TIDUF31A May 2023 – April 2024
- 1
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
-
3System Design Theory
- 3.1 High-Voltage Buck Auxiliary Power Supply
- 3.2 DC Bus Voltage Sensing
- 3.3 Motor Drive Stage
- 3.4 Bypass Capacitors
- 3.5 Phase Current Sensing With Two or Three Shunt Resistors
- 3.6 Phase Current Sensing With a Single Shunt Resistor
- 3.7 Hall-Effect Sensor or QEI Interface for Sensored Motor Control
- 3.8 DAC for Software Debug
- 3.9 Overcurrent Protection
- 3.10 Overtemperature Protection
- 3.11 Isolated UART port
- 3.12 Inverter Peak Power Capability
- 4Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 5Design and Documentation Support
- 6About the Author
4.4.4 Motor Start-Up Sequence
Figure 4-7 shows the start-up sequence waveform for a PMSM motor with a sensorless FOC algorithm. The sequence usually consists of three phases: align, open loop ramp-up, speed closed loop. Complete the following steps during aligning:
- Slowly increase aligning current to prevent any surge current
- Move to open loop ramp-up
- Ramp-up current can be set to meet the start load requirement
- The rotor position observer starts to work during ramp-up time
- Once the motor speed reaches the set point and the rotor angle error is small enough, then the software moves to closed speed and closed current loop
The following list of channels are presented in Figure 4-7.
- CH1(Blue): Observed rotor angle
- CH2 (Cyan): AC input voltage
- CH3 (Purple): DC bus voltage
- CH4 (Green): Current of phase U
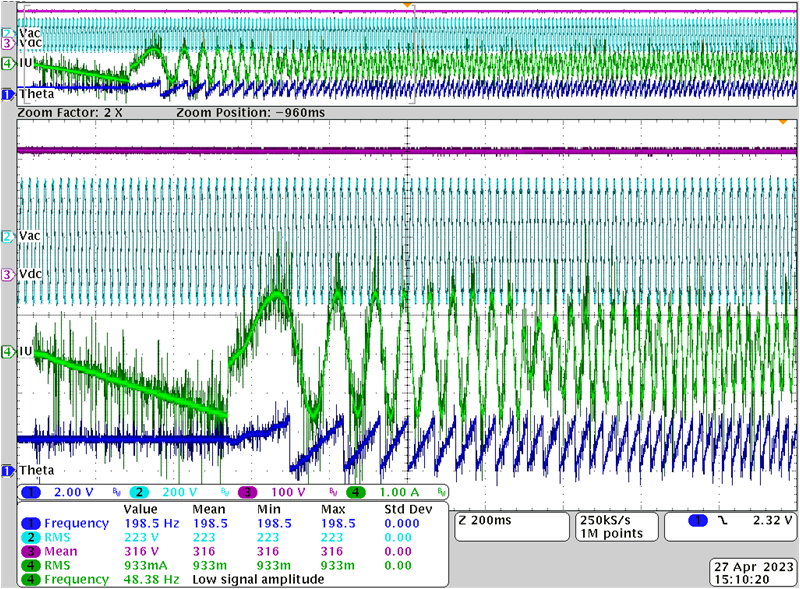 Figure 4-7 Motor Start-Up Sequence for PMSM With Senseless FOC Algorithm
Figure 4-7 Motor Start-Up Sequence for PMSM With Senseless FOC Algorithm