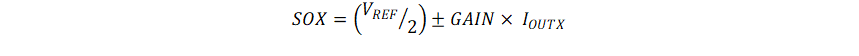SDAA048 July 2025 DRV8376
3 DRV8376 Current Sense Amplifier (CSA) Architecture
DRV8376 implements a senseFET based low side current sense architecture for the current sense amplifier (CSA) with adaptive offset calibration to mitigate the errors associated with offset error of the final stage amplifier. Figure below shows the simplified block diagram of the CSA.
 Figure 3-1 Current Sense Amplifier Architecture
Figure 3-1 Current Sense Amplifier ArchitectureThe SOx pin on the DRV8376 outputs an analog voltage proportional to the current flowing in the low-side FETs multiplied by the gain setting (GCSA). The gain setting is adjustable between four different levels which can be set by the GAIN pin (in the hardware device variant) or the GAIN bits (in the SPI device variant).The current sense is implemented with the sense FET on each low-side FET of the DRV8376 device. This current information is fed to the internal I/V converter, which generates the CSA output voltage on the SOx pin based on the voltage on the VREF pin and the Gain setting. The CSA output voltage can be calculated as: