SPRT767 November 2023 AM2431 , AM2432 , AM2434 , AM2631 , AM2631-Q1 , AM2632 , AM2632-Q1 , AM2634 , AM2634-Q1 , AM263P4 , AM263P4-Q1 , AM2732 , AM2732-Q1
Streamline the ISO 26262 and IEC 61508 certification processes with Functional Safety-Compliant products, documentation, software, and support. Arm® Cortex®-R MCUs are independently assessed and certified by TÜV SÜD to meet a systematic capability up to ASIL D and SIL 3 to help you create automotive and industrial applications requiring functional safety.
Highlights of the Arm Cortex-R functional safety offering include:
- Device architecture for functional safety
- Documentation to support customers' safety assessment at the system level
- Certified software library to implement the safety mechanisms
 AM263x Safety Mechanisms
AM263x Safety MechanismsSafety mechanisms play a key role in the overall safety of a system by detecting potentially dangerous failures and consequently helping place the system in a safe state. With over 400 built-in safety mechanisms defined and independently assessed by TÜV SÜD for the effectiveness of the MCU, Arm Cortex-R MCUs provide the required diagnostic coverage to meet the hardware integrity of ASIL-B or ASIL-D and SIL-2 or SIL-3 at a component level. Functional safety manuals provide detailed information on the safety mechanisms as well as techniques for achieving non-interference between elements and avoiding dependent failures. This aids customers in the development of compliant systems up to ASIL D and SIL 3. The tunable Failure Modes Effects and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) provides increased flexibility to customize and calculate hardware metrics with features such as package Failures in Time (FIT) estimation, product function tailoring, safety mechanism tailoring, and custom diagnostics allowing customers to tune the FMEDA to their own application-specific needs.
Learn More about Tuning the FMEDA with Video Training: Basics of FMEDA and Intro to Tunable FMEDA
| Key Safety Features | AM263x | AM243x | TMS570, RM4x |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Integrity | ASIL-D, SIL-3 | SIL-2 | ASIL-D, SIL-3 |
| Systematic Capability | ASIL-D, SIL-3 | SIL-3 | ASIL-D, SIL-3 |
| Compliant Development Process (ISO 26262 for Auto, or IEC 61508 for Industrial, or both) | ASIL-D, SIL-3 | SIL-3 | ASIL-D, SIL-3 |
| Lockstep | ✓ | X | ✓ |
| Memory Parity | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Memory ECC | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Memory BIST | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Memory Protection Unit | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Error Signaling Module | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Windowed watchdog timer with independent clock | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Firewalls, voltage, temperature, and clock monitors | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Hardware CRC acceleration | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Hardware BIST (HWBIST): Permanent fault coverage of > 90% | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Redundant and independent ADC, PWM Modules | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Safety Manual: detailed product overview, capabilities and constraints, TI development process, safety elements, and safety diagnostics | Request access | Coming soon | TMS570LSx RM44x |
| Certification | Automotive Industrial |
Coming soon | TMS570LSx RM44x |
| Safety Collateral | Description |
|---|---|
| Development Process Certificate Hardware | Software |
TÜV SÜD certificate for Functional Safety Hardware Process and Functional Safety Software Development |
| ARM Cortex-R Safety package | By request and NDA required. Package
includes the following elements:
|
| Software diagnostic library SDL Certification |
A library of modules and examples demonstrating safety features and mechanisms. Examples include CPU, memory, clocks or watchdogs, HWBIST, and so forth. |
| MCAL | Microcontroller Abstraction Layer (MCAL) – Automotive Open System Architecture (AUTOSAR) compliant drivers |
| Compiler qualification kit | Compare compiler coverage for customer use cases against coverage of TI compiler release validations |
| Safety certified RTOS | Pre-certified safety Real Time
Operating System (RTOS) options including:
|
Example of Advanced Power Conversion System
System block diagram of the advanced power conversion use case showing the possible interfaces that can be implemented. Data flows to or from peripherals and starts or ends in OCRAM or R5F TCM. Much of the data resides in TCM due to latency requirements.
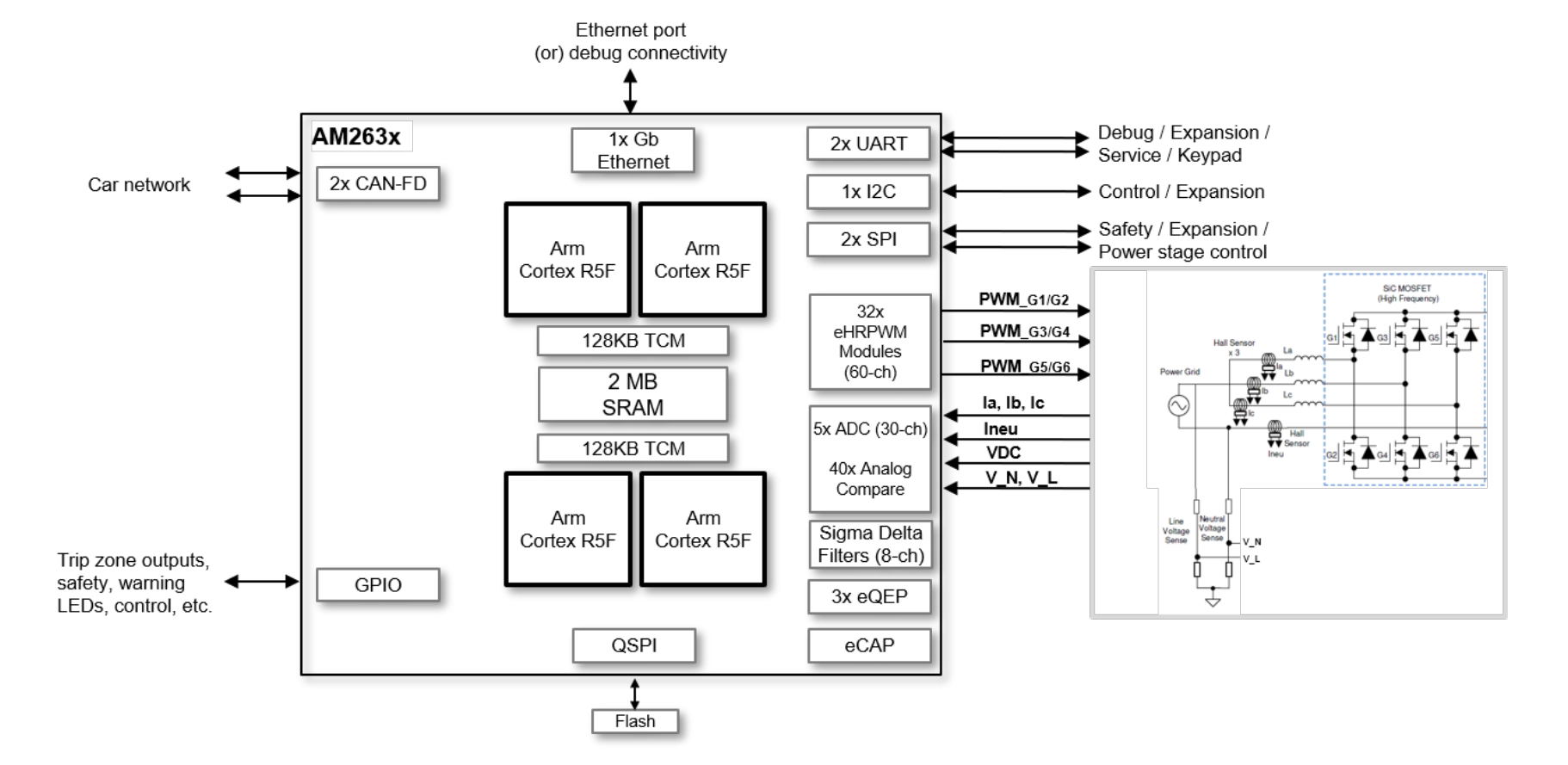
More complex AM263x power control use cases will involve partitioning of processing across R5Fs and also make sure that time-critical code and data can fit into TCM. Sensitive latencies for ADC, CMPSS, and PWM transfers must be met.
Other interfaces such as SPI, UART, and I2C can be used for purposes noted in the block diagram. GPIO is heavily used for trip zone outputs and other sensing and control.
TI Distinct Roles and Responsibilities
For more details regarding the roles and responsibilities of TI, certification bodies and system integrators, refer to the following table.
| Texas Instruments |
Certification Bodies (ex. TÜV SÜD) |
System Integrator or Customer |
|
|