JAJSED2B August 2017 – January 2018 DAC5672A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: AC Characteristics
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics: Digital Characteristics
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
7.4.4 Differential With Transformer
Using an RF transformer provides a convenient way of converting the differential output signal into a single-ended signal while achieving excellent dynamic performance. The appropriate transformer must be carefully selected based on the output frequency spectrum and impedance requirements.
The differential transformer configuration has the benefit of significantly reducing common-mode signals, thus improving the dynamic performance over a wide range of frequencies. Furthermore, by selecting a suitable impedance ratio (winding ratio) the transformer can provide optimum impedance matching while controlling the compliance voltage for the converter outputs.
Figure 20 and Figure 21 show 50-Ω doubly-terminated transformer configurations with 1:1 and 4:1 impedance ratios, respectively. Note that the center tap of the primary input of the transformer has to be grounded to enable a dc-current flow. Applying a 20-mA full-scale output current would lead to a 0.5-VPP output for a 1:1 transformer and a 1-VPP output for a 4:1 transformer. In general, the 1:1 transformer configuration will have slightly better output distortion, but the 4:1 transformer will have 6 dB higher output power.
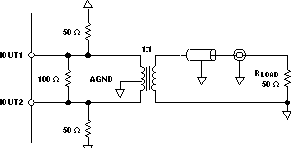 Figure 20. Driving a Doubly-Terminated 50-Ω Cable Using a 1:1 Impedance Ratio Transformer
Figure 20. Driving a Doubly-Terminated 50-Ω Cable Using a 1:1 Impedance Ratio Transformer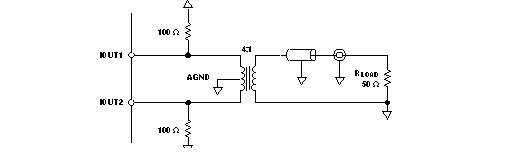 Figure 21. Driving a Doubly-Terminated 50-Ω Cable Using a 4:1 Impedance Ratio Transformer
Figure 21. Driving a Doubly-Terminated 50-Ω Cable Using a 4:1 Impedance Ratio Transformer