SBOS062D September 2000 – December 2025 INA126 , INA2126
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5.7 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, VS = ±15V, all chips site origins (CSO), unless otherwise noted

| CSO: SHE |
 Figure 5-3 Common-Mode Rejection vs Frequency
Figure 5-3 Common-Mode Rejection vs Frequency

| VS = ±5V |
vs Output Voltage

| CSO: TID |

| CSO: SHE |
 Figure 5-13 Quiescent Current vs Temperature
Figure 5-13 Quiescent Current vs Temperature
| CSO: SHE |


| G = 100 |
 Figure 5-21 0.1Hz to 10Hz Voltage Noise
Figure 5-21 0.1Hz to 10Hz Voltage Noise
| CSO: TID |
 Figure 5-4 Positive Power Supply Rejection vs Frequency
Figure 5-4 Positive Power Supply Rejection vs Frequency
| VS = ±15V |
vs Output Voltage

| CSO: SHE |
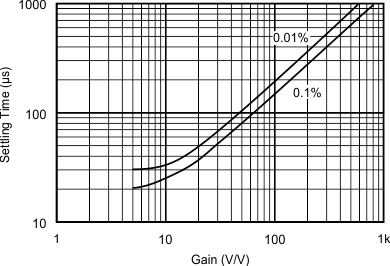

| CSO: TID |
 Figure 5-14 Slew Rate vs Temperature
Figure 5-14 Slew Rate vs Temperature
| CSO: TID |

| G = 5 |

| G = 5 |
 Figure 5-22 Channel Separation vs Frequency, RTI (Dual Version)
Figure 5-22 Channel Separation vs Frequency, RTI (Dual Version)