SNVSAH2E December 2015 – August 2020 LMR23630
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Fixed Frequency Peak Current Mode Control
- 8.3.2 Adjustable Frequency
- 8.3.3 Adjustable Output Voltage
- 8.3.4 Enable/Sync
- 8.3.5 VCC, UVLO
- 8.3.6 Minimum ON-time, Minimum OFF-time and Frequency Foldback at Dropout Conditions
- 8.3.7 Power Good (PGOOD)
- 8.3.8 Internal Compensation and CFF
- 8.3.9 Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 8.3.10 Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
- 8.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.2.2 Output Voltage Setpoint
- 9.2.2.3 Switching Frequency
- 9.2.2.4 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.6 Feed-Forward Capacitor
- 9.2.2.7 Input Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.9 VCC Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.10 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
- DRR|12
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2.2.6 Feed-Forward Capacitor
The LMR23630 is internally compensated. Depending on the VOUT and frequency fSW, if the output capacitor COUT is dominated by low-ESR (ceramic types) capacitors, it could result in low phase margin. To improve the phase boost an external feed-forward capacitor CFF can be added in parallel with RFBT. CFF is chosen such that phase margin is boosted at the crossover frequency without CFF. A simple estimation for the crossover frequency (fX) without CFF is shown in Equation 18, assuming COUT has very small ESR, and COUT value is after derating.
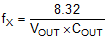
Equation 19 for CFF was tested:
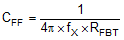
For designs with higher ESR, CFF is not needed when COUT has very high ESR and CFF calculated from Equation 19 must reduced with medium ESR. Table 9-1 can be used as a quick starting point.
For the application in this design example, a 47-pF, 50-V, COG capacitor is selected.