SPRACP7 October 2019 AM6526 , AM6528 , AM6546 , AM6548
2.2.2 NAV_CPTS
Common Platform Timestamp (CPTS) is a hardware IP block to facilitate host control of time sync operations by collecting time sync events and present to host for processing. It performs timestamping and a comparison of generic HWPUSH (0-7) or Ethernet events (Host Transmit Event, Ethernet receive event, Ethernet transmit event, timestamp push event, timestamp rollover event, and timestamp half-rollover event). Additionally, it supports generation of “tuned” frequency waveform derived from the reference clock, where tuning may be based on parts per million, or parts per hour, with fractional register controls on the tuning rate.
Figure 4 shows a functional diagram of the CPTS block.
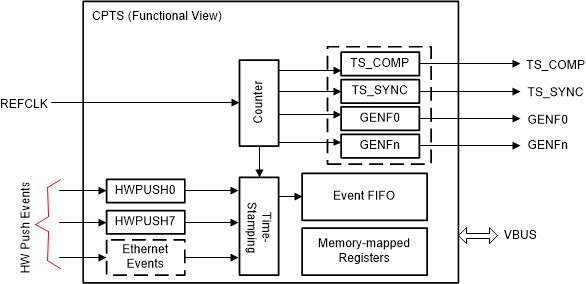 Figure 4. Functional View of CPTS Subsystem
Figure 4. Functional View of CPTS Subsystem CPTS may be integrated at the System-on-Chip (SoC) level or embedded in various subsystems where precise timestamping or event capture is needed. In the AM65xx device, there is a central CPTS in the Navigator subsystem, as well as embedded CPTS modules in each of PCIe controllers, and CPSW Ethernet controller.