SLUSCV6A April 2017 – February 2018 UCC21225A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Ratings
- 6.6 Insulation Specifications
- 6.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 6.8 Safety-Limiting Values
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics
- 6.11 Insulation Characteristics and Thermal Derating Curves
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Designing INA/INB Input Filter
- 9.2.2.2 Select External Bootstrap Diode and Series Resistor
- 9.2.2.3 Gate Driver Output Resistor
- 9.2.2.4 Estimate Gate Driver Power Loss
- 9.2.2.5 Estimating Junction Temperature
- 9.2.2.6 Selecting VCCI, VDDA/B Capacitor
- 9.2.2.7 Dead Time Setting Guidelines
- 9.2.2.8 Application Circuits with Output Stage Negative Bias
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- NPL|13
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
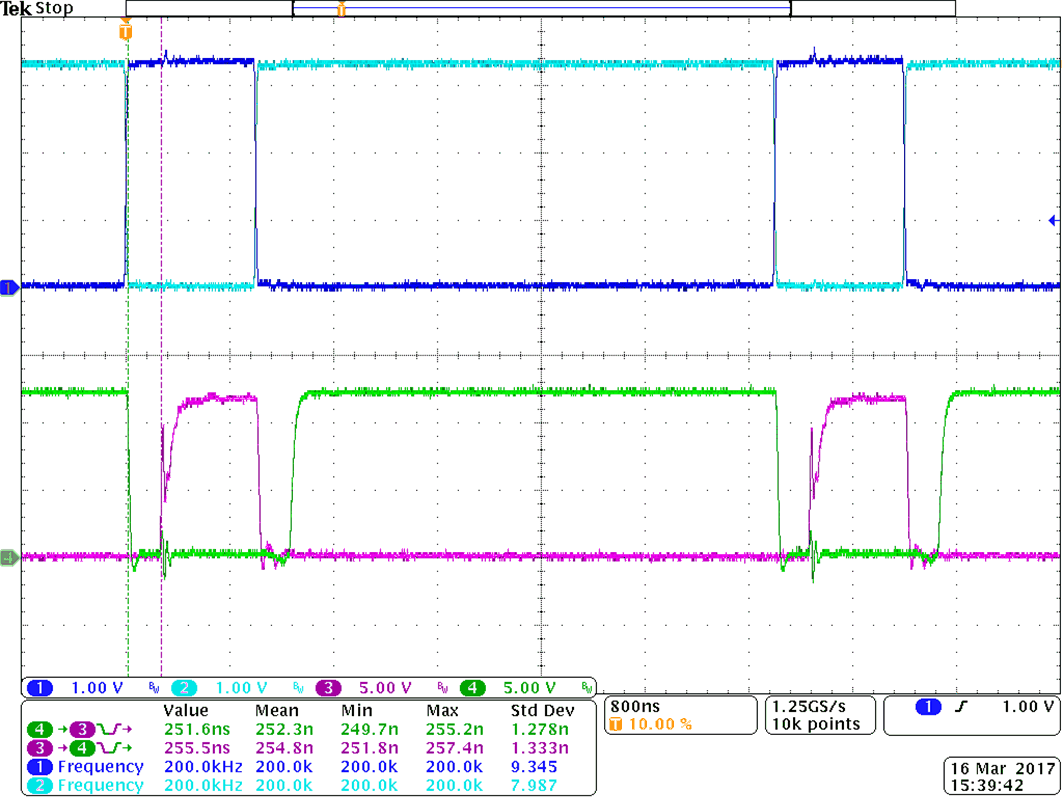
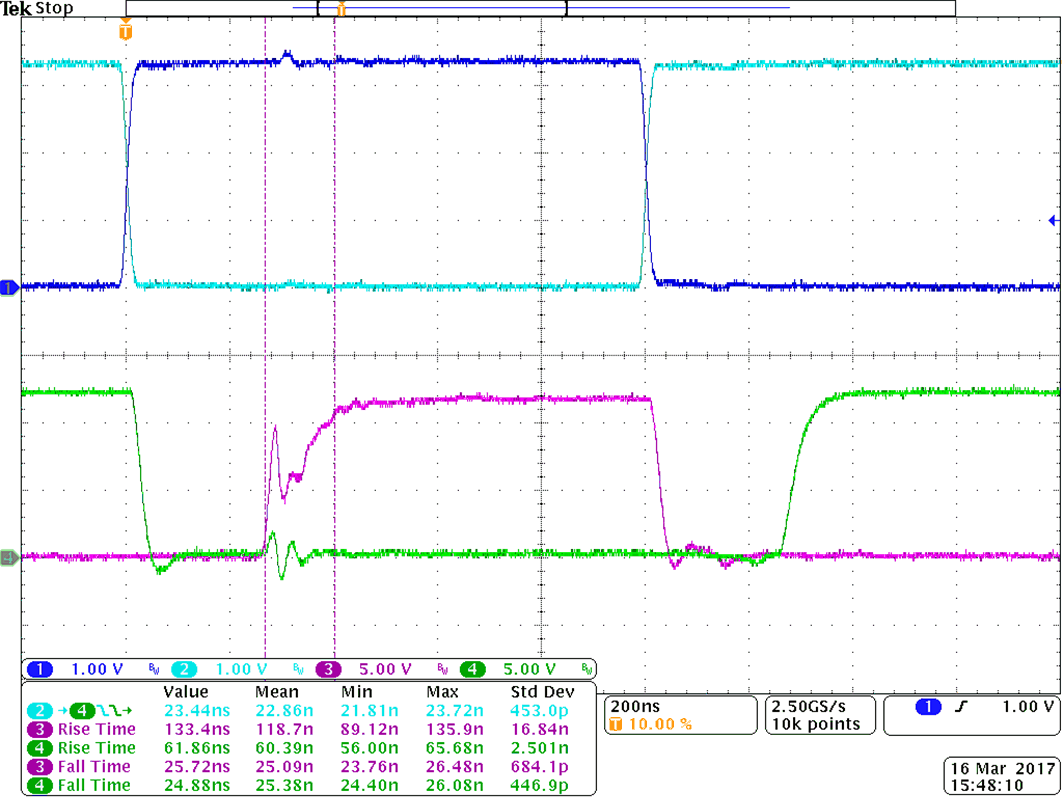
9.2.3 Application Curves
Figure 39 and Figure 40 shows the bench test waveforms for the design example shown in Figure 35 under these conditions: VCC = 5 V, VDD = 12 V, fSW = 200 kHz, VDC-Link = 400 V.
Channel 1 (Indigo): UCC21225A INA pin signal.
Channel 2 (Cyan): UCC21225A INB pin signal.
Channel 3 (Magenta): Gate-source signal on the high side power transistor.
Channel 4 (Green): Gate-source signal on the low side power transistor.
In Figure 39, INA and INB are sent complimentary 3.3-V, 20%/80% duty-cycle signals. The gate drive signals on the power transistor have a 250-ns dead time, shown in the measurement section of Figure 39. The dead time matching is approximately 10-ns with the 250-ns dead-time setting. Note that with high voltage present, lower bandwidth differential probes are required, which limits the achievable accuracy of the measurement.
Figure 40 shows a zoomed-in version of the waveform of Figure 39, with measurements for propagation delay and rising/falling time. Importantly, the output waveform is measured between the power transistors’ gate and source pins, and is not measured directly from the driver OUTA and OUTB pins. Due to the split on and off resistors (Ron, Roff), different sink and source currents, and the Miller plateau, different rising (60, 120 ns) and falling time (25 ns) are observed in Figure 40.