SLYA048B March 2020 – June 2021 FDC1004 , FDC1004-Q1 , FDC2112 , FDC2112-Q1 , FDC2114 , FDC2114-Q1 , FDC2212 , FDC2212-Q1 , FDC2214 , FDC2214-Q1 , LDC0851 , LDC1001 , LDC1041 , LDC1051 , LDC1101 , LDC1312 , LDC1312-Q1 , LDC1314 , LDC1314-Q1 , LDC1612 , LDC1612-Q1 , LDC1614 , LDC1614-Q1 , LDC2112 , LDC2114 , LDC3114 , LDC3114-Q1
- Trademarks
- 1Inductive and Capacitive Theory of Operation
- 2FDC: Capacitive Level Sensing
- 3LDC: Inductive Touch Buttons
- 4LDC: Incremental Encoder and Event Counting
- 5LDC: Metal Proximity Sensor
- 6Revision History
3 LDC: Inductive Touch Buttons
Contactless inductive buttons allow for a longer shelf-life compared to traditional mechanical buttons due to less wear and tear on the button surfaces. Contactless inductive buttons also provide a reliable performance in debris-ridden environments. The sensor is a PCB coil, and the target is a flat metal surface. When a user presses on an inductive button, the metal deflects towards the PCB coil, which registers as a button press. The coil can detect various levels of force applied to the surface to allow multi-level functionality.
Common applications include: automotive infotainment buttons, buttons on industrial appliances and POS terminals, and buttons on smart watches and speakers.
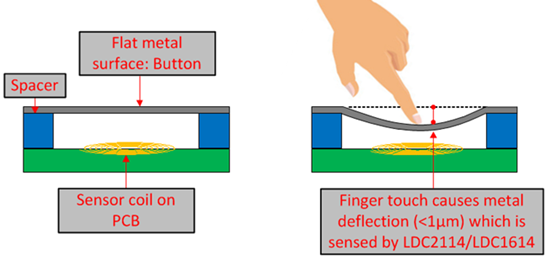 Figure 3-1 Inductive Touch Buttons
Figure 3-1 Inductive Touch Buttons