SNLU334 December 2023 DS320PR410
- 1
- Description
- Get Started
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1Evaluation Module Overview
-
2Hardware
- 2.1 DS320PR410 5-Level I/O Control Inputs
- 2.2 DS320PR410 Modes of Operation
- 2.3 DS320PR410 SMBus or I2C Register Control Interface
- 2.4 DS320PR410 Equalization Control
- 2.5 DS320PR410 RX Detect State Machine
- 2.6 DS320PR410 DC Gain Control
- 2.7 DS320PR410 EVM Global Controls
- 2.8 DS320PR410-RSC-EVM Downstream Devices Control
- 2.9 DS320PR410-RSC-EVM Upstream Devices Control
- 2.10 Quick-Start Guide (Pin Mode)
- 2.11 Quick-Start Guide (SMBus / I2C Secondary Mode)
- 3Implementation Results
- 4Hardware Design Files
- 5Additional Information
- 6References
3.1 Test Setup and Results
Figure 4-1 shows a typical system setup with the DS320PR410-RSC-EVM placed between a CPU on a server motherboard and a PCIe end point (Network Interface Card or NIC). Additional Extender cards are inserted to increase the channel loss and demonstrate the ability of the redriver to extend the reach.

Figure 3-1 Example Test Setup
Figure 4-2 is a typical test result achieved with a system shown in Figure 4-1. As the result indicates, the end point (Nvidia / Mellanox NIC) with the DS320PR410-RSC-EVM placed in the data path achieves a stable Gen5, x16 PCIe link.
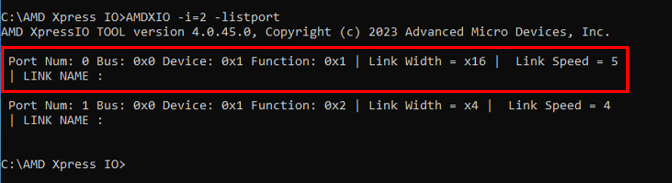
Figure 3-2 Example Test Results