TIDUF31A May 2023 – April 2024
- 1
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
-
3System Design Theory
- 3.1 High-Voltage Buck Auxiliary Power Supply
- 3.2 DC Bus Voltage Sensing
- 3.3 Motor Drive Stage
- 3.4 Bypass Capacitors
- 3.5 Phase Current Sensing With Two or Three Shunt Resistors
- 3.6 Phase Current Sensing With a Single Shunt Resistor
- 3.7 Hall-Effect Sensor or QEI Interface for Sensored Motor Control
- 3.8 DAC for Software Debug
- 3.9 Overcurrent Protection
- 3.10 Overtemperature Protection
- 3.11 Isolated UART port
- 3.12 Inverter Peak Power Capability
- 4Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 5Design and Documentation Support
- 6About the Author
4.1.1 Hardware Board Overview
Figure 4-1 shows a system block diagram of this reference design.
 Figure 4-1 TIDA-010250 System Block
Diagram
Figure 4-1 TIDA-010250 System Block
DiagramThe motor control board has functional groups that enable a complete motor drive system. The following is a list of the blocks on the board and their functions. Figure 4-2 shows the top view of the board and different blocks of the TIDA-010250 PCB.
- AC input connectors and filter
- Auxiliary power supply
- MCU controller
- Motor inverter output connector
- Phase current sensing with shunt resistors
- Hall or QEI interface
- USART serial communication
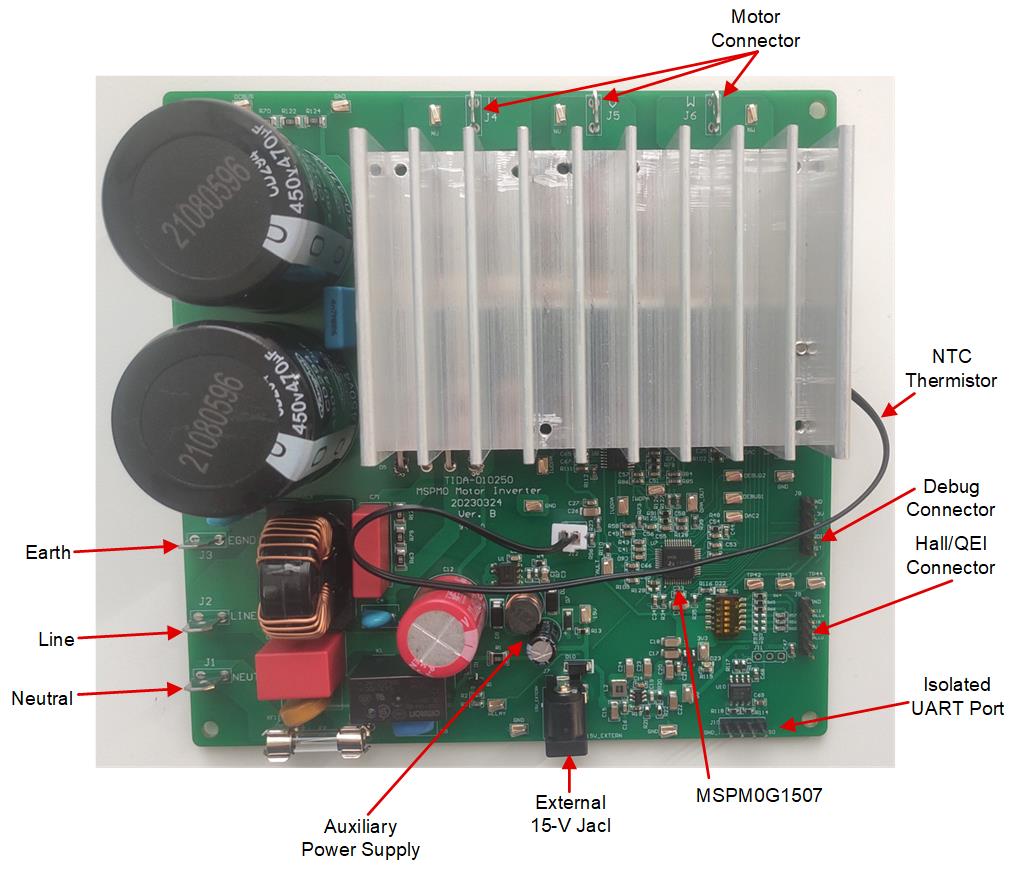 Figure 4-2 Layout of M0 Motor Inverter
Board
Figure 4-2 Layout of M0 Motor Inverter
BoardTI recommends taking the following precautions when using the board:
- Do not touch any part of the board or components connected to the board when the board is energized.
- Use the AC Mains or wall power supply to power the kit. TI recommends an isolation AC source.
- Do not touch any part of the board, the kit, or the assembly when energized. Though the power module heat sink is isolated from the board, high-voltage switching generates some capacitive coupled voltages over the heat sink body.
- Control Ground can be hot.