SPRACT6A october 2020 – march 2023 F29H850TU , F29H850TU , F29H859TU-Q1 , F29H859TU-Q1 , TMS320F2800132 , TMS320F2800132 , TMS320F2800133 , TMS320F2800133 , TMS320F2800135 , TMS320F2800135 , TMS320F2800137 , TMS320F2800137 , TMS320F2800152-Q1 , TMS320F2800152-Q1 , TMS320F2800153-Q1 , TMS320F2800153-Q1 , TMS320F2800154-Q1 , TMS320F2800154-Q1 , TMS320F2800155 , TMS320F2800155 , TMS320F2800155-Q1 , TMS320F2800155-Q1 , TMS320F2800156-Q1 , TMS320F2800156-Q1 , TMS320F2800157 , TMS320F2800157 , TMS320F2800157-Q1 , TMS320F2800157-Q1 , TMS320F280021 , TMS320F280021 , TMS320F280021-Q1 , TMS320F280021-Q1 , TMS320F280023 , TMS320F280023 , TMS320F280023-Q1 , TMS320F280023-Q1 , TMS320F280023C , TMS320F280023C , TMS320F280025 , TMS320F280025 , TMS320F280025-Q1 , TMS320F280025-Q1 , TMS320F280025C , TMS320F280025C , TMS320F280025C-Q1 , TMS320F280025C-Q1 , TMS320F280033 , TMS320F280033 , TMS320F280034 , TMS320F280034 , TMS320F280034-Q1 , TMS320F280034-Q1 , TMS320F280036-Q1 , TMS320F280036-Q1 , TMS320F280036C-Q1 , TMS320F280036C-Q1 , TMS320F280037 , TMS320F280037 , TMS320F280037-Q1 , TMS320F280037-Q1 , TMS320F280037C , TMS320F280037C , TMS320F280037C-Q1 , TMS320F280037C-Q1 , TMS320F280038-Q1 , TMS320F280038-Q1 , TMS320F280038C-Q1 , TMS320F280038C-Q1 , TMS320F280039 , TMS320F280039 , TMS320F280039-Q1 , TMS320F280039-Q1 , TMS320F280039C , TMS320F280039C , TMS320F280039C-Q1 , TMS320F280039C-Q1 , TMS320F280040-Q1 , TMS320F280040-Q1 , TMS320F280040C-Q1 , TMS320F280040C-Q1 , TMS320F280041 , TMS320F280041 , TMS320F280041-Q1 , TMS320F280041-Q1 , TMS320F280041C , TMS320F280041C , TMS320F280041C-Q1 , TMS320F280041C-Q1 , TMS320F280045 , TMS320F280045 , TMS320F280048-Q1 , TMS320F280048-Q1 , TMS320F280048C-Q1 , TMS320F280048C-Q1 , TMS320F280049 , TMS320F280049 , TMS320F280049-Q1 , TMS320F280049-Q1 , TMS320F280049C , TMS320F280049C , TMS320F280049C-Q1 , TMS320F280049C-Q1 , TMS320F28075 , TMS320F28075 , TMS320F28075-Q1 , TMS320F28075-Q1 , TMS320F28076 , TMS320F28076 , TMS320F28374D , TMS320F28374D , TMS320F28374S , TMS320F28374S , TMS320F28375D , TMS320F28375D , TMS320F28375S , TMS320F28375S , TMS320F28375S-Q1 , TMS320F28375S-Q1 , TMS320F28376D , TMS320F28376D , TMS320F28376S , TMS320F28376S , TMS320F28377D , TMS320F28377D , TMS320F28377D-EP , TMS320F28377D-EP , TMS320F28377D-Q1 , TMS320F28377D-Q1 , TMS320F28377S , TMS320F28377S , TMS320F28377S-Q1 , TMS320F28377S-Q1 , TMS320F28378D , TMS320F28378D , TMS320F28378S , TMS320F28378S , TMS320F28379D , TMS320F28379D , TMS320F28379D-Q1 , TMS320F28379D-Q1 , TMS320F28379S , TMS320F28379S , TMS320F28384D , TMS320F28384D , TMS320F28384D-Q1 , TMS320F28384D-Q1 , TMS320F28384S , TMS320F28384S , TMS320F28384S-Q1 , TMS320F28384S-Q1 , TMS320F28386D , TMS320F28386D , TMS320F28386D-Q1 , TMS320F28386D-Q1 , TMS320F28386S , TMS320F28386S , TMS320F28386S-Q1 , TMS320F28386S-Q1 , TMS320F28388D , TMS320F28388D , TMS320F28388S , TMS320F28388S , TMS320F28P650DH , TMS320F28P650DH , TMS320F28P650DK , TMS320F28P650DK , TMS320F28P650SH , TMS320F28P650SH , TMS320F28P650SK , TMS320F28P650SK , TMS320F28P659DH-Q1 , TMS320F28P659DH-Q1 , TMS320F28P659DK-Q1 , TMS320F28P659DK-Q1 , TMS320F28P659SH-Q1 , TMS320F28P659SH-Q1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Input Settling Design Steps
-
3Example Circuit Design
- 3.1 Select the ADC
- 3.2 Find the Minimum Op-Amp Bandwidth and RC Filter Ranges
- 3.3 Verify the Op-amp Model
- 3.4 Build the ADC Input Model
- 3.5 DC Node Analysis
- 3.6 Refine RC Filter Values Via Simulation (Part 1)
- 3.7 Refine RC Filter Values Via Simulation (Part 2)
- 3.8 Refine RC Filter Values Via Simulation (Part 3)
- 3.9 Further Refinement
- 3.10 Further Simulations
- 3.11 Completed Worksheet
- 4Working With Existing Circuits or Additional Constraints
- 5Summary
- 6References
- 7Revision History
1.1 Mechanism of ADC Input Settling
To convert a sensed analog voltage to a digital conversion result, the ADC first must accurately capture the applied input voltage into its sample-and-hold circuit (S+H). As shown in Figure 1-1, this entails charging the internal ADC S+H capacitor (Ch) to within some acceptable tolerance (typically 0.5 LSBs) of the applied voltage within the configured acquisition window time (also referred to as the S+H time).
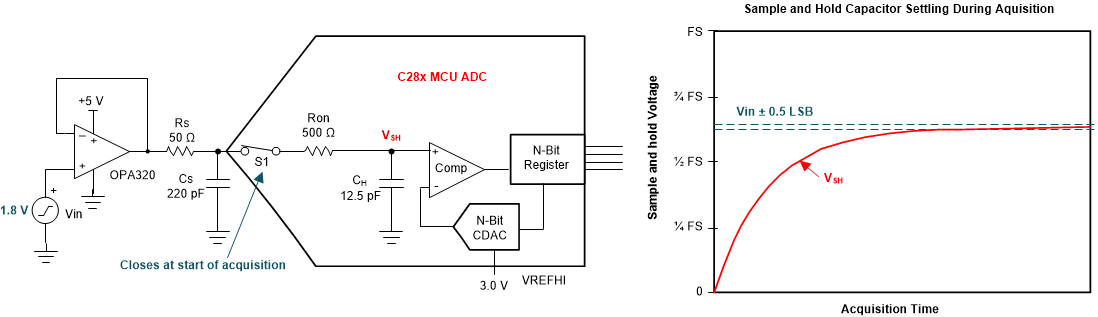 Figure 1-1 Settling of the ADC S+H
Capacitor
Figure 1-1 Settling of the ADC S+H
CapacitorQuickly charging Ch to the applied voltage is complicated by the finite bandwidth and settling time of the external ADC driver circuit and of the settling time of the internal ADC S+H circuit. In Figure 1-1, the driver is show as an op-amp (OPA320), which has a finite bandwidth, and the driver circuit also has intentionally placed source resistance (Rs) and intentionally placed source capacitance (Cs) which have a finite settling time determined by their RC time constant. Note that other circuit topologies are possible for driving the ADC, and these circuits may have additional components that need to be modeled to ensure appropriate settling time. These components could include unintentional parasitics such as the output impedance of a sensor or the effective source resistance of a voltage divider. Figure 1-1 also shows that the ADC has an internal parasitic switch resistance (Ron). This, along with Ch, provides an additional RC time constant that limits settling speed.