The 'ABTH18504A and 'ABTH182504A scan test devices with 20-bit
universal bus transceivers are members of the Texas Instruments
SCOPETM testability integrated-circuit family. This family
of devices supports IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990 boundary scan to
facilitate testing of complex circuit-board assemblies. Scan access
to the test circuitry is accomplished via the 4-wire test access port
(TAP) interface.
In the normal mode, these devices are 20-bit universal bus
transceivers that combine D-type latches and D-type flip-flops to
allow data flow in transparent, latched, or clocked modes. The test
circuitry can be activated by the TAP to take snapshot samples of the
data appearing at the device pins or to perform a self test on the
boundary-test cells. Activating the TAP in the normal mode does not
affect the functional operation of the SCOPETM universal
bus transceivers.
Data flow in each direction is controlled by output-enable (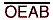 and
and 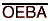 ), latch-enable (LEAB and LEBA),
clock-enable (
), latch-enable (LEAB and LEBA),
clock-enable (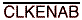 and
and 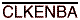 ), and clock (CLKAB and CLKBA)
inputs. For A-to-B data flow, the device operates in the transparent
mode when LEAB is high. When LEAB is low, the A-bus data is latched
while
), and clock (CLKAB and CLKBA)
inputs. For A-to-B data flow, the device operates in the transparent
mode when LEAB is high. When LEAB is low, the A-bus data is latched
while 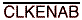 is high and/or
CLKAB is held at a static low or high logic level. Otherwise, if LEAB
is low and
is high and/or
CLKAB is held at a static low or high logic level. Otherwise, if LEAB
is low and 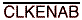 is low, A-bus
data is stored on a low-to-high transition of CLKAB. When
is low, A-bus
data is stored on a low-to-high transition of CLKAB. When 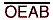 is low, the B outputs are active.
When
is low, the B outputs are active.
When 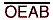 is high, the B
outputs are in the high-impedance state. B-to-A data flow is similar
to A-to-B data flow, but uses the
is high, the B
outputs are in the high-impedance state. B-to-A data flow is similar
to A-to-B data flow, but uses the 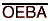 , LEBA,
, LEBA, 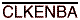 , and
CLKBA inputs.
, and
CLKBA inputs.
In the test mode, the normal operation of the SCOPETM
universal bus transceivers is inhibited, and the test circuitry is
enabled to observe and control the I/O boundary of the device. When
enabled, the test circuitry performs boundary-scan test operations
according to the protocol described in IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990.
Four dedicated test pins observe and control the operation of the
test circuitry: test data input (TDI), test data output (TDO), test
mode select (TMS), and test clock (TCK). Additionally, the test
circuitry performs other testing functions such as parallel-signature
analysis (PSA) on data inputs and pseudo-random pattern generation
(PRPG) from data outputs. All testing and scan operations are
synchronized to the TAP interface.
Improved scan efficiency is accomplished through the adoption of a
one boundary-scan cell (BSC) per I/O pin architecture. This
architecture is implemented in such a way as to capture the most
pertinent test data. A PSA/COUNT instruction also is included to ease
the testing of memories and other circuits where a binary count
addressing scheme is useful.
Active bus-hold circuitry holds unused or floating data inputs at
a valid logic level.
The B-port outputs of 'ABTH182504A, which are designed to source
or sink up to 12 mA, include 25- series resistors to reduce overshoot and undershoot.
series resistors to reduce overshoot and undershoot.
The SN54ABTH18504A and SN54ABTH182504A are characterized for
operation over the full military temperature range of -55°C to
125°C. The SN74ABTH18504A and SN74ABTH182504A are characterized
for operation from -40°C to 85°C.
A-to-B data flow is shown. B-to-A data flow is similar but
uses OEBA\, LEBA, CLKENBA\, and CLKBA.
Output level before the indicated steady-state input
conditions were established
The 'ABTH18504A and 'ABTH182504A scan test devices with 20-bit
universal bus transceivers are members of the Texas Instruments
SCOPETM testability integrated-circuit family. This family
of devices supports IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990 boundary scan to
facilitate testing of complex circuit-board assemblies. Scan access
to the test circuitry is accomplished via the 4-wire test access port
(TAP) interface.
In the normal mode, these devices are 20-bit universal bus
transceivers that combine D-type latches and D-type flip-flops to
allow data flow in transparent, latched, or clocked modes. The test
circuitry can be activated by the TAP to take snapshot samples of the
data appearing at the device pins or to perform a self test on the
boundary-test cells. Activating the TAP in the normal mode does not
affect the functional operation of the SCOPETM universal
bus transceivers.
Data flow in each direction is controlled by output-enable (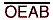 and
and 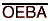 ), latch-enable (LEAB and LEBA),
clock-enable (
), latch-enable (LEAB and LEBA),
clock-enable (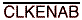 and
and 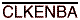 ), and clock (CLKAB and CLKBA)
inputs. For A-to-B data flow, the device operates in the transparent
mode when LEAB is high. When LEAB is low, the A-bus data is latched
while
), and clock (CLKAB and CLKBA)
inputs. For A-to-B data flow, the device operates in the transparent
mode when LEAB is high. When LEAB is low, the A-bus data is latched
while 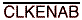 is high and/or
CLKAB is held at a static low or high logic level. Otherwise, if LEAB
is low and
is high and/or
CLKAB is held at a static low or high logic level. Otherwise, if LEAB
is low and 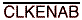 is low, A-bus
data is stored on a low-to-high transition of CLKAB. When
is low, A-bus
data is stored on a low-to-high transition of CLKAB. When 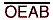 is low, the B outputs are active.
When
is low, the B outputs are active.
When 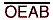 is high, the B
outputs are in the high-impedance state. B-to-A data flow is similar
to A-to-B data flow, but uses the
is high, the B
outputs are in the high-impedance state. B-to-A data flow is similar
to A-to-B data flow, but uses the 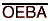 , LEBA,
, LEBA, 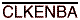 , and
CLKBA inputs.
, and
CLKBA inputs.
In the test mode, the normal operation of the SCOPETM
universal bus transceivers is inhibited, and the test circuitry is
enabled to observe and control the I/O boundary of the device. When
enabled, the test circuitry performs boundary-scan test operations
according to the protocol described in IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990.
Four dedicated test pins observe and control the operation of the
test circuitry: test data input (TDI), test data output (TDO), test
mode select (TMS), and test clock (TCK). Additionally, the test
circuitry performs other testing functions such as parallel-signature
analysis (PSA) on data inputs and pseudo-random pattern generation
(PRPG) from data outputs. All testing and scan operations are
synchronized to the TAP interface.
Improved scan efficiency is accomplished through the adoption of a
one boundary-scan cell (BSC) per I/O pin architecture. This
architecture is implemented in such a way as to capture the most
pertinent test data. A PSA/COUNT instruction also is included to ease
the testing of memories and other circuits where a binary count
addressing scheme is useful.
Active bus-hold circuitry holds unused or floating data inputs at
a valid logic level.
The B-port outputs of 'ABTH182504A, which are designed to source
or sink up to 12 mA, include 25- series resistors to reduce overshoot and undershoot.
series resistors to reduce overshoot and undershoot.
The SN54ABTH18504A and SN54ABTH182504A are characterized for
operation over the full military temperature range of -55°C to
125°C. The SN74ABTH18504A and SN74ABTH182504A are characterized
for operation from -40°C to 85°C.
A-to-B data flow is shown. B-to-A data flow is similar but
uses OEBA\, LEBA, CLKENBA\, and CLKBA.
Output level before the indicated steady-state input
conditions were established