SPRABA5D January 2014 – January 2019 AM1802 , AM1802 , AM1806 , AM1806 , AM1808 , AM1808 , AM1810 , AM1810
-
Using the AM18xx Bootloader
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Boot Modes
- 3 Non-AIS Boot Modes
- 4
Application Image Script (AIS) Boot
- 4.1 Section Load Command (0x58535901)
- 4.2 Section Fill Command (0x5853590A)
- 4.3 Enable CRC Command (0x58535903)
- 4.4 Disable CRC Command (0x58535904)
- 4.5 Validate CRC Command (0x58535902)
- 4.6 Jump & Close Command (0x58535906)
- 4.7 Jump Command (0x58535905)
- 4.8 Sequential Read Enable Command (0x58535963)
- 4.9 Function Execute Command (0x5853590D)
- 4.10 Boot Table Command (0x58535907)
- 5
AISgen: Tool to Generate Boot Script (AIS Image)
- 5.1 Installation
- 5.2 Getting Started
- 5.3
Generating AIS
- 5.3.1 Boot Mode and Boot Peripheral Setup
- 5.3.2 Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Setup
- 5.3.3 Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (SDRAM) Setup
- 5.3.4 DDR Setup
- 5.3.5 PSC Setup
- 5.3.6 Pin Multiplexing Setup
- 5.3.7 Application File Selection
- 5.3.8 AIS File Selection
- 5.3.9 Status and Messages
- 5.3.10 Additional AIS Options
- 5.3.11 Command Line Usage
- 6 Master Boot – Booting From a Slave Memory Device
- 7 Slave Boot – Booting From an External Master Host
- 8 UART Boot Host - Using Your PC as a UART Boot Master
- 9 Boot Requirements, Constraints and Default Settings
- 10 References
- A Boot Mode Selection Table
- B Details of Supported NAND Devices
- C CRC Computation Algorithm
-
D Details of Pre-Defined ROM Functions
- D.1 PLL0 Configuration (Index = 0, Argument Count = 2)
- D.2 PLL1 Configuration (Index = 1, Argument Count = 2)
- D.3 Clock Configuration (Index = 2, Argument Count = 1)
- D.4 mDDR/DDR2 Controller Configuration (Index = 3, Argument Count = 8)
- D.5 EMIFA SDRAM Configuration (Index = 4, Argument Count = 5)
- D.6 EMIFA Async Configuration (Index = 5, Argument Count = 5)
- D.7 PLL and Clock Configuration (Index = 6, Argument Count = 3)
- D.8 Power and Sleep Configuration (PSC) (Index = 7, Argument Count = 1)
- D.9 Pinmux Configuration (Index = 8, Argument Count = 3)
- E ROM Revision History
- Revision History
5.3.10.1 CRC
When the Enable CRC checkbox is selected, AISgen adds extra commands in the AIS to check for errors while transferring/loading the application data.
For master boot modes, the bootloader calculates the CRC over each section of the application data and checks it against the expected value from AIS. In case of an error, the bootloader loads the section again, re-calculates the CRC and checks again with the expected value. If a CRC error is found in three successive attempts, the boot process is aborted.
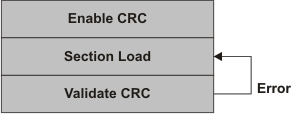
For slave-boot modes, the external master reads the calculated CRC from the device and validates it against the expected value from AIS. In case of an error, it is up to the external master to decide how many times it wants to retry loading the section before reporting failure.