS25740A , TPS25750 , TPS65982 , TPS65983B , TPS65987D , TPS65988 , TPS65994AD , TUSB1042I , TUSB1046A-DCI , TUSB1210 , TUSB1310A , TUSB320 , TUSB542 , TUSB544 , TUSB546A-DCI , TUSB564
- At a glance
- Authors
- 3
- Introduction
- Data and power roles
- USB Type-C UFP sink: USB 2.0 without USB PD
- USB Type-C DFP: USB 2.0 without USB PD
- USB Type-C DRP/DRD USB 2.0 without USB PD
- USB Type-C DRP/DRD: USB 2.0 with USB PD
- USB 3.1 Gen 1 (SuperSpeed) and Gen 2 (SuperSpeed+)
- Alternate Mode
- USB Type-C pinout and reversibility
- Conclusion
- References
USB Type-C DRP/DRD USB 2.0 without USB PD
The last USB 2.0 non-USB PD application available is the DRP/DRD. For non-USB PD applications, DRD and DRP are identical. A common example is a slower-speed laptop port that can send power in either direction – to charge or be charged, and act as either a host or a device. Another common application for this system type is tablets and smartphones. Figure 5 is an updated block diagram.
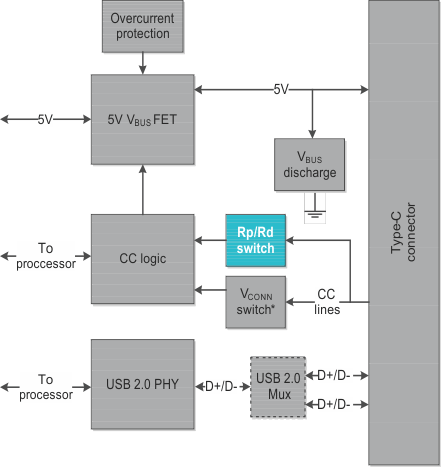 Figure 5 USB Type-C DRP/DRD USB 2.0
without USB PD block diagram. Note that the VCONN switch is not always
required.
Figure 5 USB Type-C DRP/DRD USB 2.0
without USB PD block diagram. Note that the VCONN switch is not always
required.The only noticeable change from Figure 4 is adding the Rp/ Rd switch. A DRP/DRD can present itself as either a UFP or DFP. As a result, this design must have a method to pull the CC lines up with Rp or pull the lines down with Rd (default on a dead battery in order to charge), as shown in Figure 6. Notice how the switch can toggle between pulling the CC line up (in this case, with a current source to create a specific voltage across Rd), or pulling the CC line down to GND.
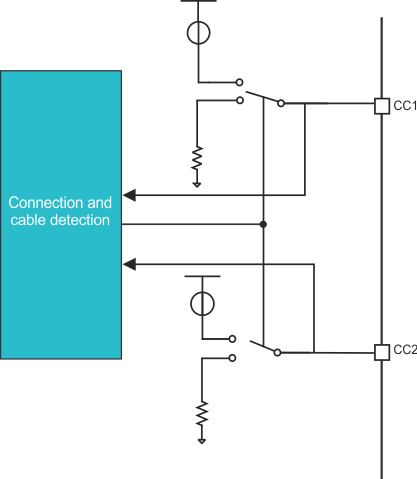 Figure 6 Rp/Rd switch
schematic.
Figure 6 Rp/Rd switch
schematic.TI has a variety of devices that address DRP/DRD USB 2.0 without USB PD applications. These devices integrate the CC logic, Rp/Rd switch and – depending on the device – the VCONN switch.