SBOS394E November 2007 – July 2019 VCA824
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: VS = ±5 V
- 7.6 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5 V, AVMAX = 2 V/V
- 7.7 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5 V, AVMAX = 10 V/V
- 7.8 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5 V, AVMAX = 40 V/V
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- D|14
Orderable Information
11.1.1 Thermal Considerations
The VCA824 does not require heatsinking or airflow in most applications. The maximum desired junction temperature sets the maximum allowed internal power dissipation as described in this section. In no case should the maximum junction temperature be allowed to exceed 150°C.
Operating junction temperature (TJ) is given by Equation 12:
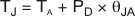
The total internal power dissipation (PD) is the sum of quiescent power (PDQ) and additional power dissipated in the output stage (PDL) to deliver load power. Quiescent power is simply the specified no-load supply current times the total supply voltage across the part. PDL depends on the required output signal and load; for a grounded resistive load, however, it is at a maximum when the output is fixed at a voltage equal to one-half of either supply voltage (for equal bipolar supplies). Under this worst-case condition, PDL = VS2/(4 × RL), where RL is the resistive load.
Note that it is the power in the output stage and not in the load that determines internal power dissipation. As a worst-case example, compute the maximum TJ using a VCA824ID (SO-14 package) in the circuit of Figure 75 operating at maximum gain and at the maximum specified ambient temperature of 85°C.
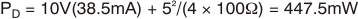
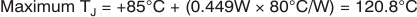
This maximum operating junction temperature is well below most system level targets. Most applications should be lower because an absolute worst-case output stage power was assumed in this calculation of VCC/2, which is beyond the output voltage range for the VCA824.