JAJSW71 February 2025 ADC3683-EP , ADC3683-SEP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics - Power Consumption
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics - DC Specifications
- 5.7 Electrical Characteristics - AC Specifications
- 5.8 Timing Requirements
- 5.9 Typical Characteristics - ADC3683
- 6 Parameter Measurement Information
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application Information Disclaimer
- 9 Register Map
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RSB|40
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
8.4 Power Supply Recommendations
The ADC3683-xEP requires two different power-supplies. The AVDD rail provides power for the internal analog circuits and the ADC itself while the IOVDD rail powers the digital interface and the internal digital circuits like decimation filter or output interface mapper. Power sequencing is not required.
The AVDD power supply must be low noise to achieve data sheet performance. In applications operating near DC, the 1/f noise contribution of the power supply needs to be considered as well. The ADC is designed for good PSRR which aides with the power supply filter design.
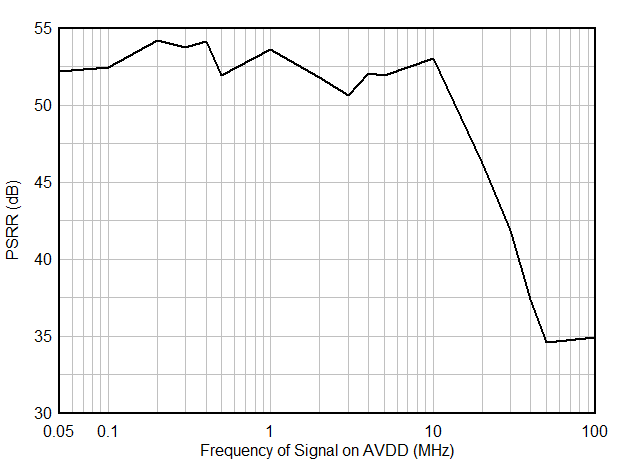 Figure 8-7 Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) vs frequency
Figure 8-7 Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) vs frequencyThere are two recommended power-supply architectures:
- Step down using high-efficiency switching converters, followed by a second stage of regulation using a low noise LDO to provide switching noise reduction and improved voltage accuracy.
- Directly step down the final ADC supply voltage using high-efficiency switching converters. This approach provides the best efficiency, but care must be taken to make sure switching noise is minimized to prevent degraded ADC performance.
TI WEBENCH® Power Designer are used to select and design the individual power-supply elements needed: see the WEBENCH® Power Designer
Recommended switching regulators for the first stage include the TPS7H4010-SEP, and similar devices.
Recommended low dropout (LDO) linear regulators include the TPS73801-SE, TPS7H1111-SEP, and similar devices.
For the switch regulator only approach, the ripple filter must be designed with a notch frequency that aligns with the switching ripple frequency of the DC/DC converter. Note the switching frequency reported from WEBENCH® and design the EMI filter and capacitor combination to have the notch frequency centered as needed. Figure 8-8 and Figure 8-9 illustrate the two approaches.
AVDD and IOVDD supply voltages should not be shared to prevent digital switching noise from coupling into the analog signal chain.
 Figure 8-8 Example: LDO Linear Regulator Approach
Figure 8-8 Example: LDO Linear Regulator Approach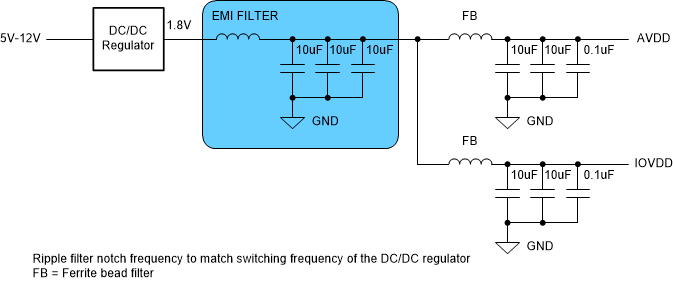 Figure 8-9 Example Switcher-Only Approach
Figure 8-9 Example Switcher-Only Approach