SBVS336C september 2021 – june 2023 TPS7A94
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Output Voltage Setting and Regulation
- 7.3.2 Ultra-Low Noise and Ultra-High Power-Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR)
- 7.3.3 Programmable Current Limit and Power-Good Threshold
- 7.3.4 Programmable Soft Start (NR/SS Pin)
- 7.3.5 Precision Enable and UVLO
- 7.3.6 Active Discharge
- 7.3.7 Thermal Shutdown Protection (TSD)
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Output Voltage Restart (Overshoot Prevention Circuit)
- 8.1.2 Precision Enable (External UVLO)
- 8.1.3 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) Operation
- 8.1.4 Dropout Voltage (VDO)
- 8.1.5 Power-Good Feedback (FB_PG Pin) and Power-Good Threshold (PG Pin)
- 8.1.6 Adjusting the Factory-Programmed Current Limit
- 8.1.7 Programmable Soft-Start and Noise-Reduction (NR/SS Pin)
- 8.1.8 Inrush Current
- 8.1.9 Optimizing Noise and PSRR
- 8.1.10 Adjustable Operation
- 8.1.11 Paralleling for Higher Output Current and Lower Noise
- 8.1.12 Recommended Capacitor Types
- 8.1.13 Load Transient Response
- 8.1.14 Power Dissipation (PD)
- 8.1.15 Estimating Junction Temperature
- 8.1.16 TPS7A94EVM-046 Thermal Analysis
- 8.2 Typical Application
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4 Layout
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DSC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.1.11 Paralleling for Higher Output Current and Lower Noise
Achieving higher output current and lower noise is achievable by paralleling two or more LDOs. Implementation must be carefully planned out to optimize performance and minimize output current imbalance.
Because the TPS7A94 output voltage is set by a resistor driven by a current source, the NR/SS resistor and capacitor must be adjusted as per the following:
where:
- n is the number of LDOs in parallel
- INR/SS is the NR/SS current as provided in the data sheet Electrical Characteristics table
- CNR/SS_single is the NR/SS capacitor for a single LDO
When connecting the input and NR/SS pin together, and with the LDO being a buffer, the current imbalance is only affected by the error offset voltage of the error amplifier. As such, the current imbalance can be expressed as:
where:
- εI is the current imbalance
- VOS is the LDO error offset voltage
- RBALLAST is the ballast resistor
- ΔRBALLAST is the deviation of the ballast resistor value from the nominal value
With the typical offset voltage of 200 μV, considering no error from the design of the PCB ballast resistor (ΔRBALLAST = 0) and a 100-mA maximum current imbalance, the ballast resistor must be 4 mΩ or greater; see Figure 8-17.
Using the configuration described, the LDO output noise is reduced by:
where:
- n is the numbers of LDOs in parallel
- eO_single is the output noise density from a single LDO
- eO_parallel is the output noise density for the resulting parallel LDO
In Figure 8-17, the noise is reduced by 1 / √2.
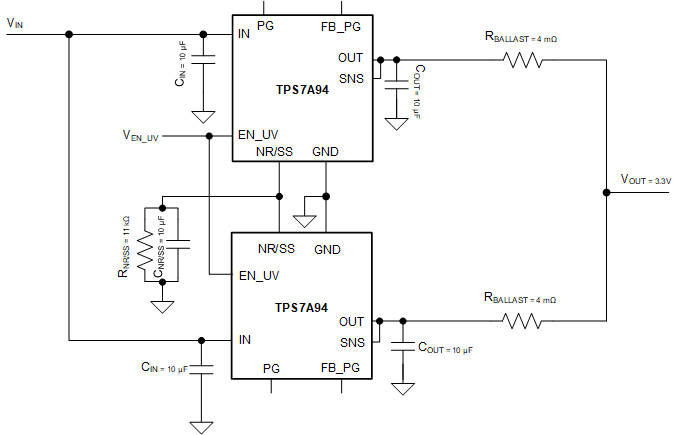 Figure 8-17 Paralleling Multiple TPS7A94
Devices
Figure 8-17 Paralleling Multiple TPS7A94
Devices