SBAS999A June 2019 – January 2021 ADS125H01
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Map
- 9.6.1 Device Identification (ID) Register (address = 00h) [reset = 4xh]
- 9.6.2 Main Status (STATUS0) Register (address = 01h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.3 Mode 0 (MODE0) Register (address = 02h) [reset = 24h]
- 9.6.4 Mode 1 (MODE1) Register (address = 03h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.5 Reserved (RESERVED) Register (address = 04h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.6 Mode 3 (MODE3) Register (address = 05h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.7 Reference Configuration (REF) Register (address = 06h) [reset = 05h]
- 9.6.8 Offset Calibration (OFCALx) Registers (address = 07h, 08h, 09h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 00h]
- 9.6.9 Full-Scale Calibration (FSCALx) Registers (address = 0Ah, 0Bh, 0Ch) [reset = 00h, 00h, 40h]
- 9.6.10 Reserved (RESERVED) Register (address = 0Dh) [reset = FFh]
- 9.6.11 Reserved (RESERVED) Register (address = 0Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.12 Reserved (RESERVED) Register (address = 0Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.13 MODE4 (MODE4) Register (address = 10h) [reset = 50h]
- 9.6.14 PGA Alarm (STATUS1) Register (address = 11h) [reset = xxh]
- 9.6.15 Status 2 (STATUS2) Register (address = 12h) [reset = 0xh]
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Orderable Information
10.2 Typical Application
Figure 10-1 illustrates an example of the ADS125H01 used in a ±10-V analog input programmable logic controller (PLC) module. The ADC inputs are protected by external ESD diodes to provide system-level protection. The external 100-MΩ resistor is used to pull the positive analog input to 15 V if the field-wiring connection is open or the transmitter connected the ADC inputs has a failed open circuit. A failed input results in a full-scale code value.
The signal from the transmitter is filtered to remove EMI and RFI interference to enhance noise immunity. The resistor also serves to limit input current in the event of a DC overvoltage, including if the module loses power while the input signal is present. The negative input is connected to AINN, which is also connected to AGND. Connection to AGND is necessary if the sensor power supply is not referenced to the ADC ground.
The input configuration is single-ended with the input voltage driven to 0 V and –10 V relative to AINN (AGND).
The reference voltage is applied to the REFP and REFN pins. A 100-kΩ resistor biases the differential reference voltage to 0 V when either reference input is open circuit. With the resistor, a failed or missing reference voltage is detected by the internal monitor.
The internal oscillator is selected by grounding the CLKIN pin. The serial interface and digital control lines of the ADC connect to the host.
The Zener diode clamps the high-voltage supply (HV_AVDD – HV_AVSS) to 40 V to provide overvoltage protection if an input signal is applied with module power off.
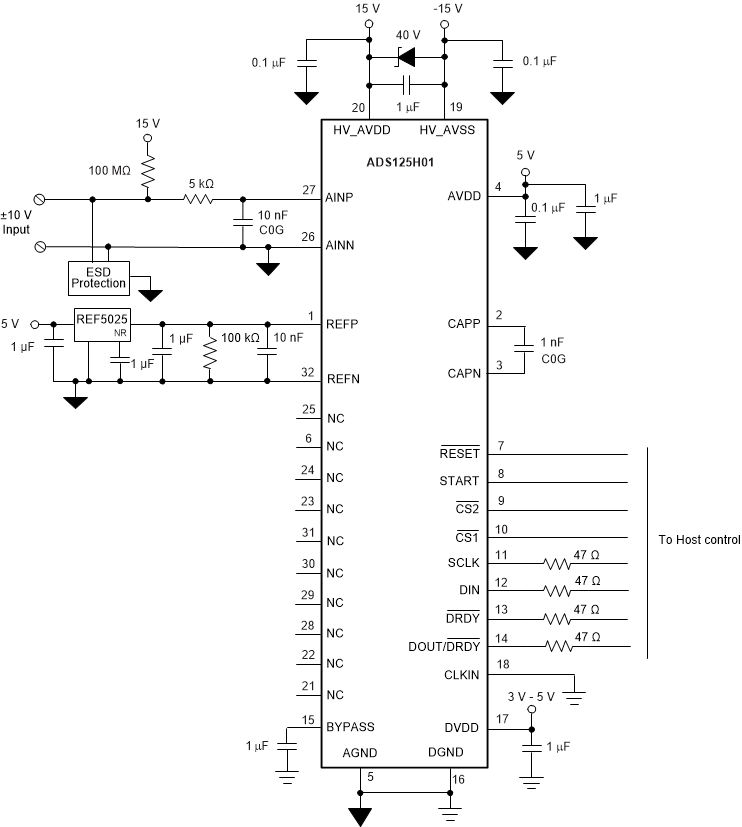 Figure 10-1 ±10-V Analog
Input PLC Module
Figure 10-1 ±10-V Analog
Input PLC Module