SLVUBT8B November 2020 – June 2022 LP8764-Q1 , TPS6594-Q1
- Scalable PMIC's GUI User’s Guide
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Supported Features
- 3 Revisions
- 4 Overview
- 5 Getting Started
- 6 Quick-start Page
- 7 Register Map Page
- 8 NVM Configuration Page
- 9 NVM Validation Page
- 10Watchdog Page
- 11Additional Resources
- 12Appendix A: Troubleshooting
- 13Appendix B: Advanced Topics
- 14Appendix C: Known Limitations
- 15Appendix D: Migration Topics
- 16Revision History
8.2.2 NVM Configuration Special Use Case: Changing the Communication Interface
The GUI tool writes the register settings using the identified interface and then uses the bulk programming method to transfer the register settings to the NVM. In the event that the NVM image uses a different interface, then it is important that the device being programmed supports both interfaces. When the GUI writes to the register settings to change the interface (SPI to I2C or I2C to SPI), the GUI will pause and display a prompt, see Figure 8-33, to change the hardware configuration to enable the new interface. This message specifically refers to the EVM, but can be generalized to any hardware configuration where changes are made to transition from I2C to SPI or SPI to I2C.
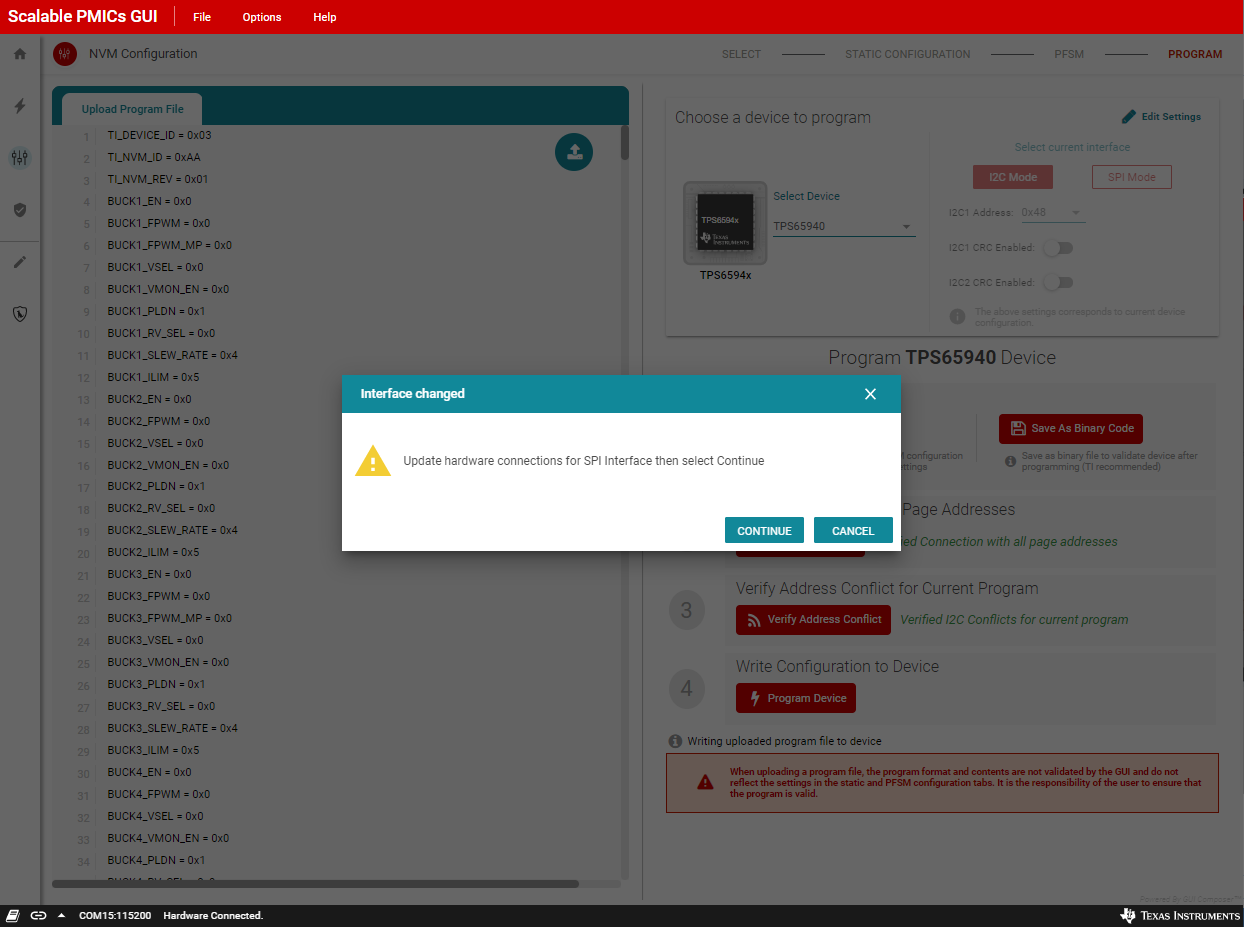 Figure 8-33 Interface Change during
Programming
Figure 8-33 Interface Change during
Programming