SLVSD19A June 2015 – July 2015 DRV8881
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Motor Driver Current Ratings
- 7.3.2 PWM Motor Drivers
- 7.3.3 Bridge Control
- 7.3.4 Current Regulation
- 7.3.5 Decay Modes
- 7.3.6 Smart tune
- 7.3.7 Adaptive Blanking Time
- 7.3.8 Parallel Mode
- 7.3.9 Charge Pump
- 7.3.10 LDO Voltage Regulator
- 7.3.11 Logic and Tri-Level Pin Diagrams
- 7.3.12 Protection Circuits
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.1 Bulk Capacitance Sizing
Having appropriate local bulk capacitance is an important factor in motor drive system design. It is generally beneficial to have more bulk capacitance, while the disadvantages are increased cost and physical size.
The amount of local capacitance needed depends on a variety of factors, including:
- The highest current required by the motor system
- The power supply’s capacitance and ability to source current
- The amount of parasitic inductance between the power supply and motor system
- The acceptable voltage ripple
- The type of motor used (brushed DC, brushless DC, stepper)
- The motor braking method
The inductance between the power supply and motor drive system will limit the rate current can change from the power supply. If the local bulk capacitance is too small, the system will respond to excessive current demands or dumps from the motor with a change in voltage. When adequate bulk capacitance is used, the motor voltage remains stable and high current can be quickly supplied.
The data sheet generally provides a recommended value, but system-level testing is required to determine the appropriate sized bulk capacitor.
The voltage rating for bulk capacitors should be higher than the operating voltage, to provide margin for cases when the motor transfers energy to the supply.
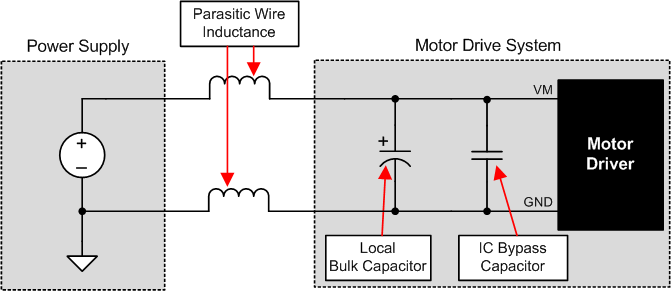 Figure 32. Setup of Motor Drive System With External Power Supply
Figure 32. Setup of Motor Drive System With External Power Supply