SBAU230C August 2014 – March 2021 ADS8688
7.1 Connecting the Hardware
After installing the software connect the EVM as shown in Figure 7-1
- Physically connect P2 of the PHI to J2 of the ADS8688EVM. Install the screws to assure a robust connection
- Connect USB on PHI to the computer first
- LED D5 on the PHI lights up, indicating that the PHI is powered up
- LEDs D1 and D2 on the PHI start blinking to indicate that the PHI is booted up and communicating with the PC; Figure 7-1 shows the resulting LED indicators
- Start the software GUI as shown in Figure 7-2. You will notice that the LEDs blink slowly as the FPGA firmware is loaded on the PHI. This will take a few seconds then the AVDD and DVDD power supplies will turn on.
- Connect the signal generators to SMA inputs or headers (8 channels available). The input range is ±10.25V.
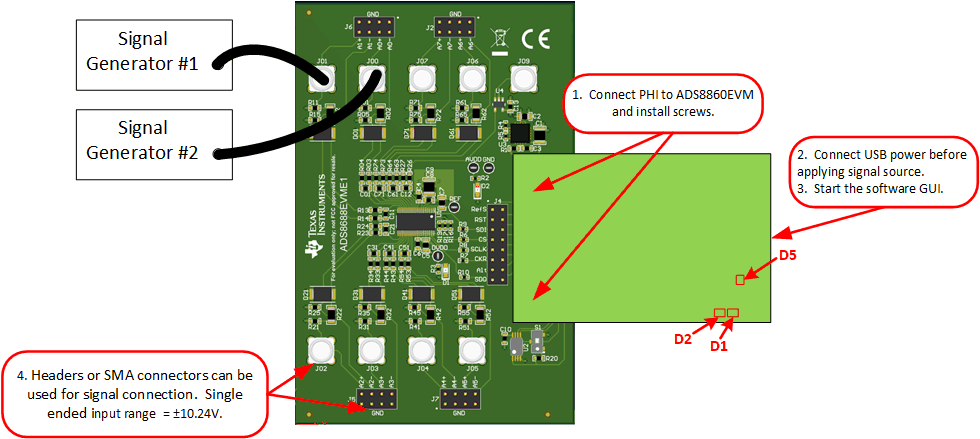 Figure 7-1 ADS8688EVM Hardware Setup and LED Indicators
Figure 7-1 ADS8688EVM Hardware Setup and LED Indicators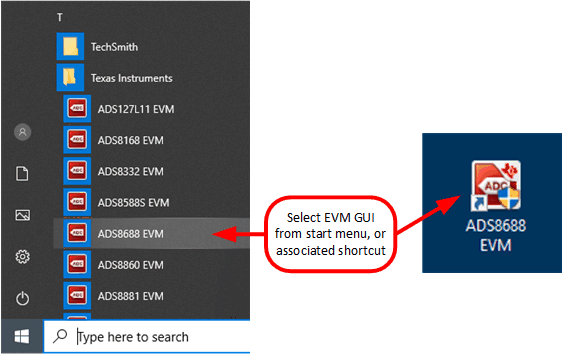 Figure 7-2 Launch the EVM GUI Software
Figure 7-2 Launch the EVM GUI Software