SBOS394E November 2007 – July 2019 VCA824
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: VS = ±5 V
- 7.6 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5 V, AVMAX = 2 V/V
- 7.7 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5 V, AVMAX = 10 V/V
- 7.8 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5 V, AVMAX = 40 V/V
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.1.1 Difference Amplifier
Because both inputs of the VCA824 are high-impedance, a difference amplifier can be implemented without any major problem. Figure 65 shows this implementation. This circuit provides excellent common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) as long as the input is within the CMRR range of –2.1 V to 1.6 V. Note that this circuit does not make use of the gain control pin, VG. Also, it is recommended to choose RS such that the pole formed by RS and the parasitic input capacitance does not limit the bandwidth of the circuit. Figure 66 shows the common-mode rejection ratio for this circuit implemented in a gain of 10 V/V for VG = 1 V. Note that because the gain control voltage is fixed and is normally set to 1V, the feedback element can be reduced in order to increase the bandwidth. When reducing the feedback element, make sure that the VCA824 is not limited by common-mode input voltage, the current flowing through RG, or any other limitation described in this data sheet.
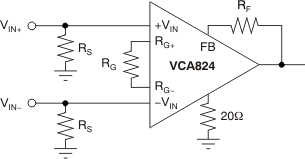 Figure 65. Difference Amplifier
Figure 65. Difference Amplifier 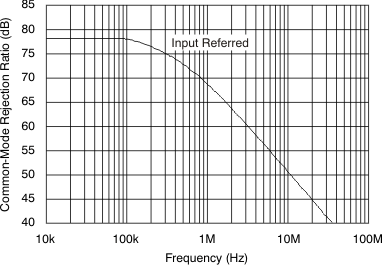 Figure 66. Common-Mode Rejection Ratio
Figure 66. Common-Mode Rejection Ratio 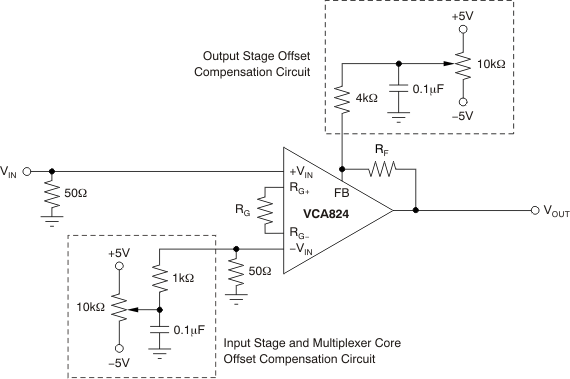 Figure 67. Adjusting the Input and Output Voltage Sources
Figure 67. Adjusting the Input and Output Voltage Sources 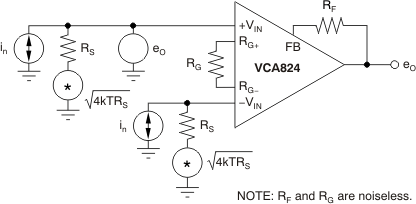 Figure 68. Simple Noise Model
Figure 68. Simple Noise Model 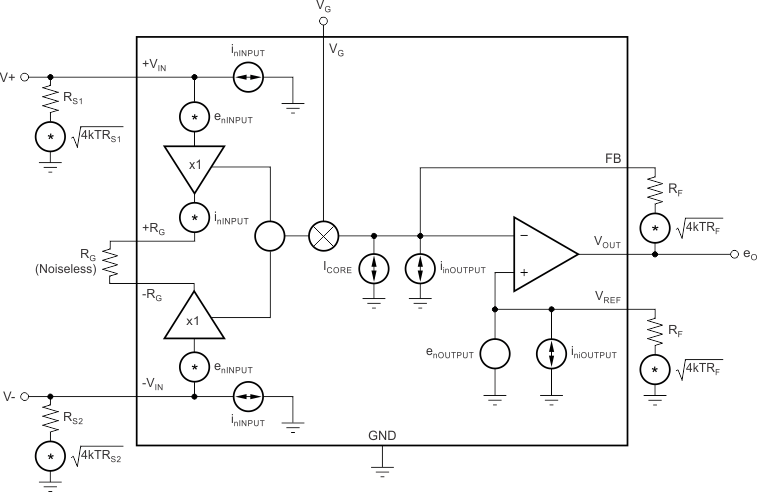 Figure 69. Full Noise Model
Figure 69. Full Noise Model