SLOA277B january 2019 – july 2023 LM124 , LM124-N , LM124A , LM158 , LM158-N , LM158A , LM224 , LM224-N , LM224A , LM258 , LM258-N , LM258A , LM2902 , LM2902-N , LM2902-Q1 , LM2902K , LM2902KAV , LM2904 , LM2904-N , LM2904-Q1 , LM2904B , LM2904B-Q1 , LM2904BA , LM321 , LM324 , LM324-N , LM324A , LM358 , LM358-N , LM358A , LM358B , LM358BA , TS321 , TS321-Q1
6.4 Slew Rate
Slew rate (SR) limits the output rise and fall times, which are defined as (VOH – VOL)/SR. Slew rate, as specified in the op amp data sheet, is applicable for large differential input voltages. Dedicated comparator parts, on the other hand, may have much smaller differential input voltages. Note that the slew rate is reduced when the input difference voltage is small. Figure 6-3 shows that an input difference of 100 mV provides a slew rate 90% as fast as the data sheet setup result and a 10-mV input difference voltage has a slew rate that is only 16% of the data sheet slew rate.
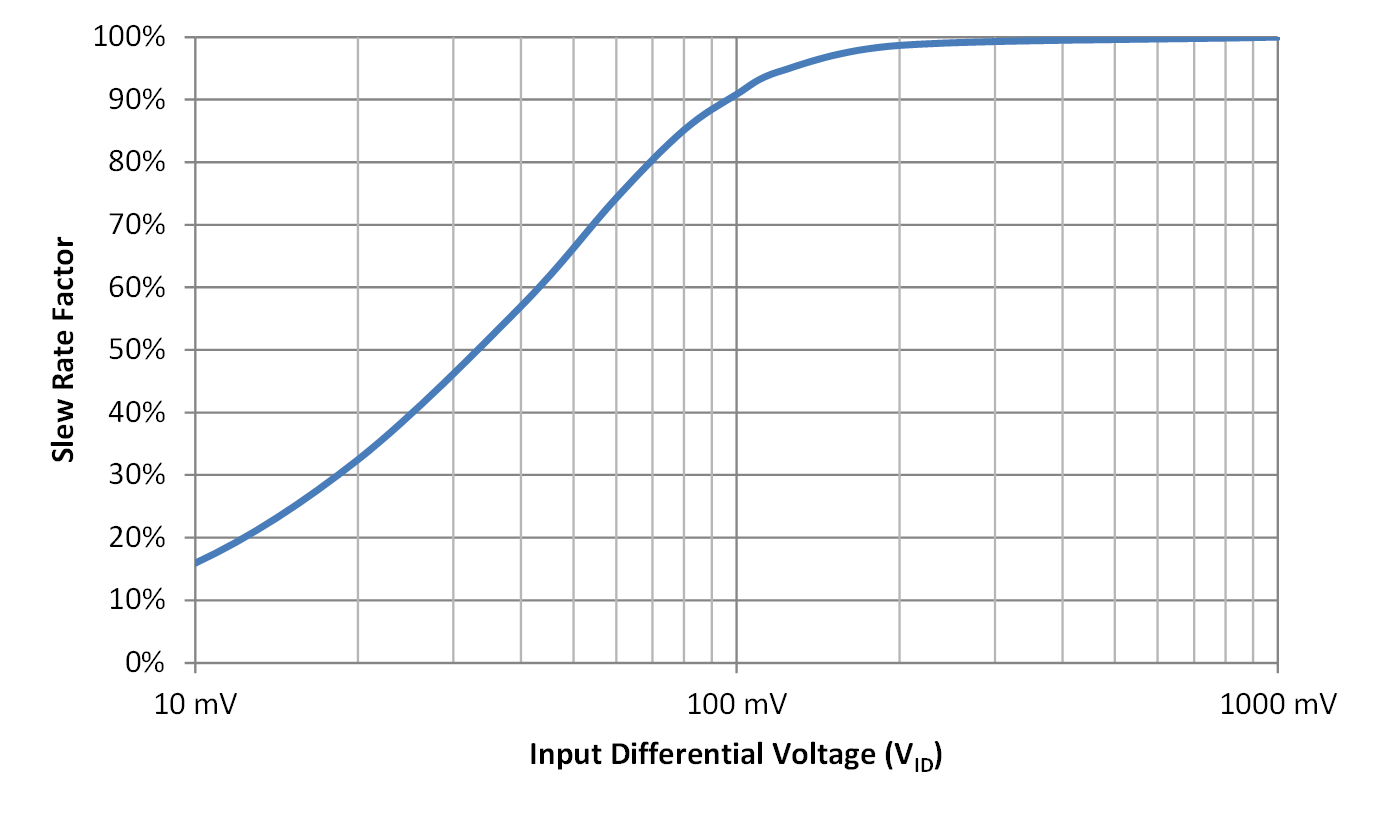 Figure 6-4 Slew Rate Factor vs Input Differential Voltage (VID)
Figure 6-4 Slew Rate Factor vs Input Differential Voltage (VID)