JAJSPB7 February 2024 TMP110
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Related Products
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.5.2 Bus Overview
The physical I2C interface consists of the serial clock (SCL) and serial data (SDA) lines. The SDA line must be connected to a supply through a pullup resistor. The size of the pullup resistor is determined by the amount of capacitance on the I2C lines, the communication frequency and I2C bus voltage. For further details, see the I2C Pullup Resistor Calculation application note. Data transfer can be initiated only when the bus is idle. A bus is considered idle if both SDA and SCL lines are high after a STOP condition or time out events (see Definition of Start and Stop Conditions and Figure 7-8).
The following is the general procedure for a controller to access a target device:
- If a controller wants to send
data to a target:
- Controller-transmitter sends a START condition and addresses the target-receiver.
- Controller-transmitter sends the requested register to write target-receiver.
- Controller-transmitter sends data to target-receiver.
- Controller-transmitter terminates the transfer with a STOP condition.
- If a controller wants to receive
or read data from a target:
- Controller-receiver sends a START condition and addresses the target-transmitter
- Controller-receiver sends the requested register to read to target-transmitter.
- Controller-receiver receives data from the target-transmitter
- Controller-receiver terminates the transfer with a STOP condition.
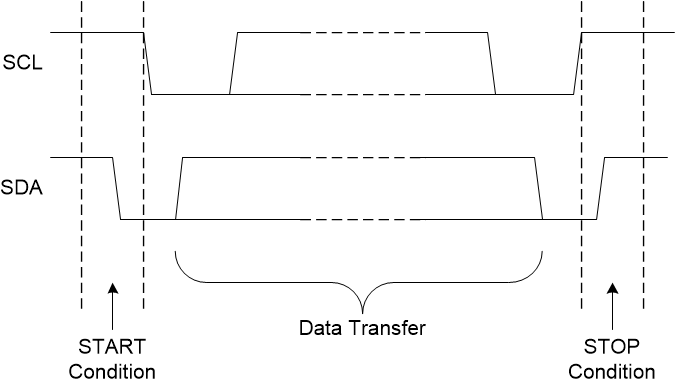 Figure 7-7 Definition of Start and Stop
Conditions
Figure 7-7 Definition of Start and Stop
Conditions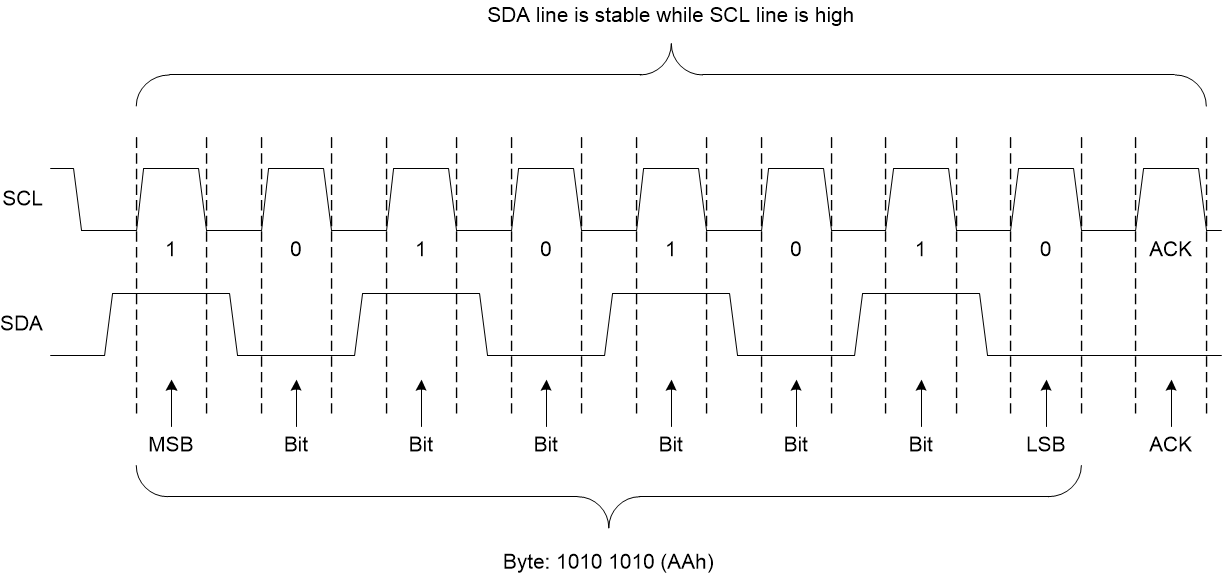 Figure 7-8 Bit Transfer
Figure 7-8 Bit Transfer