SLVSDW2B December 2018 – November 2020 TPS23755
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 CLS Classification
- 7.3.2 DEN Detection and Enable
- 7.3.3 Internal Pass MOSFET
- 7.3.4
DC-DC Controller Features
- 7.3.4.1 VCC, VB and Advanced PWM Startup
- 7.3.4.2 CS, Current Slope Compensation and Blanking
- 7.3.4.3 COMP, FB, CP and Opto-less Feedback
- 7.3.4.4 FRS Frequency Setting and Synchronization
- 7.3.4.5 Frequency Dithering for Spread Spectrum Applications
- 7.3.4.6 SST and Soft-Start of the Switcher
- 7.3.4.7 AUX_V, AUX_D and Secondary Adapter Or'ing
- 7.3.5 Internal Switching FET - DRAIN, RSNS, SRF and SRR
- 7.3.6 VPD Supply Voltage
- 7.3.7 VDD Supply Voltage
- 7.3.8 GND
- 7.3.9 VSS
- 7.3.10 Exposed Thermal PAD
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Input Bridges and Schottky Diodes
- 8.2.2.2 Protection, D1
- 8.2.2.3 Capacitor, C1
- 8.2.2.4 Detection Resistor, RDEN
- 8.2.2.5 Classification Resistor, RCLS
- 8.2.2.6 Bulk Capacitance, CBULK
- 8.2.2.7 Output Voltage Feedback Divider, RAUX, R1,R2
- 8.2.2.8 Setting Frequency, RFRS
- 8.2.2.9 Frequency Dithering, RDTR and CDTR
- 8.2.2.10 Bias Voltage, CVB and DVB
- 8.2.2.11 Transformer design, T1
- 8.2.2.12 Current Sense Resistor, RCS
- 8.2.2.13 Current Slope Compensation, RS
- 8.2.2.14 Bias Supply Requirements, CCC, DCC
- 8.2.2.15 Switching Transformer Considerations, RVCC and CCC2
- 8.2.2.16 Primary FET Clamping, RCL, CCL, and DCL
- 8.2.2.17 Converter Output Capacitance, COUT
- 8.2.2.18 Secondary Output Diode Rectifier, DOUT
- 8.2.2.19 Slew rate control, RSRF and RSRR
- 8.2.2.20 Shutdown at Low Temperatures, DVDD and CVDD
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RJJ|23
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.4.7 AUX_V, AUX_D and Secondary Adapter Or'ing
The TPS23755’s unique auxiliary power detect capability provides priority for a secondary side power adapter, while ensuring smooth transition to and from the PoE power. This can be applied for example in applications where the auxiliary power is the main power, while the PoE input acts as the backup power. The auxiliary voltage is “Ore’d” directly at the output of flyback transformer, on secondary side. See Figure 7-4 below where the output voltage is nominally 12 V.
When the auxiliary is present, a signal (AUX_D) tells the PD PWM to lower its output voltage slightly below the auxiliary voltage to ensure the auxiliary has priority to power the main output. When the auxiliary power goes away, the DC-DC converter increases back its output voltage, to ensure seamless transition. One significant advantage of this approach is that the efficiency of the PoE-powered flyback power stage can be optimized independently of the need for seamless transition. The adjustability of the lower voltage level allows the use of highly inaccurate auxiliary voltage sources. Such feature eases the thermal design, in particular when secondary diode rectification is used, since when PoE powered, the flyback stage can deliver power at a higher output voltage, and hence at a lower output current.
In Figure 7-4 below, ROUT1 ensures that the PSE maintains power while the auxiliary is present, ensuring there will be no power interruption when the auxiliary power is removed.
The lower voltage level is programmable with the RAUX resistor, which impacts the feedback network division ratio. Note however that the flyback power transformer design and resistor selection must be such that VVCC will remain above nominally 6.1 V (VCUVF) while the auxiliary power is present.
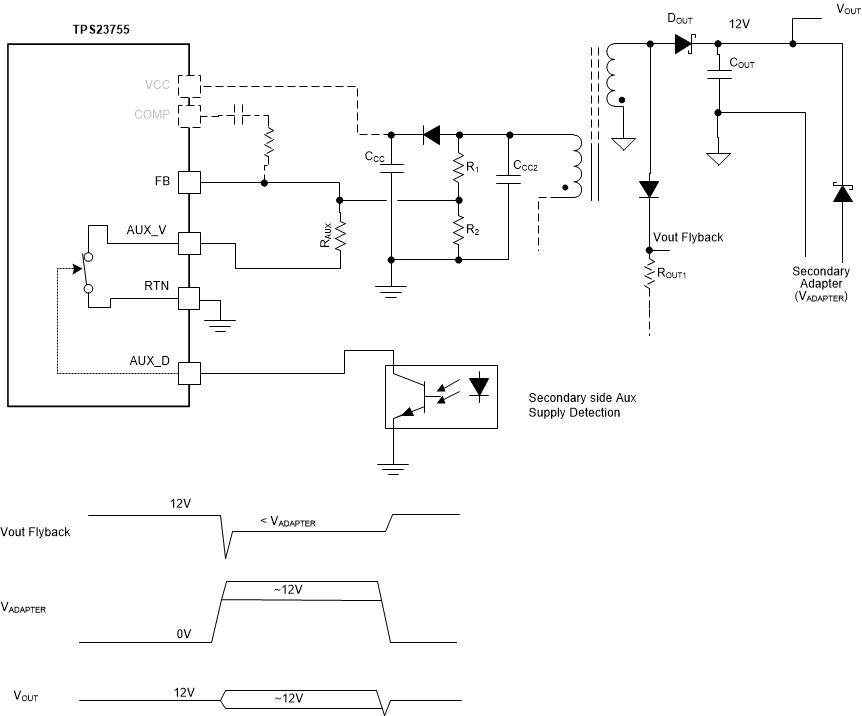 Figure 7-4 Secondary Side Priority Control with Smooth Transition
Figure 7-4 Secondary Side Priority Control with Smooth Transition