TIDUF00 November 2021
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
-
3Hardware, Software, Testing
Requirements, and Test Results
- 3.1 Required Hardware and Software
- 3.2
Testing and Results
- 3.2.1 Test Setup
- 3.2.2
Test Results
- 3.2.2.1 Use Case – Vehicle, Bicycle, Pedestrian Detection
- 3.2.2.2 Use Case – Traffic Cone, Grocery Cart, Sign Pole, Pipe, Shrub
- 3.2.2.3 Use Case – Pedestrian Standing in Empty Parking Space
- 3.2.2.4 Use Case – Pedestrian Standing Next to Car
- 3.2.2.5 Use Case – Empty Parking Space
- 3.2.2.6 Use Case – Cross Traffic Alert
- 3.2.2.7 Use Case – Parking Block, Curb Detection
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
3.2.2.3 Use Case – Pedestrian Standing in Empty Parking Space
In this test we use the capabilities of the ultra-short range (0m-10m) sub-frame to detect a pedestrian standing in an empty parking space. The adjacent parking spaces are occupied. The processing chain is configured to perform 3D MIMO detection (azimuth and elevation, 1 Tx enabled at a time) with a maximum range of 10m. The sensor is placed at bumper height at 45 degrees. Testing is performed with both static and moving sensor. The setup is shown in Figure 3-4.
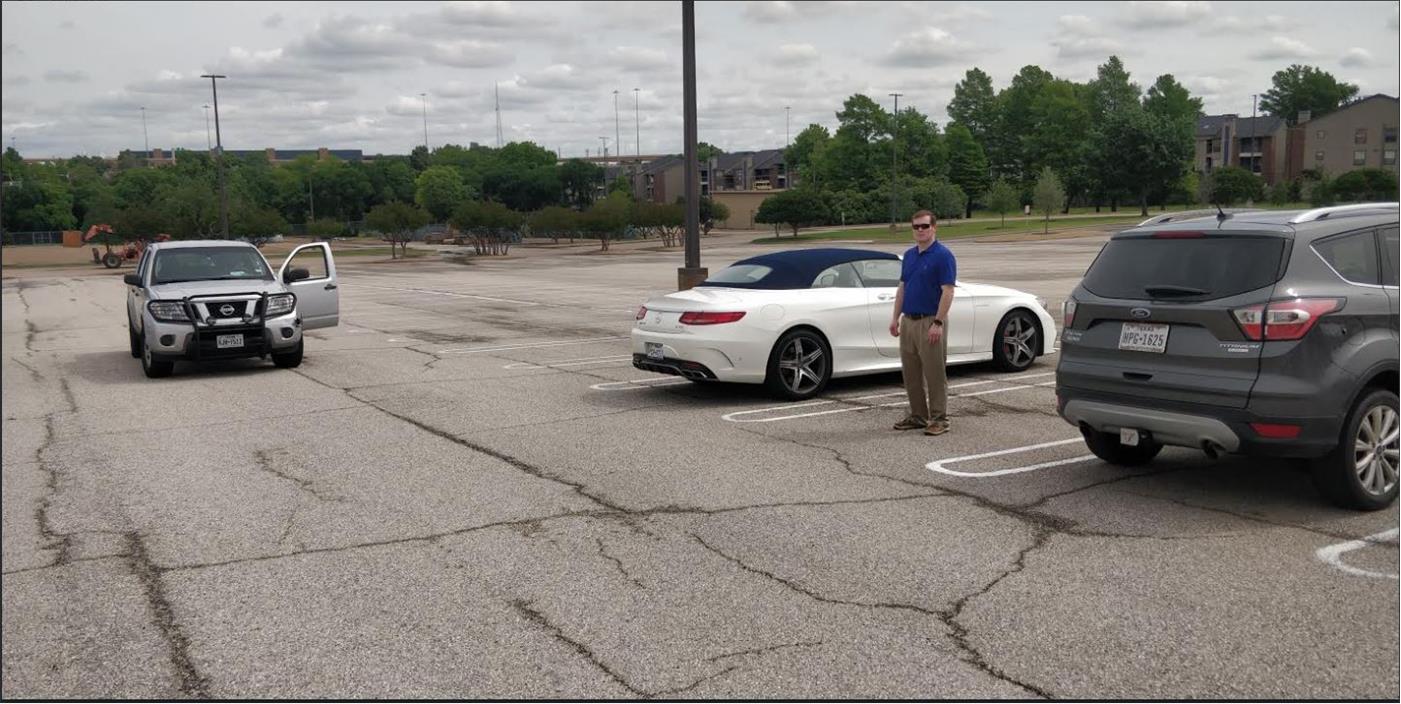 Figure 3-4 Pedestrian Standing in Empty
Parking Space
Figure 3-4 Pedestrian Standing in Empty
Parking SpaceFigure 3-5 shows the point cloud for static detection. The sensor, the car, and pedestrian in the parking space are all static. This is the most challenging detection case.
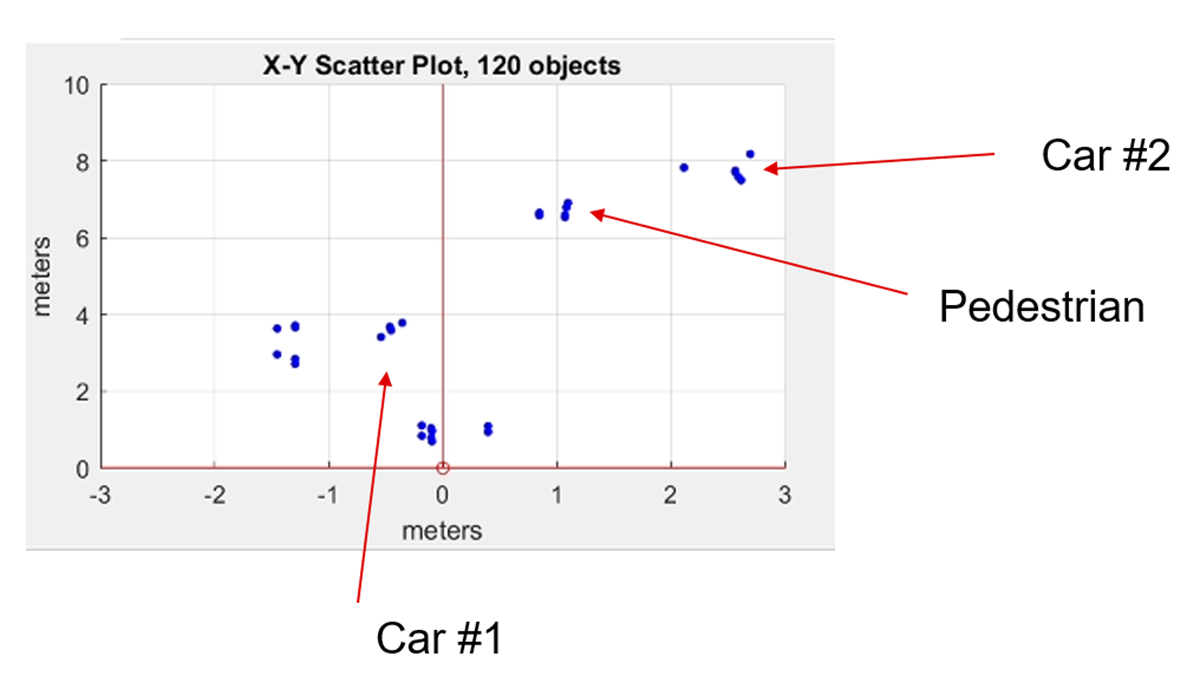 Figure 3-5 Detection Point Cloud of
Pedestrian Standing in Empty Parking Space
Figure 3-5 Detection Point Cloud of
Pedestrian Standing in Empty Parking SpaceWhen there is movement in the scene, the detection is better because Doppler information is used to detect movement.